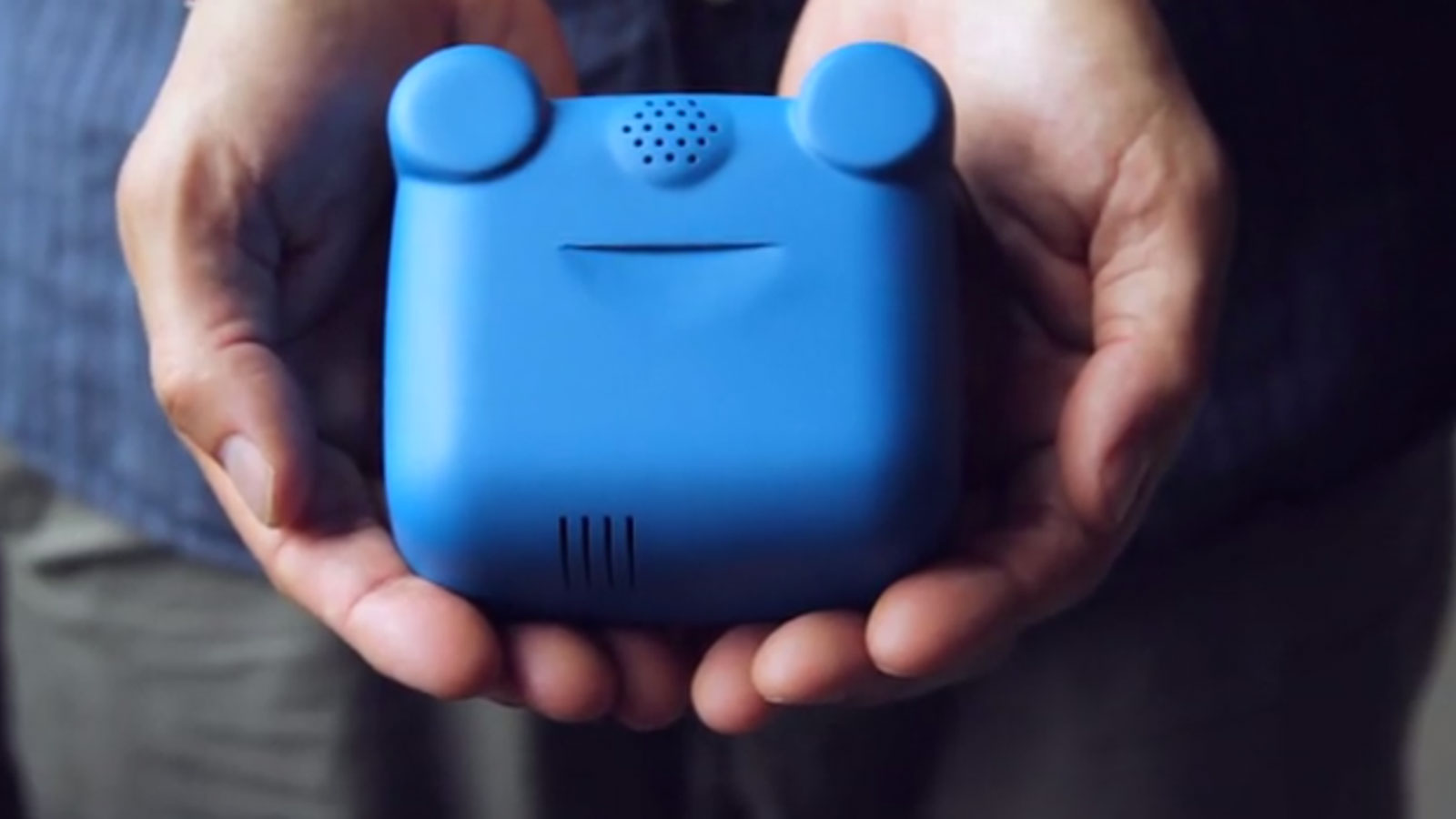
Here’s a Kickstarter that got our attention this month: The AirBeam, a wearable air monitor designed by Brooklyn-based environmental justice nonprofit HabitatMaps. The device costs $200 to produce, fits in your palm (if you’re Sasquatch), and is designed to measure particulate pollution on city streets, as well as temperature and humidity. It’s also kinda adorable — which is good, considering that the group is counting on hundreds of people wearing them around NYC in the near future.
But don’t let those cute blue Mickey ears fool you — the AirBeam is a response to a very real problem: Air pollution costs the U.S. $78 billion a year, HabitatMaps claim on their Kickstarter page:
The negative impacts of air pollution rank it among the most serious and widespread human health hazards in the world. Breathing dirty air causes chronic illnesses such as asthma and bronchitis and contributes to terminal illnesses such as cancer and heart disease. Unfortunately, despite the very real impacts air pollution has on our every day lives, it often goes unnoticed because it is largely invisible. In addition, because government-run air quality monitoring networks are sparse, publicly available air quality measurements don’t translate into an accurate assessment of personal exposure. The answer? Low-cost, portable air quality instruments.
Most official air monitoring occurs well above street level, where the air tends to be cleaner. The AirBeam monitors — once fully deployed by a team of citizen scientists — will measure pollution where it counts: where you actually breathe it. From GigaOm:
Michael Heimbinder, executive director at HabitatMaps, said that the nonprofit had developed the cheapest, portable air quality monitoring sensor it could in hopes of gathering data that it can then use to make policy arguments in the city. It’s also helpful for individuals who may want to change their own habits.
That is, if you know that levels of air pollution are pretty bad at a certain time and place on your commute, you might be able to tinker with your habits to limit your own exposure. But the real solutions will come from the sum total of all the data — cities will be able to identify hot spots for pollution, and then (er, hopefully) be better equipped to address them.
If you pledge $200, you’ll get an AirBeam of your own come launch — and a healthy dose of civic engagement to boot.