01-12-2013 20:00; PM2.5; 886.0; 755; Beyond Index
— BeijingAir (@BeijingAir) January 12, 2013
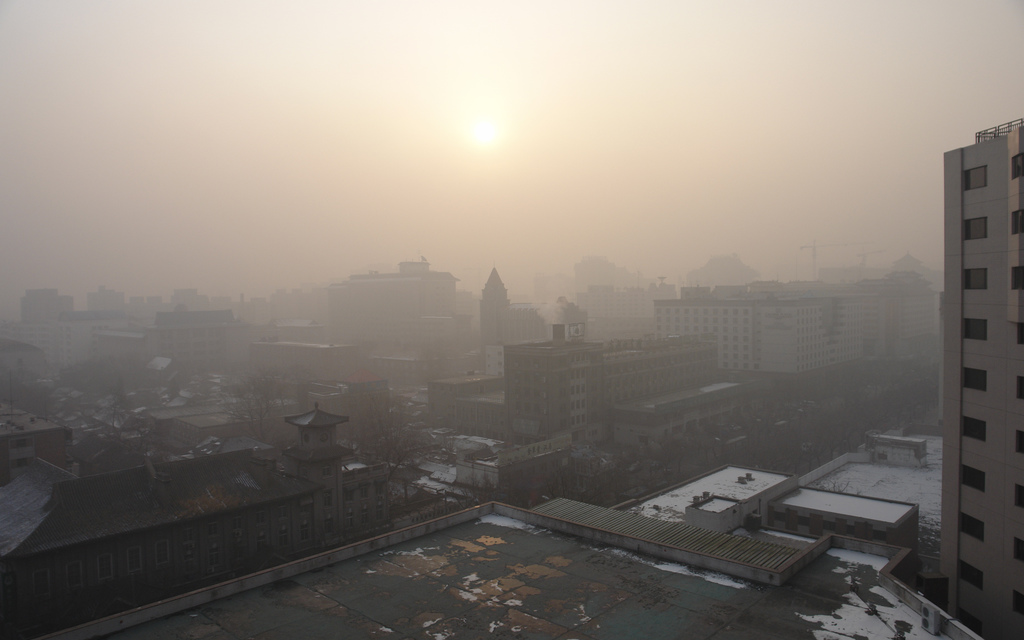
Allow me to translate the information above. According to the air pollution sensor atop the U.S. embassy in Beijing, the amount of particulate matter (soot) in the air on Saturday at 8 p.m. local time was indescribably bad. At 886 micrograms per cubic meter, the level was “Beyond Index,” past the end of a scale that goes from “Unhealthy” to “Very Unhealthy” to “Hazardous.” Then: “Beyond Index.”
Once, the system got creative. From the New York Times:
One Friday more than two years ago, an air-quality monitoring device atop the United States Embassy in Beijing recorded data so horrifying that someone in the embassy called the level of pollution “Crazy Bad” in an infamous Twitter post. That day the Air Quality Index, which uses standards set by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, had crept above 500, which was supposed to be the top of the scale. …
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, levels between 301 and 500 are “Hazardous,” meaning people should avoid all outdoor activity. The World Health Organization has standards that judge a score above 500 to be more than 20 times the level of particulate matter in the air deemed safe.
In online conversations, Beijing residents tried to make sense of the latest readings.
“This is a historic record for Beijing,” Zhao Jing, a prominent Internet commentator who uses the pen name Michael Anti, wrote on Twitter. “I’ve closed the doors and windows; the air purifiers are all running automatically at full power.”
Other Beijing residents online described the air as “postapocalyptic,” “terrifying” and “beyond belief.”
One broadcaster provided a visual representation of the pollution. He is not sitting in front of a yellow backdrop.
How bad is the smog in Beijing? Let a CNN producer show you in one simple shot: twitter.com/StevenCNN/stat…(via @thestalwart)
— Slade Sohmer (@SladeHV) January 14, 2013
The BBC has a gallery of similarly murky images.
In an attempt to ameliorate the problem, the city has cracked down on causes of soot pollution. From the Los Angeles Times:
A prolonged spell of air pollution across a large area of China has led to the cancellation of flights and sporting activities and the closure of highways, factories and construction sites. …
As an emergency measure, the Beijing Environmental Protection Ministry announced Sunday that factories and construction sites had agreed to reduce or stop work entirely until the air cleared up. …
“The air pollution is unprecedented. This is the first time in China’s history we have seen it this bad,’’ said Zhao Zhangyuan of the Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences.
http://www.newslook.com/videos/533251-beijing-pollution-reaches-highly-hazardous-levels
The health effects have been immediate. From Bloomberg:
Hospitals were inundated with patients complaining of heart and respiratory ailments and the website of the capital’s environmental monitoring center crashed. Hyundai Motor Co.’s venture in Beijing suspended production for a day to help ease the pollution, the official Xinhua News Agency reported.
Official measurements of PM2.5, fine airborne particulates that pose the largest health risks, rose as high as 993 micrograms per cubic meter in Beijing on Jan. 12, compared with World Health Organization guidelines of no more than 25. It was as high as 500 at 6 a.m. today. Long-term exposure to fine particulates raises the risk of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases as well as lung cancer, according to the WHO. …
Exposure to PM2.5 helped cause a combined 8,572 premature deaths in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Xi’an in 2012, and led to economic losses of $1.08 billion, according to estimates given in a study by Greenpeace and Peking University’s School of Public Health published Dec. 18. The burning of coal is the main source of pollution, accounting for 19 percent, while vehicle emissions contribute 6 percent, the report said.
The link between coal power and pollution is clear to some Chinese residents, despite official news agencies downplaying the choking air as “fog.” Last year, one Chinese village protested a planned coal power plant in their area, worried about the health effects.
But isolated protests haven’t slowed coal power. Earlier today, Chinese stock indices spiked on good economic news — including an increase in electricity consumption. From Business Insider:
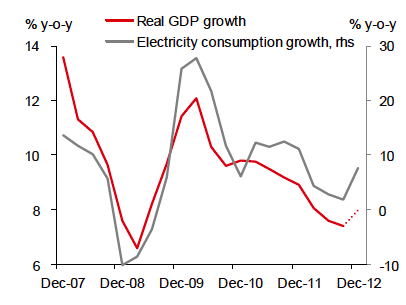
[O]n the real economy side of things, there was a very nice reading in Chinese electricity consumption, which correlates nicely to GDP. Per Nomura (which made the chart below) electricity consumption in “secondary industries” grew over 7% yearover-year, which is a strong sign.
The word “nice” in the paragraph above should be understood to refer to economic benefits, not health ones. The description you choose might be different. We recommend: “Crazy Bad.”

NASAThe massive swath of pollution on Saturday covered Beijing (blue circle) and extended south and east.