ACICAFOCA Barbados nut plantation.
To fight climate change, some scientists think we should vegetate the hell out of deserts. The latest such idea calls for large plantations of a hardy species of Central American tree to be planted in near-coastal desert areas and irrigated with desalinated water.
While forests soak up carbon dioxide, deserts do comparatively little to help with climate change. So should these seas of sand be planted and watered out of existence in a bid to reduce CO2 levels?
Some say yes. The approach would be like geoengineering, but rooted in a more natural system. Scientists call it bioengineering or carbon farming.
The idea of replacing deserts with forests to help the climate is not brand new. A few years ago, for example, scientists proposed planting eucalyptus trees through the Saharan and Australian deserts to help absorb carbon dioxide.
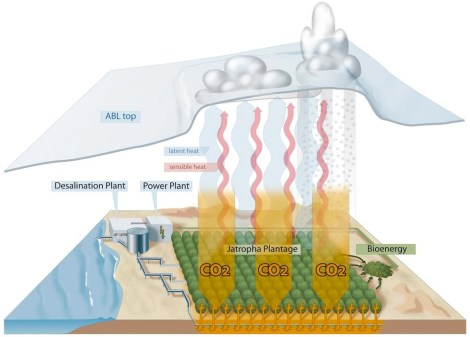
The latest suggested approach, which would involve the planting of vast orchards of Barbados nut trees, technically known as Jatropha curcas trees, was proposed Wednesday by a group of German researchers in the journal Earth System Dynamics. They say vegetating the world’s near-coastal deserts with this species, which can withstand harsh growing conditions, could provide an alternative to mechanical carbon-sequestration techniques.
The researchers crunched some numbers and determined that the carbon-farming costs would be competitive over 20 years with carbon capture and storage, an embryonic technology in which a power plant’s carbon emissions are captured and funneled underground. Carbon farming could be funded by governments through carbon taxes and through the sale of carbon allowances.
“Suitably deployed, these plants could transform unused, barren lands into long-term carbon sinks,” they write in the paper. “The carbon efficiency of this bio-ecosystem would compare favourably with all other existing processes for carbon storage and sequestration, including the cultivation of bio fuels.”
Not only would the trees soak up CO2 and deposit some of it into the soil, but their growth could influence rainfall patterns, soil quality, and regional climates, paving the way for the natural growth of other plants.
Jatropha curcas can withstand conditions that would make most plants wither, but they’re not magical. They still need water. The scientists propose desalinating water from the sea to irrigate the orchards. This is an expensive and energy-intensive way of obtaining fresh water, but the scientists incorporated that into their cost estimates.
Oil from the trees is already used extensively for biofuel, and the scientists say that after an orchard had been growing for a few years it would produce nuts and leaves that could be burned to provide some of the power needed for desalination.
The idea seems worthy of further investigation — although it wouldn’t be much good for the tortoises and other wildlife that revel in the world’s deserts.
Here’s a graphic from the paper that helps explain the proposal: