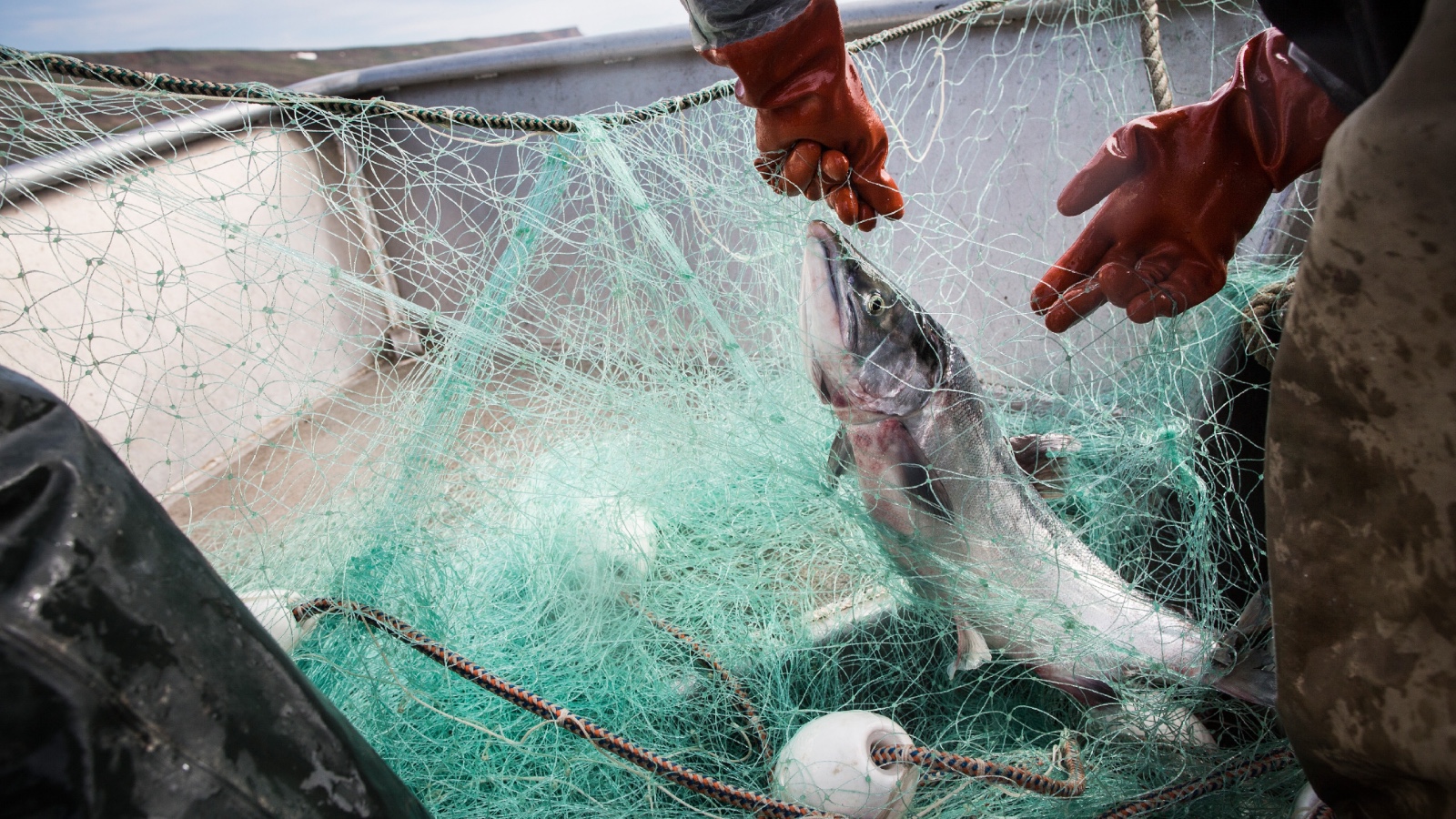
When salmon all but vanished from western Alaska in 2021, thousands of people in the region faced disaster. Rural families lost a critical food source. Commercial fisherfolk found themselves without a major stream of income. And Alaska Native children stopped learning how to catch, cut, dry, and smoke fish — a tradition passed down since the time of their ancestors.
Behind the scenes, the salmon shortage has also inflamed a long-simmering legal fight among Native stakeholders, the Biden administration, and the state over who gets to fish on Alaska’s vast federal lands.
At the heart of the dispute is a provision in a 1980 federal law called the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act, which gives rural Alaskans priority over urban residents to fish and hunt on federal lands. Most rural families are Indigenous, so the law is considered by some lawyers and advocates as key to protecting the rights of Alaska Natives. State officials, however, believe the law has been misconstrued to infringe on the state’s rights by giving federal regulators authority over fisheries that belong to Alaskans.
Now, a lawsuit alleges the state has overstepped its reach. Federal officials argue that state regulators tried to usurp control of fishing along the Kuskokwim River in western Alaska, where salmon make up about half of all food produced in the region. The suit, originally filed in 2022 by the Biden administration against the Alaska Department of Fish and Game, escalated this fall when the state’s lawyers effectively called for the end of federal oversight of fishing across much of Alaska. Indigenous leaders say the state’s actions threaten Alaska Native people statewide.
“What’s at stake is our future,” said Vivian Korthuis, chief executive officer of the Association of Village Council Presidents, a consortium of more than 50 Indigenous nations in western Alaska that’s one of four Alaska Native groups backing the Biden administration in the case. “What’s at stake is our children. What’s at stake is our families, our communities, our tribes.”
The lawsuit is a microcosm of how climate change is raising the stakes of fishing disputes around the world. While tensions over salmon management in Alaska aren’t new, they’ve been exacerbated by recent marine heat waves in the Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska and rising temperatures in rivers like the Yukon and Kuskokwim, where king, chum, and coho salmon populations have plummeted. In warmer waters, salmon burn more calories. They’re more likely to become malnourished and less likely to make it to their freshwater spawning grounds. With fewer fish in places like western Alaska, the question of who should manage them — and who gets access to them — has become even more urgent.
The Alaska dispute erupted in 2021, when state regulators on the Kuskokwim issued fishing restrictions that conflicted with regulations set by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. People along the river, who are predominantly Yup’ik, were forced to navigate contradictory rules about whether and when they could fish legally — adding to the pain and frustration of an already disastrous season shaped by the coronavirus pandemic and historic salmon shortages.
“We can face large penalties and fines if we make mistakes,” Ivan M. Ivan, an elder in the Yup’ik village of Akiak, said in an affidavit.
The conflict spilled into 2022, another year of abysmal salmon returns, when state and federal regulators again issued contradictory restrictions. Alaska officials blamed the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service for opening up fishing prematurely, before salmon had begun their migration upstream, and with an “apparent lack of concern” for the species’ conservation. The Biden administration sued, arguing that the state illegally imposed its own rules in the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge, a federal reserve of wetlands and spruce and birch forest that encircles more than 30 Indigenous communities.
The fight played out quietly for more than a year — until September, when the state’s attorneys filed a brief that explicitly asked the court to undo legal precedent widely viewed as a safeguard for rural, mostly Indigenous families who depend on salmon. That move caused Alaska’s biggest Indigenous organization, the Alaska Federation of Natives, to join three smaller Native groups that had intervened on behalf of the federal government.
Those organizations are concerned that the state wants to reverse a string of court decisions, known as the “Katie John” cases, which held that rural Alaskans have priority to fish for food in rivers that flow through federal conservation areas, including long sections of the Yukon, Kuskokwim, and Copper rivers. Alaska Native leaders fear that doing away with that priority would endanger salmon populations and limit access for locals by opening fishing up to more people.
“It really will put a lot of pressure on stocks,” said Erin Lynch, an Anchorage-based attorney at the Native American Rights Fund, which is representing the Association of Village Council Presidents.
That concern isn’t limited to western Alaska. Ahtna Inc., a corporation owned by Indigenous shareholders in the Copper River region — some 500 miles east of the Kuskokwim — has also sided with the Biden administration. Without federal protections on the Copper River, Ahtna anglers would risk getting “pushed out,” according to John Sky Starkey, a lawyer representing Ahtna.
“There are only so many fish. There are only so many places [to fish],” Starkey said. “It’s a significant danger.”
State officials see the issue differently. They say there would be no threat of overfishing or competition between urban and rural residents, partly because rivers like the Yukon and Kuskokwim are so hard to reach from cities like Anchorage. They note that state law explicitly protects the subsistence rights of all Alaskans, including Alaska Natives. And they blame the feds for picking the fight by taking the issue to court.
“We did not initiate this lawsuit,” said Doug Vincent-Lang, commissioner of the Alaska Department of Fish and Game. “We provide for subsistence priority, and we take that seriously.”
The state’s lawyers also claim that federal policy is unfair for Alaska Natives who have moved to cities because it bars them from fishing with relatives in rural areas. Some Indigenous leaders see it as flawed, too, but they disagree with the state about the solution. Rather than do away with federal management, they have called on Congress to strengthen protections for Alaska Natives.
The case, now before the U.S. District Court for Alaska, is likely to heat up even more in the coming months. A ruling is expected in the spring.