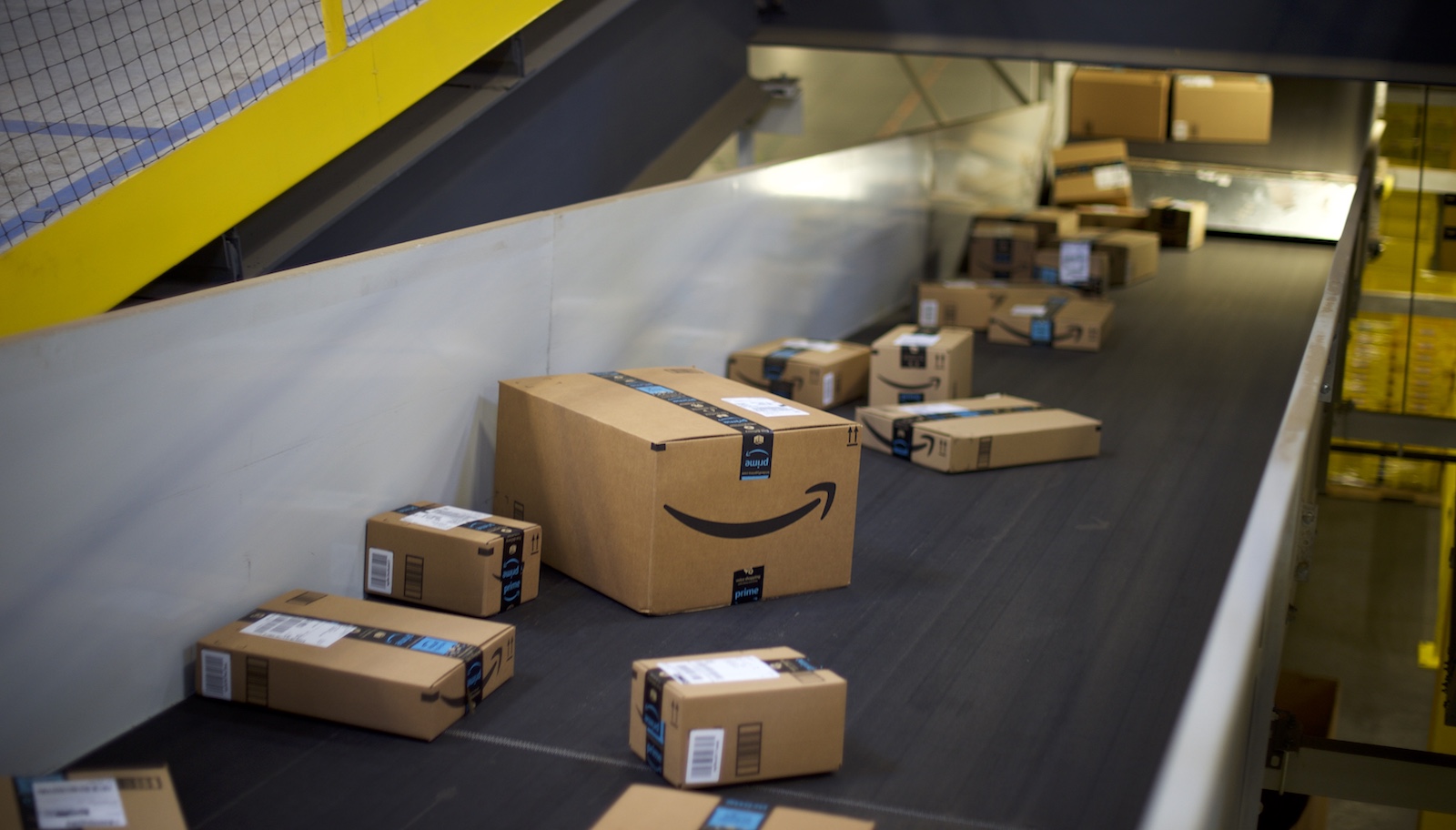
This Tuesday is day two of Prime Day, a late-capitalist online extravaganza for Amazon Prime members only. The once-a-year sale, which Amazon says rivals Black Friday for low prices, has become famous for its deals on increasingly bizarre items. But before you rush to purchase a hot dog toaster or a life-size yeti garden statue, consider the environmental footprint of that purchase — and Prime in general.
Transportation experts are split over whether online shopping reduces or increases emissions. In theory, online shopping can be more environmentally friendly than a traditional brick-and-mortar store: Either way, a truck has to deliver the items, and in the case of online shopping, you don’t have to drive to the store as well.
“Our research shows that delivering a typical order to an Amazon customer is more environmentally friendly than that customer driving to a store,” said Melanie Janin, sustainability representative at Amazon, in an email.
But research has shown that it’s a different story when companies incorporate “rush” shipping. Free two-day shipping — the hallmark of Amazon’s plan to squeeze out traditional retailers — burns through significantly more emissions than standard shipping or traditional in-store shopping.
And Amazon has only increased its shipping speeds, offering select products on Prime Now that can be delivered in one to two hours.“With one-hour or two-hour delivery, there is no time for companies to consolidate shipments,” says Miguel Jaller, professor of civil and environmental engineering at University of California Davis. “And that means more vehicles, more emissions, and more health impacts.”
When you wait three to five days for shipment, Jaller explains, Amazon has time to find the most efficient (and cheapest) way to deliver goods. Aviation is by far the most carbon-intensive transit option, and with more time the company can route your package by land, instead of by air. Slower shipping also allows Amazon to group your package with other, similar deliveries. But with Prime, there’s almost no incentive to choose a slower option.
“The concept of Amazon Prime pushes us towards more emissions,” Dan Sperling, another professor at UC Davis, tells Grist. “It makes the marginal cost of purchases very small, so you have motivation to buy more. And of course, that’s what Amazon wants.”
Emissions aren’t the only problem — the company has previously come under fire for truly unreasonable amounts of packaging for small items and more recently for troubling labor practices. But transport continues to be a sustainability problem for Amazon, and we don’t even know the full extent of the problem: the Seattle-based conglomerate is highly secretive about what their emissions actually are.
It’s not hopeless: Jeff Bezos, Amazon’s CEO, could take a stance on green delivery and prioritize low-emission vehicles. (Not a bad decision for a man recently named the richest in modern history). According to Jaller, Amazon could also offer higher incentives for Prime customers to opt for slower shipping. Other researchers have suggested labeling standard shipping as the green choice, or giving consumers the chance to purchase carbon offsets.
At the end of the day, however, it will take consumer pressure to make any of these changes. So please, consider whether you can wait a few days to receive your garden yeti — or better yet, whether you even need it at all.
“Amazon isn’t the villain in this,” says Sperling. “The villain is us — it’s what people are willing to pay for.”