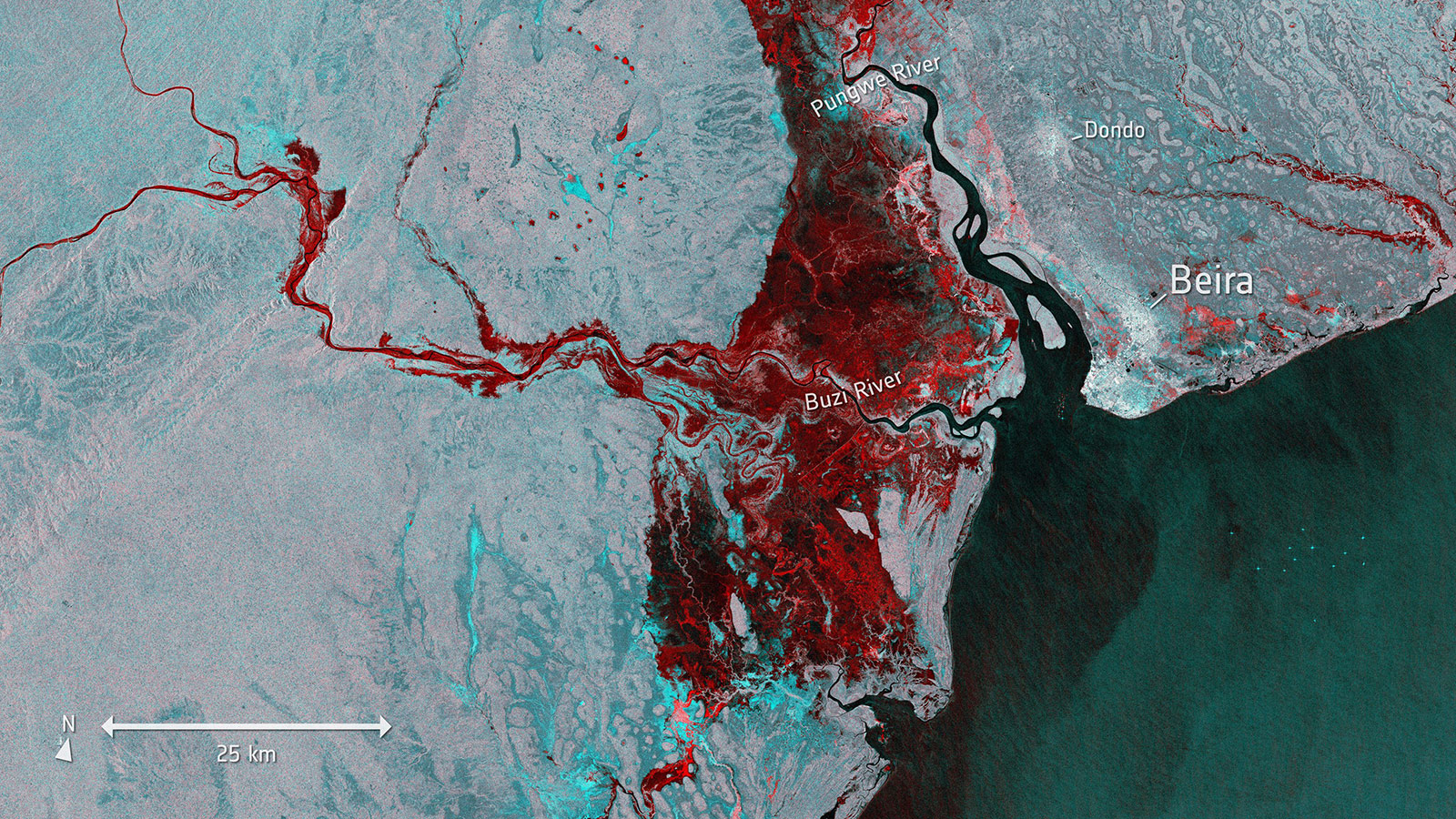
Post-flood satellite images of Mozambique show that Cyclone Idai submerged about 835 square miles of homes and fields — an area larger than New York City, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and Boston combined. Aid workers in Mozambique describe the floodwaters as “inland oceans extending for miles and miles.”
Idai’s official death toll in Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and Malawi reached 761 on Monday, but that total will surely rise. There are reports of hundreds of bodies alongside a single road as floodwaters began to recede.
Beira, Mozambique, reportedly the hardest hit city, “will go down in history as having been the first city to be completely devastated by climate change,” said Graça Machel, the country’s former first lady and a prominent humanitarian in an interview with the Mozambique newspaper Verdade on Monday.
The United Nations has characterized the storm and its aftermath as one of the worst weather-related disasters ever recorded in the Southern Hemisphere. As a result, the UN World Food Program now considers it one of its top concerns globally — on par with the wars in Syria, Yemen, and South Sudan — estimating that some 3 million people have been affected, nearly half of them children.
On Monday, the UN launched a $282 million appeal for aid to cover the initial three months of its response to the cyclone. Over the weekend, President Donald Trump agreed to send the US military to help support the ongoing international relief operation — three days after a formal request from the Mozambique government.
It's been more than a week since #CycloneIdai hit #Mozambique.
The humanitarian needs are still enormous. pic.twitter.com/hPf3dvjlaC
— IFRC (@ifrc) March 24, 2019
Mozambique received nearly a year’s worth of rainfall in the days following Cyclone Idai, consistent with findings that rainstorms are becoming stronger and more common as Earth’s atmosphere warms up. After centuries of colonial rule by Portugal and decades of war after independence (in which the U.S. played an active role), Mozambique is one of the poorest countries in the world — a stark reminder of the inherent injustice of climate change, that those least responsible for greenhouse gas emissions are bearing its worst consequences.
An estimated 128,000 survivors have made their way to temporary camps near Beira, with an escalating risk of cholera and other waterborne diseases. The Red Cross announced plans to provide humanitarian support to 200,000 people for up to two years. “The scale and scope of suffering and damage is breathtaking,” said Red Cross secretary general, Elhadj As Sy, after touring the region around Beira.