This post originally appeared on Energy Self-Reliant States, a resource of the Institute for Local Self-Reliance’s New Rules Project.
Grid parity is an approaching target for distributed solar power, and can be helped along with smarter electricity pricing policy.
Consider a residential solar photovoltaic (PV) system installed in Los Angeles. A local buying group negotiated a price of $4.78 per watt for the solar modules and installation, a price that averages out to 23.1 cents per kilowatt-hour over the 25 year life of the system. With the federal tax credit, that cost drops to 17.9 cents. Since the average electricity price in Los Angeles is 11.5 cents (according to National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s PV Watts Version 2 calculator), solar doesn’t compete.
Or does it?
In Los Angeles, there are three sets of electricity prices. From October to May, all pricing plans have a flat rate per kilowatt-hour and total consumption. During peak season (June to September), however, the utility offers two different pricing plans: time-of use pricing and tiered pricing. Time-of-use pricing offers lower rates — 10.8 cents — during late evening and early morning hours, but costs as much as 22 cents per kilowatt-hour during peak hours. Prices fluctuate by the hour. Tiered pricing offers the same, flat rate at any hour of the day, but as total consumption increases, the rate does as well. For monthly consumption of 350 kilowatt-hours or less, the price is 13.2 cents. From 350 to 1,050 kilowatt-hours, the price is 14.7 cents. Above 1,050 kilowatt-hours, each unit of electricity costs 18.1 cents.
The following chart illustrates the difficulty in determining whether solar has reached “grid parity” (i.e., the same price as electricity from the grid). For some marginal prices, solar PV is cheaper than grid electricity when coupled with the federal tax credit.
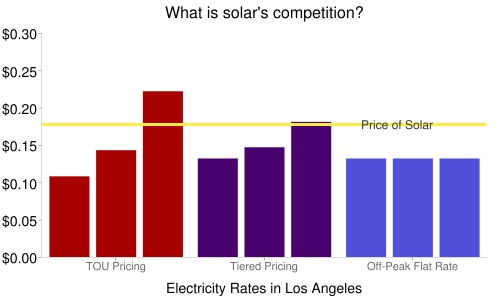 Click for a larger version.Over the course of the year, solar is not less than grid electricity. A very rough calculation of the expected time of day production of a solar array in Los Angeles finds that the average value of a solar-produced kilowatt-hour is 15.1 cents over a year. That suggests that solar power is not yet at grid parity, even with time-of-use pricing.
Click for a larger version.Over the course of the year, solar is not less than grid electricity. A very rough calculation of the expected time of day production of a solar array in Los Angeles finds that the average value of a solar-produced kilowatt-hour is 15.1 cents over a year. That suggests that solar power is not yet at grid parity, even with time-of-use pricing.
There are other considerations, as well.
For one, there are additional incentives for solar power, including federal accelerated depreciation (for commercially-owned systems) as well as state and utility incentive programs. These programs substitute taxpayer dollars for ratepayer ones, making the cost of solar to the grid lower.
There are also policy complications for a grid connected solar PV system. Net metering is the rule that governs on-site power generation and it allows self-generators to roll their electricity meter backward as they generate electricity, but there are limits. Users typically only get a credit for the energy charges on their bill, and not for fixed charges utilities apply to recover the costs of grid maintenance (and associated taxes and fees). Producing more than is consumed on-site can mean giving free electrons to the utility company. So even if a solar array could produce all the electricity consumed on-site, the billing arrangement would not allow the customer to zero out their electricity bill.
Where can distributed solar compete?
Based on ILSR’s analysis, solar PV at $5 per watt can only compete with grid electricity prices in the 16 largest metropolitan areas in the United States — when adding in both federal incentives and assuming availability of time-of-use pricing. With those parameters, 40 million Americans (in California and New York) would live in areas where solar PV’s levelized cost would beat their local retail electricity price.
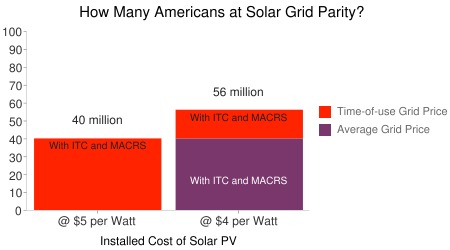 Click for a larger version.With solar at $4 per watt, those same 40 million Americans could beat grid prices without a time-of-use plan. Another 16 million Americans could use $4 per watt solar and a time-of-use plan to beat grid prices with distributed solar.
Click for a larger version.With solar at $4 per watt, those same 40 million Americans could beat grid prices without a time-of-use plan. Another 16 million Americans could use $4 per watt solar and a time-of-use plan to beat grid prices with distributed solar.
Across America, distributed solar is — with just federal incentives — nearing a cost-effectiveness threshold. As installed prices continue to fall — in Germany they average $4.11 per Watt for small systems — millions of Americans will leave their utility and electricity bills behind.



