Most Caribbean coral reefs will disappear within the next 20 years unless action is taken to protect them, primarily due to the decline of grazers such as sea urchins and parrotfish, a new report has warned.
A comprehensive analysis by 90 experts of more than 35,000 surveys conducted at nearly 100 Caribbean locations since 1970 shows that the region’s corals have declined by more than 50 percent.
But restoring key fish populations and improving protection from overfishing and pollution could help the reefs recover and make them more resilient to the impacts of climate change, according to the study from the Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network, the International Union for Conservation of Nature, and the United Nations Environment Program.
While climate change and the resulting ocean acidification and coral bleaching does pose a major threat to the region, the report — Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012 — found that local pressures such as tourism, overfishing, and pollution posed the biggest problems.
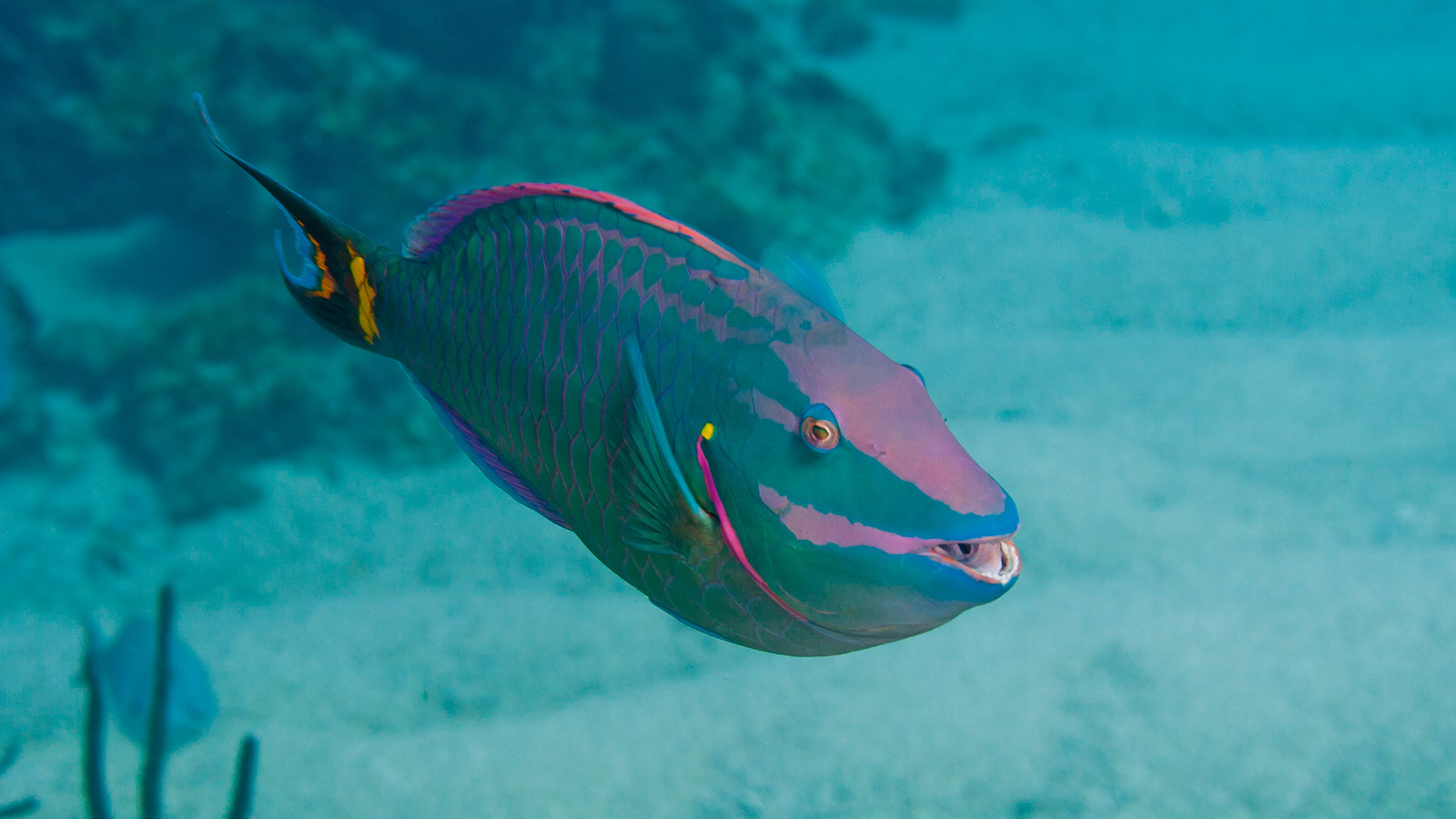
And these factors have made the loss of the two main grazer species, the parrotfish and sea urchin, the key driver of coral decline in the Caribbean.
Grazers are important fish in the marine ecosystem as they eat the algae that can smother corals. An unidentified disease led to a mass mortality of the sea urchin in 1983 and overfishing throughout the 20th century has brought the parrotfish population to the brink of extinction in some regions, according to the report.
Reefs where parrotfish are not protected have suffered significant declines, including Jamaica, the entire Florida reef tract from Miami to Key West, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. At the same time, the report showed that some of the healthiest Caribbean coral reefs are those that are home to big populations of grazing parrotfish. These include the U.S. Flower Garden Banks national marine sanctuary in the northern Gulf of Mexico, Bermuda, and Bonaire — all of which have restricted or banned fishing practices that harm parrotfish.
The Caribbean is home to 9 percent of the world’s coral reefs, but only around one-sixth of the original coral cover remains. The reefs, which span 38 countries, are vital to the region’s economy and support the more than 43 million people, generating more than $3 billion annually from tourism and fisheries and much more in other goods and services.
According to the authors, restoring parrotfish populations and improving other management strategies could help the reefs recover. “The rate at which the Caribbean corals have been declining is truly alarming,” said Carl Gustaf Lundin, director of IUCN’s global marine and polar program. “But this study brings some very encouraging news: The fate of Caribbean corals is not beyond our control and there are some very concrete steps that we can take to help them recover.”
Reefs that are protected from overfishing, as well as other threats such as excessive coastal pollution, tourism, and coastal development, are more resilient to pressures from climate change, according to the authors.
“Even if we could somehow make climate change disappear tomorrow, these reefs would continue their decline,” said Jeremy Jackson, lead author of the report and IUCN’s senior adviser on coral reefs. “We must immediately address the grazing problem for the reefs to stand any chance of surviving future climate shifts.”
 This story was produced by The Guardian as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
This story was produced by The Guardian as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.