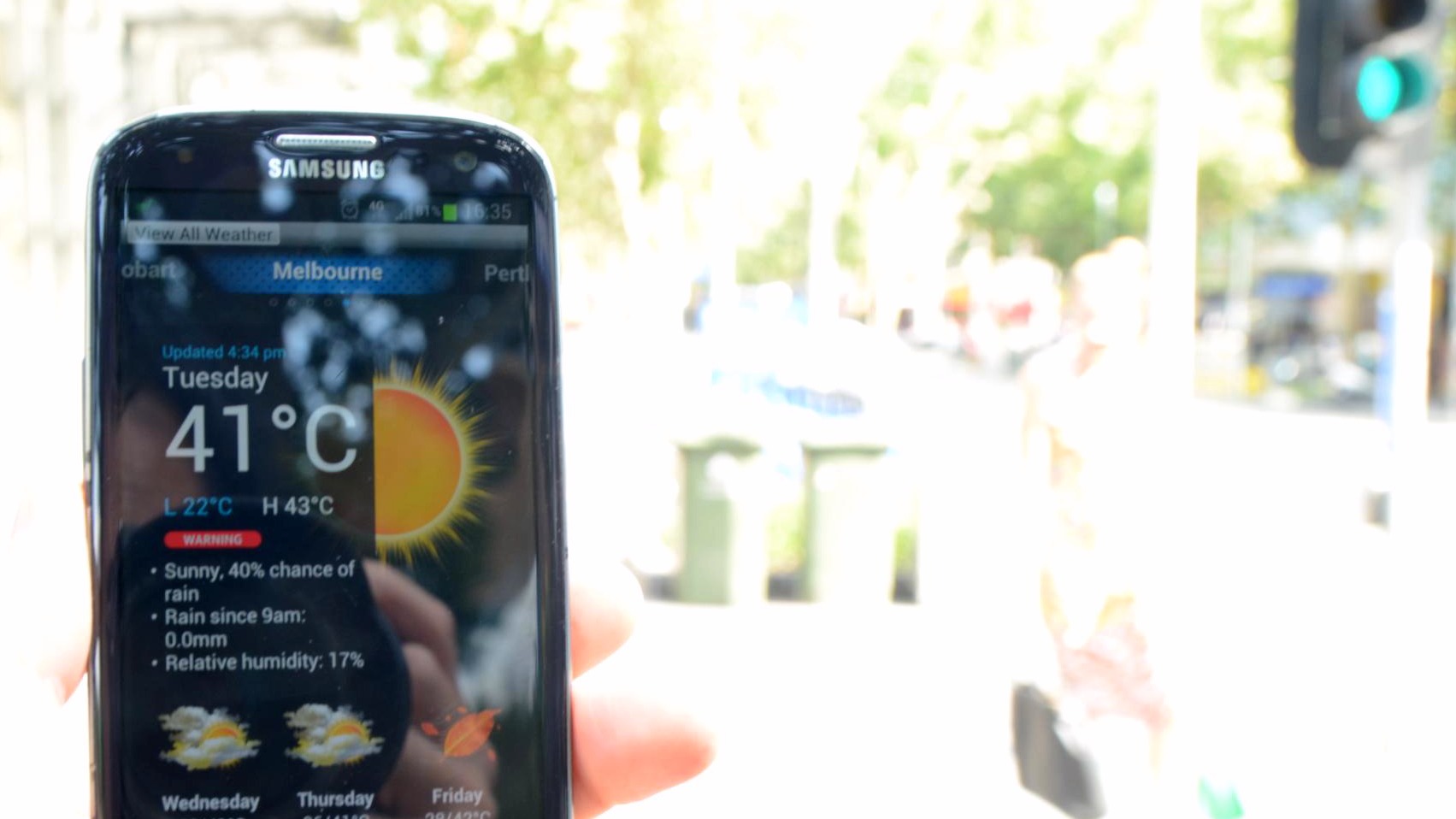
Alpha41 degrees Celsius is 106 Fahrenheit.
The Australian Open ended in Melbourne on Sunday, when a Swiss man wearing a sweat-drenched shirt with yellow and red stripes won in four sets. It was bloody hot, and his nose burned red as he smooched a silver trophy.
In fact, the sweltering heat captivated the world’s media and arguably stole the show. One player burned her bum when she sat down on a chair; another’s plastic water bottle melted on the court’s artificial surface. Athletes collapsed left and right, and one of them hallucinated. Emergency rules designed to help players survive the scorching heat slowed down play.
January is Melbourne’s hottest month, where temperatures routinely break triple digits. And summertime temperatures in this capital of the southeastern state of Victoria will only keep rising as the globe keeps warming. “In Melbourne we are seeing an increase in the amount of extreme heat,” one scientist told The Guardian. Victoria’s profile as a fire-whipped example of the global climate crisis can only go up from here. The following chart, produced by the country’s nonprofit Climate Council, shows that the number of extreme heat days per year (defined as exceeding 35 C, or 95 F) is rising:
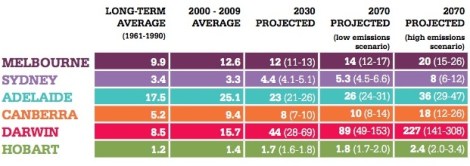
Climate CouncilExtreme heat days per year. Click to embiggen.
Professional tennis players are in their athletic prime and have access to top-notch medical care when the heat gets crazy. Millions of regular Victorians might not cope as well. Unprecedented bushfires linked to climate change killed 173 Victorians in 2009. “With populations at the rural-urban interface growing and the impact of climate change, the risks associated with bushfire are likely to increase,” a team of experts working for the state government concluded in a report. Meanwhile, hundreds more in the state died during that same summer because of heat exposure. Hot and fiery conditions in southeastern Australia this summer have mirrored those of 2009 — and such conditions are forecast to become more common.
Yet even in Victoria, where global warming’s toll is so visible, doctors say the conservative state government is failing to adapt. The Sydney Morning Herald reports:
Doctors and public health experts are calling for the Victorian government to urgently review its management of heatwaves as the death toll from this month’s record-breaking period appears to climb.
The Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine, which works with the State Coroner to investigate reportable deaths, said that as of Friday it had recorded 139 deaths in excess of the average expected between Monday, January 13, and Thursday, January 23.
Dr Liz Hanna, a fellow at the National Centre for Epidemiology and Population Health at ANU, said it was “unfathomable” that Victoria had not learnt enough from the catastrophic 2009 heatwave, when 374 lives were lost, and the Victorian Greens are demanding a formal inquiry into what they call the state’s “clear lack of preparation” for periods of extreme heat.
While Institute of Forensic Medicine director Stephen Cordner said he could not be sure the deaths were due to the heat, most of the deceased were elderly people and those with chronic and mental illnesses, who are known to be vulnerable in extreme heat.
As somebody who spent countless parched days at Australian Open games during a childhood in Melbourne, I always felt that the city had no business hosting the Grand Slam event in January. Now I’m sure of it: It seems inevitable that the competition dates will eventually change, or that another city will need to take over.
In the scope of climate disasters with growing body counts, a too-hot tennis tournament seems a trifling matter. But it has helped broadcast Melbourne’s weather woes to the world — and if that’s what it takes to get people to rally, then it does us good service.



