Royal Dutch Shell spilled an estimated 2,100 barrels of oil off Louisiana’s coast in the Gulf of Mexico this week, the U.S. Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement confirmed on Thursday. Though officials don’t know what caused the spill just yet, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said it’s now contained.
That contained spill has left a sheen of oil the size of Manhattan in the Gulf.
For now, drilling activities at Shell’s Brutus platform have been suspended. The platform, which sits tethered to the sea floor atop 2,900 feet of water, has a maximum capacity of 100,000 barrels of oil per day.
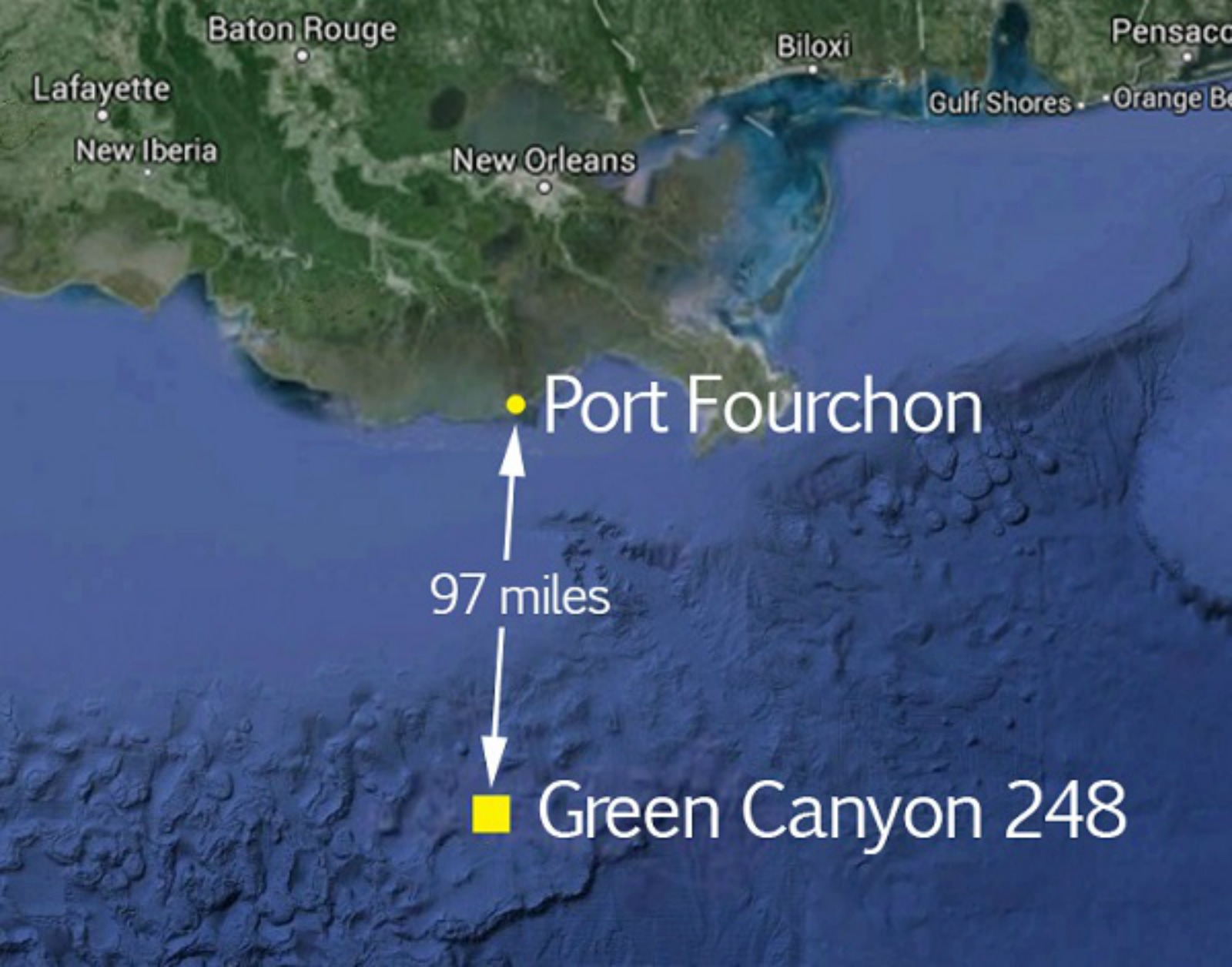
The oil spill occurred 97 miles off Louisiana’s southern coast. BSEE
Still, this spill is tiny in comparison to BP’s 2010 Deepwater Horizon disaster, which released a 4-million-barrel gusher of oil into the Gulf. But Shell’s and BP’s spills aren’t the only ones to hit these waters — according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the area has seen six other large disasters in last few decades.
Despite the known risks of offshore drilling, the Gulf’s oil activities are ramping up. Oil and gas production in the Gulf is expected to hit new highs in 2016 and 2017, despite low crude oil and gas prices. Every time companies punch another drill-sized hole in the sea floor, they risk more harm.



