On Wednesday, while the rest of the nation was busy scrolling through Pelosi State of the Union golf clap memes, two major panels — the House Natural Resources Committee and a separate subcommittee on energy and commerce — met to discuss the impact of global warming on the nation as a whole.
This marks the first time the Natural Resources Committee has held a hearing on climate change in a decade, and newly empowered House Democrats have even more hearings on climate planned throughout the month.
The hearing started off on a contentious foot, with speakers calling into question everything from climate science, to poverty, to whether the timing of the hearings was somehow disrespectful to Black History Month.
“I know you have made February as climate change month, I appreciate the fact that that you picked the shortest month of the year to to do that,” said Republican Rob Bishop, former chair of the Natural Resources Committee, to the current chair Raul Grijalva. “It also happens to be of course Black History Month, which I wish we could deal with other things.”
Bishop, who is white, went on argue that it would be more within the committee’s purview to focus on the preservation of sites historically relevant to the African-American community — such as historically black colleges or Central High School, where teens later known as the “Little Rock Nine” forced Arkansas to enforce federal desegregation laws — than for the panel to pontificate on climate change.
Throughout the hearing, speakers both emphasized and clashed over climate and energy as a racial and social justice issues.
Reverend Lennox Yearwood, president of the Hip Hop Caucus, a nonprofit organization that produces a podcast combining hip hop music and climate action, called climate change “a civil and human rights issue,” and the “lunch counter moment for the 21st century.”
Elizabeth Yeampierre, representing the Brooklyn community-based organization UPROSE and the nationwide Climate Justice Alliance said that, “Our communities are the first and most impacted by the storms, fires, floods and droughts, and are disproportionately burdened by the pollution, poverty and systemic violence associated with the multinational corporations driving these ecological crises.” While she called for a transition away from fossil fuels, she acknowledged that it would not be “smooth” and that efforts would need to be made so no communities are left behind.
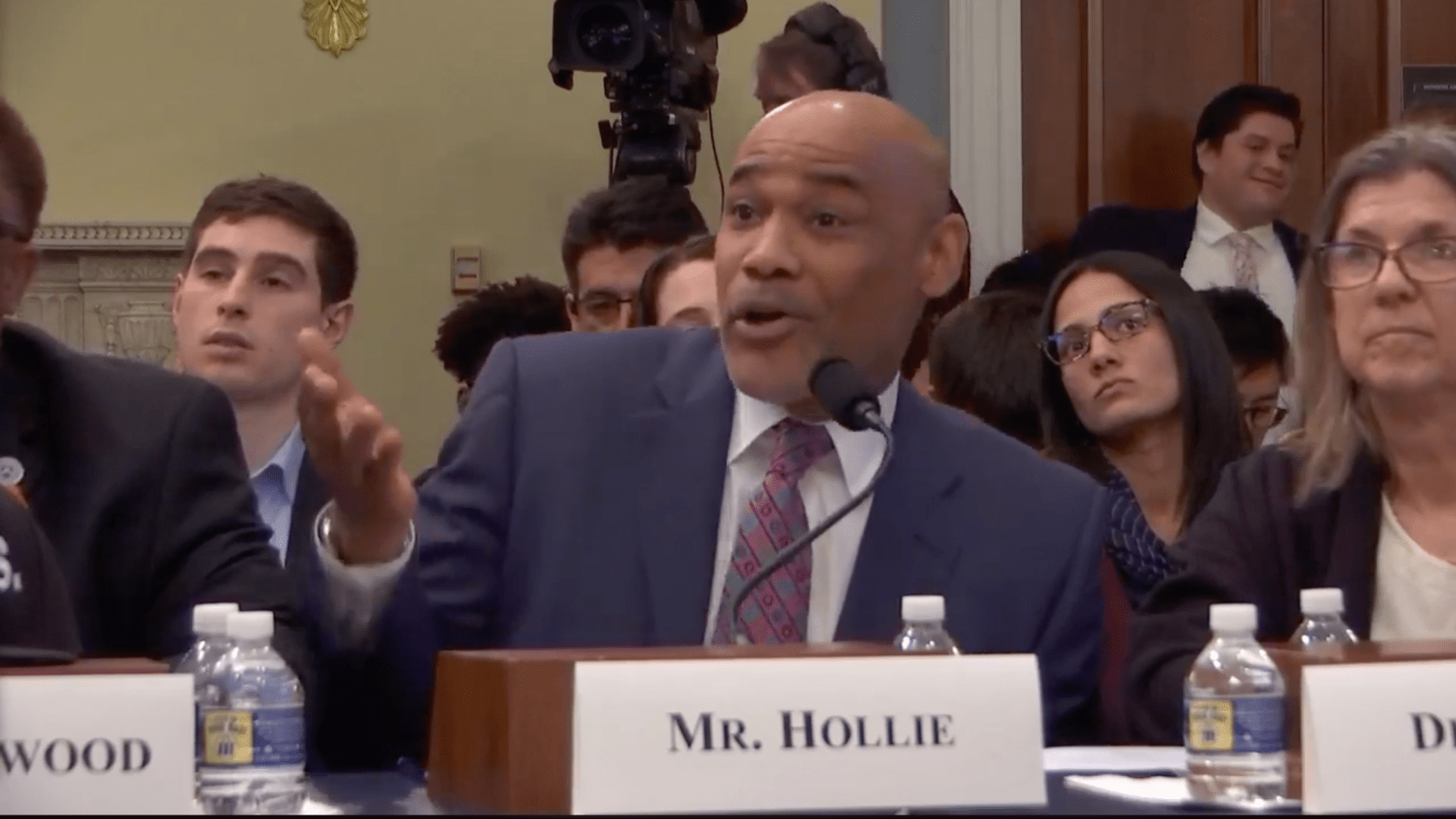
Not everyone agreed on how to uplift low-income families and neighborhoods of color. Derrick Hollie, president of Reaching for America, a group that advocates for affordable energy for communities of color, argued that African-American communities need cheaper sources of energy, as black residents tend to spend a larger proportion of their budgets on heating and cooling costs, partially due to lower-quality housing construction and insulation.
“The African-American community, we don’t have the luxury to pay more for green technologies, we need access to affordable energy to help heat our homes, power our stoves, and get back and forth to work,” said Hollie, who is black.
Instead of focusing on a transition to renewable energy, Hollie argued for greater investment in natural gas, which he said was more affordable. “For many Americans, this allows them not to have to choose between keeping the lights on and feeding their families,” he said.
Reverend Yearwood and Representative Joe Neguse of Colorado — both of whom are black — pushed back on Hollie, pointing to research into how black communities have disproportionately borne the health burdens of natural gas and other fossil fuels.
“For me as a minister, having buried a young girl because of asthma, that mother no longer cares about how much that utility bill would have cost.” said Yearwood. “We can definitely fight poverty and pollution at the same time.”
Several other speakers highlighted the ways in which Americans are already coping with the effects of climate change on health and safety.
“North Carolinians know about [climate change] the hard way. We have weathered two so-called 500 year floods within two years,” Governor Roy Cooper of North Carolina told the committee. “For survivors of these storms, the true costs are incalculable.”
Governor Cooper (a Democrat) and Governor Charlie Baker of Massachusetts (a Republican) then teamed up to defend climate science and denounce efforts to open the Atlantic to offshore drilling.
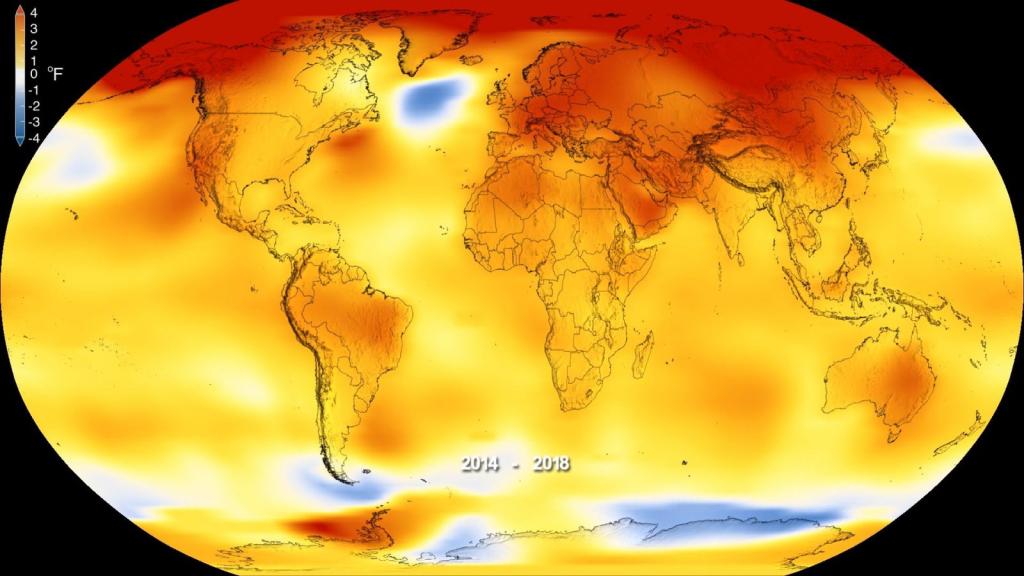
Republicans invited controversial climatologist Judith Curry, whose work has been used by climate skeptics as an argument against taking action, to speak to the committee. She has voiced doubts over how much of an impact human activity has on the climate, and questions whether climate models projecting the effects of a warming world are reliable. (As a group, climate scientists overwhelmingly agree that climate change is a real threat and a result of human activity)
Curry was joined on the panel by her former colleague Kim Cobb, a climate scientist and professor at the Georgia Institute of Technology (Curry retired in 2017). Unlike Curry, Cobb gave vehement testimony during the hearing’s second panel on the disastrous consequences of climate change, including prolonged droughts, wildfires, and storms.
Although the economic costs of those events “can be measured in the hundreds of billions of dollars,” Cobb said,“their real toll, the vast human suffering left in their wake, is immeasurable.”
The Natural Resources Committee will meet again Thursday afternoon for more livestreamed debate on climate change and ocean health.