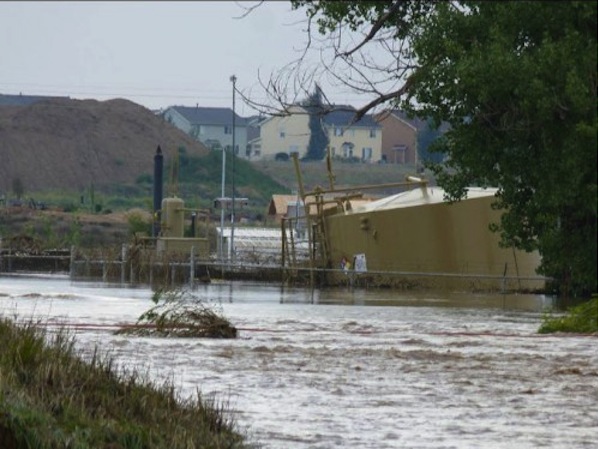
TXsharonFracking equipment overwhelmed by floodwaters in Weld County, Colo, northeast of Denver.
Heavy rains returned to Colorado on Sunday and hampered rescue efforts after last week’s flash floods. The confirmed death toll has risen to seven, and hundreds are still unaccounted for. An estimated 1,500 homes are destroyed. Some 1,000 people in Larimer County, north of Boulder, were awaiting airlifts that never came on Sunday — they were called off because of the foul weather.
The floods have also triggered other problems that have gotten a lot less media attention: Fracking infrastructure has been inundated and its toxic contents have spilled out. Pipelines that transport fossil fuels are sagging and snapping under pressure. Tanks that store chemicals and polluted water are being overwhelmed and toppling over. Oil and gas wells are flooding.
The Boulder Daily Camera reports:
Lafayette-based anti-fracking activist Cliff Willmeng said he spent two days “zig-zagging” across Weld and Boulder counties documenting flooded drilling sites, mostly along the drainageway of the St. Vrain River. He observed “hundreds” of wells that were inundated. He also saw many condensate tanks that hold waste material from fracking at odd angles or even overturned.
“It’s clear that the density of the oil and gas activity there did not respect where the water would go,” Willmeng said. “What we immediately need to know is what is leaking and we need a full detailed report of what that is. This is washing across agricultural land and into the waterways. Now we have to discuss what type of exposure the human population is going to have to suffer through.” …
A spokesman for the Colorado Oil and Gas Conservation Commission said the agency is aware of the potential for contamination from flooded drilling sites, but there simply is no way to get to those sites while flooding is ongoing and while resources are concentrated on saving lives.
The Denver Post interviewed a farmer who ignored evacuation orders and watched as floodwaters overwhelmed a drilling operation on his land and released some oil. The newspaper also reported that at least one oil pipeline was confirmed to have been broken open by the floodwaters. From the article:
Oil drums, tanks and other industrial debris mixed into the swollen [South Platte River] flowing northeast. …
One pipeline has broken and is leaking, Weld County Emergency Manager Roy Rudisill. Other industry pipelines are sagging as saturated sediment erodes around the expanding river.
East Boulder County United, a group that fights fracking, has been posting photographs on its Facebook page of fracking tanks and other equipment toppled over or submerged by floodwaters. Blogger TXsharon has also been posting updates and photographs.
Meanwhile, experts are beginning to discuss the links between climate change and the floods. The flooding was worsened by drought and wildfires, both of which have been linked to global warming and which left the ground dry and hard. That reduced the amount of water that the soil could absorb from the unusual late-summer inundation.
“This was a totally new type of event: an early fall widespread event during one of the driest months of the year,” Brad Udall of the University of Colorado-Boulder told National Geographic News. “As the climate warms further, the hydrologic cycle is going to get more intense.”
Climate Central notes that it “will take climate scientists many months to complete studies into whether manmade global warming made the Boulder flood more likely.” But the wild weather hitting the state lately fits general climate change projections:
An increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme precipitation events is expected to take place even though annual precipitation amounts are projected to decrease in the Southwest. Colorado sits right along the dividing line between the areas where average annual precipitation is expected to increase, and the region that is expected to become drier as a result of climate change.
That may translate into more frequent, sharp swings between drought and flood, as has recently been the case. Last year, after all, was Colorado’s second-driest on record, with the warmest spring and warmest summer on record, leading to an intense drought that is only just easing.
Might the fracking industry have worsened Colorado’s floods by contributing to climate change, then spilled its toxic chemicals into those floodwaters? That would be a cruel double-punch.