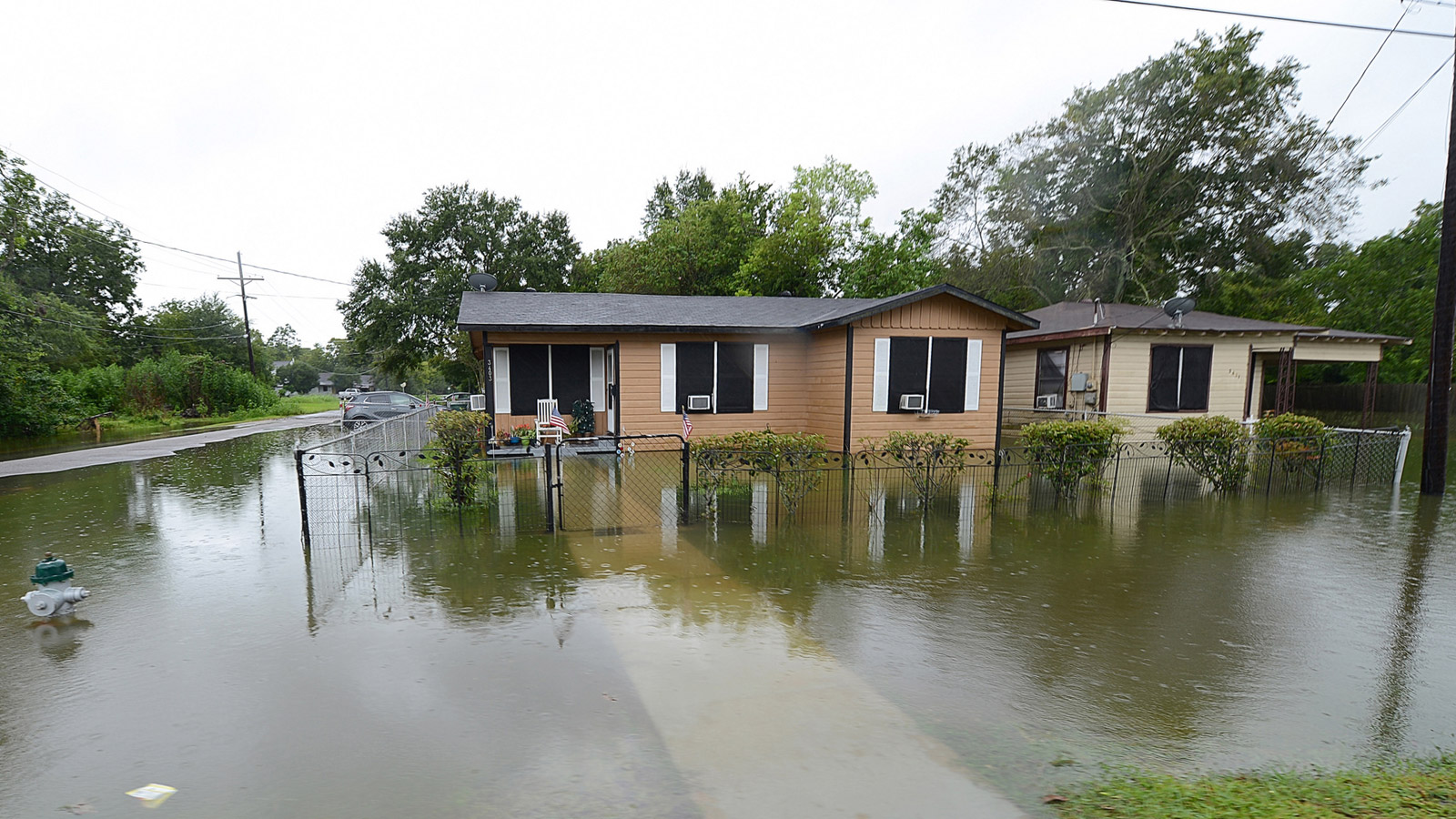
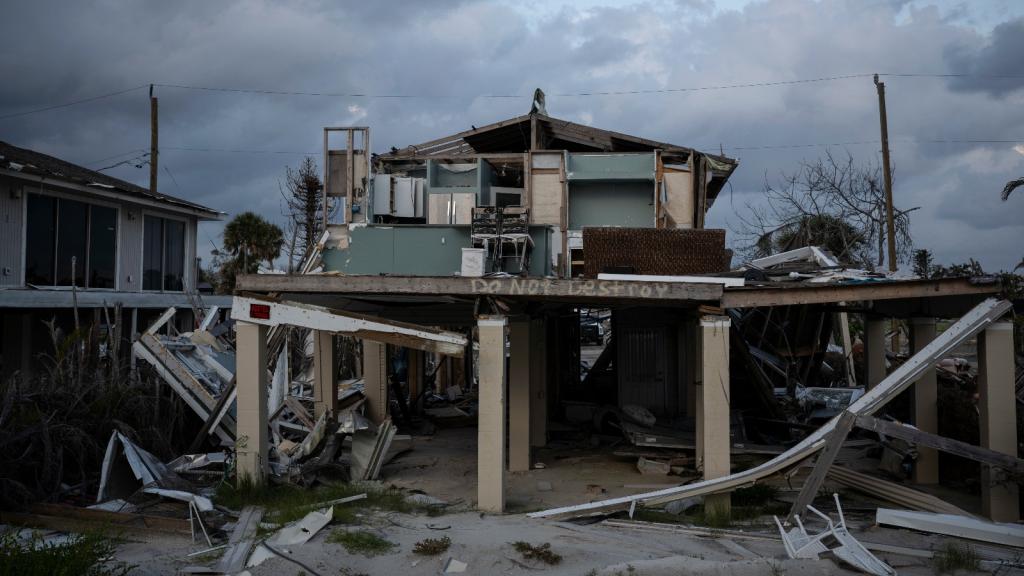
At long last, skies are clearing over Houston. Yet the floodwaters have left an exacting mark, and human tragedy abounds. America’s fourth-largest city will never be the same.
After moving on from Houston, Harvey has wrought new devastation further east. The storm made a second landfall in Texas early Wednesday morning, bringing with it a fresh torrent of rain to the oil industry hubs of Port Arthur and Beaumont, 100 miles east of Houston.
Port Arthur and Beaumont are home to some 380,000 people — about the same population as the city of New Orleans — and Harvey dumped more rain on them than it did on Houston. Beaumont received more than 26 inches of rain on Tuesday alone, more than double what the city had ever seen on a single day — and about as much as Houston received during its rainiest 48 hours last weekend. Harvey has left the area’s residents stranded and its oil facilities battered.
In a Facebook post, the mayor of Port Arthur, Derrick Freeman, wrote, “Our whole city is underwater.” The county sheriff said most people couldn’t be reached to be rescued. The so-called “Cajun Navy” of fishing boats sprung into action, with a 60-mile convoy of boats departing Galveston, 100 miles southwest, toward the region. Even the designated evacuation center in Port Arthur flooded, complete with floating Red Cross cots, and residents forced to again flee. A local stretch of Interstate-10 looked like a lake, complete with waves and whitecaps. And north, in Beaumont, Harvey knocked out the municipal water system; local authorities say it will be out indefinitely.
Southeastern Texas is home to massive oil refineries and industry infrastructure — and Harvey has damaged much of it. In Crosby, east of Houston, a flooded chemical plant exploded early Thursday night, sending up plumes of black smoke. An ExxonMobil plant in Baytown, also an eastern suburb of Houston, reported a Harvey-related hazardous spill.
Now add facilities in the Beaumont and Port Arthur region to the list. There was a sulfur-dioxide release at an ExxonMobil refinery in Beaumont, which could cause respiratory issues for locals. And the nation’s largest refinery, run by Valero in Port Arthur, went offline on Wednesday.
About 20 percent of the nation’s refining capacity is now offline due to Harvey. Facilities have to file regulatory notices when floodwaters force them to shut down, a process that could result in releases of chemicals beyond what the law normally allows. ExxonMobil did that in association with its two damaged refineries. According to the Texas Tribune, “most of the other facilities belonging to major companies also filed notices with the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality,” meaning nearly every industry facility in the path of Harvey has the potential of a hazardous spill.
The scale of Harvey’s disaster across Texas remains nearly incomprehensible. More than 24 trillion gallons of water fell from the sky in five days, enough to cover Washington, D.C., in a 1,400-foot-high wall of water taller than the Empire State Building. Houston-area officials think it will take months to drain two key flood-protection reservoirs.
Meanwhile, it’s still peak hurricane season, and two new storms popped up on forecasters’ radars on Wednesday. (One meteorologist called them a “sick joke,” considering Harvey’s devastation.) Tropical Storm Irma, currently off the coast of West Africa, looks primed to grow into a large hurricane thanks in part to water temperatures in the tropical Atlantic that are currently near all-time highs. It may take nearly two weeks to cross the ocean, and its path is uncertain. It could make landfall anywhere from Texas to Bermuda.
The Gulf of Mexico has also spawned another area of interest to meteorologists. By early next week, it could become Tropical Storm Jose. One of its potential destinations: Texas.