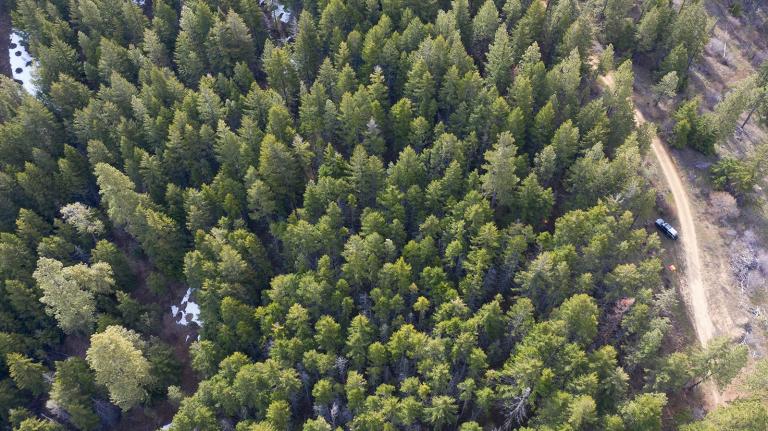
In the early spring of 2012, U.S. farmers were on their way to planting some 96 million acres in corn, the most in 75 years. A warm early spring got the crop off to a great start. Analysts were predicting the largest corn harvest on record.
The United States is the leading producer and exporter of corn, the world’s feedgrain. At home, corn accounts for four-fifths of the U.S. grain harvest. Internationally, the U.S. corn crop exceeds China’s rice and wheat harvests combined. Among the big three grains – corn, wheat, and rice – corn is now the leader, with production well above that of wheat and nearly double that of rice.
The corn plant is as sensitive as it is productive. Thirsty and fast-growing, it is vulnerable to both extreme heat and drought. At elevated temperatures, the corn plant, which is normally so productive, goes into thermal shock.
As spring turned into summer, the thermometer began to rise across the Corn Belt. In St. Louis, Missouri, in the southern Corn Belt, the temperature in late June and early July climbed to 100 degrees Fahrenheit or higher 10 days in a row. For the past several weeks, the Corn Belt has been blanketed with dehydrating heat.
Weekly drought maps published by the University of Nebraska show the drought-stricken area spreading across more and more of the country until, by mid-July, it engulfed virtually the entire Corn Belt. Soil moisture readings in the Corn Belt are now among the lowest ever recorded.
While temperature, rainfall, and drought serve as indirect indicators of crop growing conditions, each week the U.S. Department of Agriculture releases a report on the actual state of the corn crop. This year the early reports were promising. On May 21st, 77 percent of the U.S. corn crop was rated as good to excellent. The following week the share of the crop in this category dropped to 72 percent. Over the next eight weeks, it dropped to 26 percent, one of the lowest ratings on record. The other 74 percent is rated very poor to fair. And the crop is still deteriorating.
Over a span of weeks, we have seen how the more extreme weather events that come with climate change can affect food security. Since the beginning of June, corn prices have increased by nearly one half, reaching an all-time high on July 19th.
Although the world was hoping for a good U.S. harvest to replenish dangerously low grain stocks, this is no longer in the cards. World carryover stocks of grain will fall further at the end of this crop year, making the food situation even more precarious. Food prices, already elevated, will follow the price of corn upward, quite possibly to record highs.
Not only is the current food situation deteriorating, but so is the global food system itself. We saw early signs of the unraveling in 2008 following an abrupt doubling of world grain prices. As world food prices climbed, exporting countries began restricting grain exports to keep their domestic food prices down. In response, governments of importing countries panicked. Some of them turned to buying or leasing land in other countries on which to produce food for themselves.
Welcome to the new geopolitics of food scarcity. As food supplies tighten, we are moving into a new food era, one in which it is every country for itself.
The world is in serious trouble on the food front. But there is little evidence that political leaders have yet grasped the magnitude of what is happening. The progress in reducing hunger in recent decades has been reversed. Unless we move quickly to adopt new population, energy, and water policies, the goal of eradicating hunger will remain just that.
Time is running out. The world may be much closer to an unmanageable food shortage – replete with soaring food prices, spreading food unrest, and ultimately political instability – than most people realize.
*NOTE: This piece originally appeared in The Guardian on Tuesday, July 24, 2012.