Just weeks before the international climate summit in Dubai, one of the biggest climate agreements ever proposed between Middle Eastern countries unraveled.
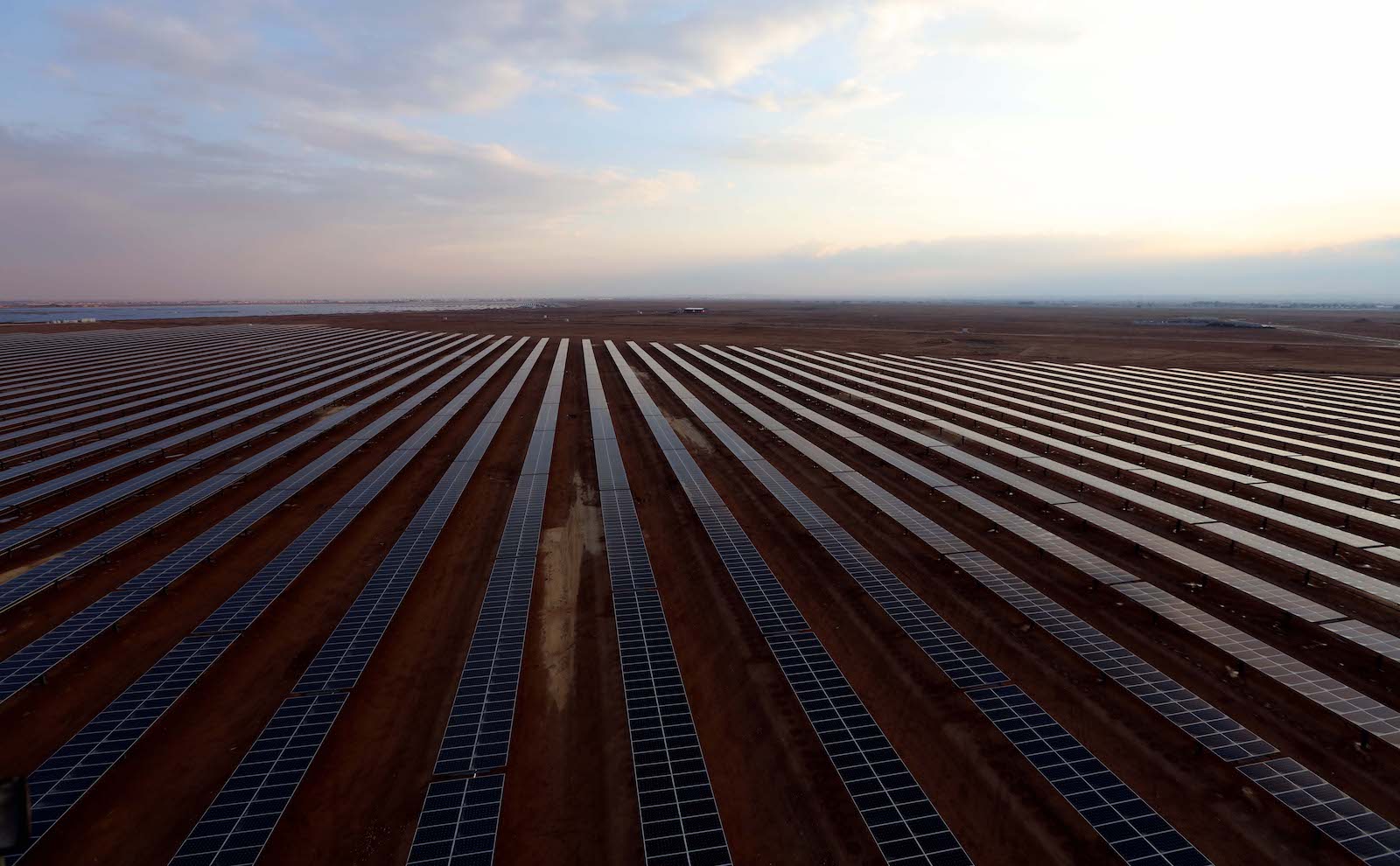
For two years, Israel and Jordan had negotiated a trade of precious resources they’ll need in a hotter future: renewable energy and drinking water. Under their proposed deal, Israel would dip into its water surplus to send its neighbor billions of gallons each year. In return, Jordan would share electricity from a new 600-megawatt solar farm in its sun-soaked desert.
The plan, dubbed Project Prosperity, had the financial support of the United Arab Emirates, which seeks to lead the region in tackling climate change, and the diplomatic blessing of the United States, which said it exemplified how Israel might weave into the political and economic fabric of the Middle East. With talks picking up in mid-2023, all hoped to finalize the deal in December, at the United Nations’ 28th annual climate conference, called COP28.
The October 7 attack on Israel, in which fighters with Hamas — an organization the U.S. and others consider a terrorist group — killed an estimated 1,139 people and took some 200 hostages, changed everything.
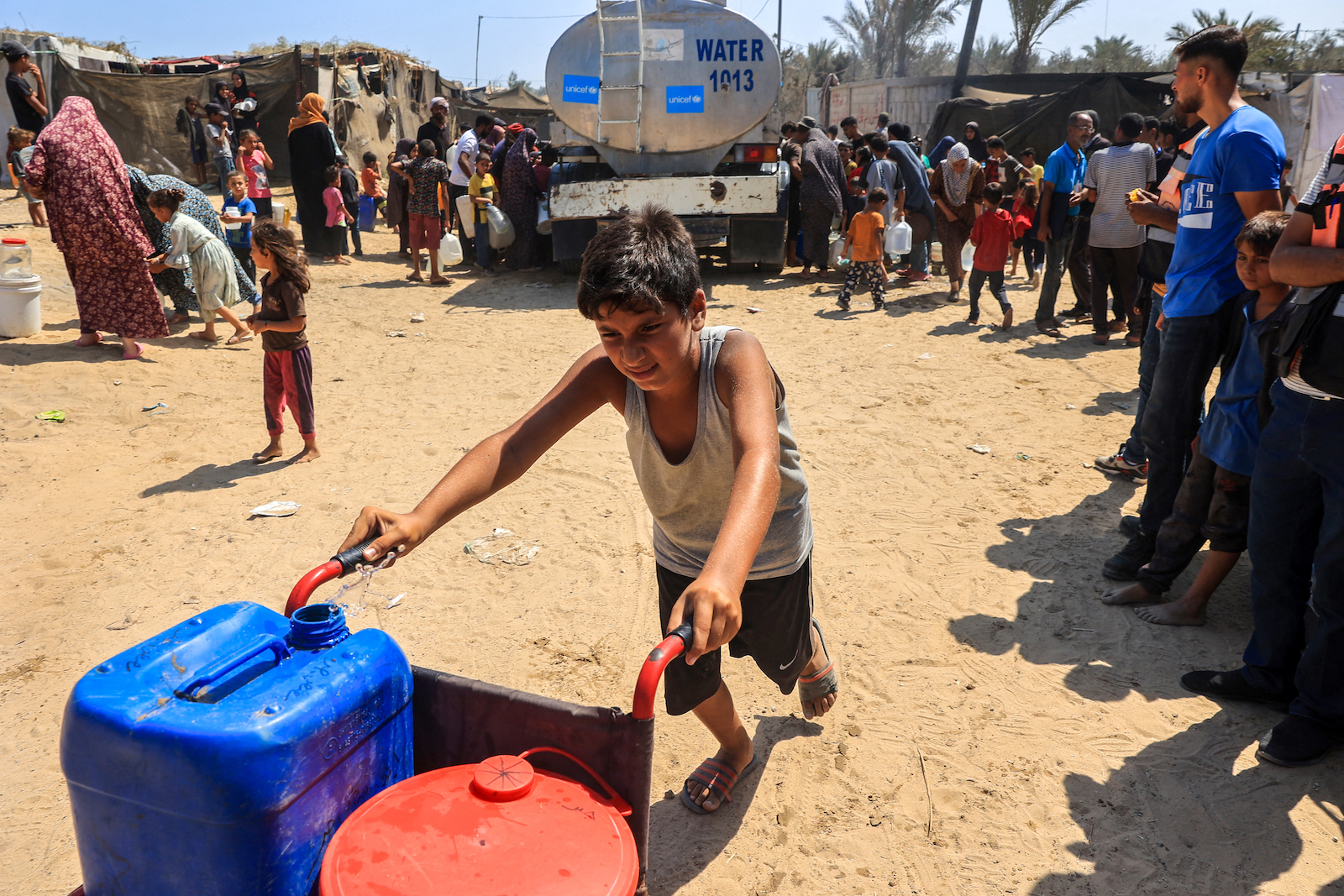
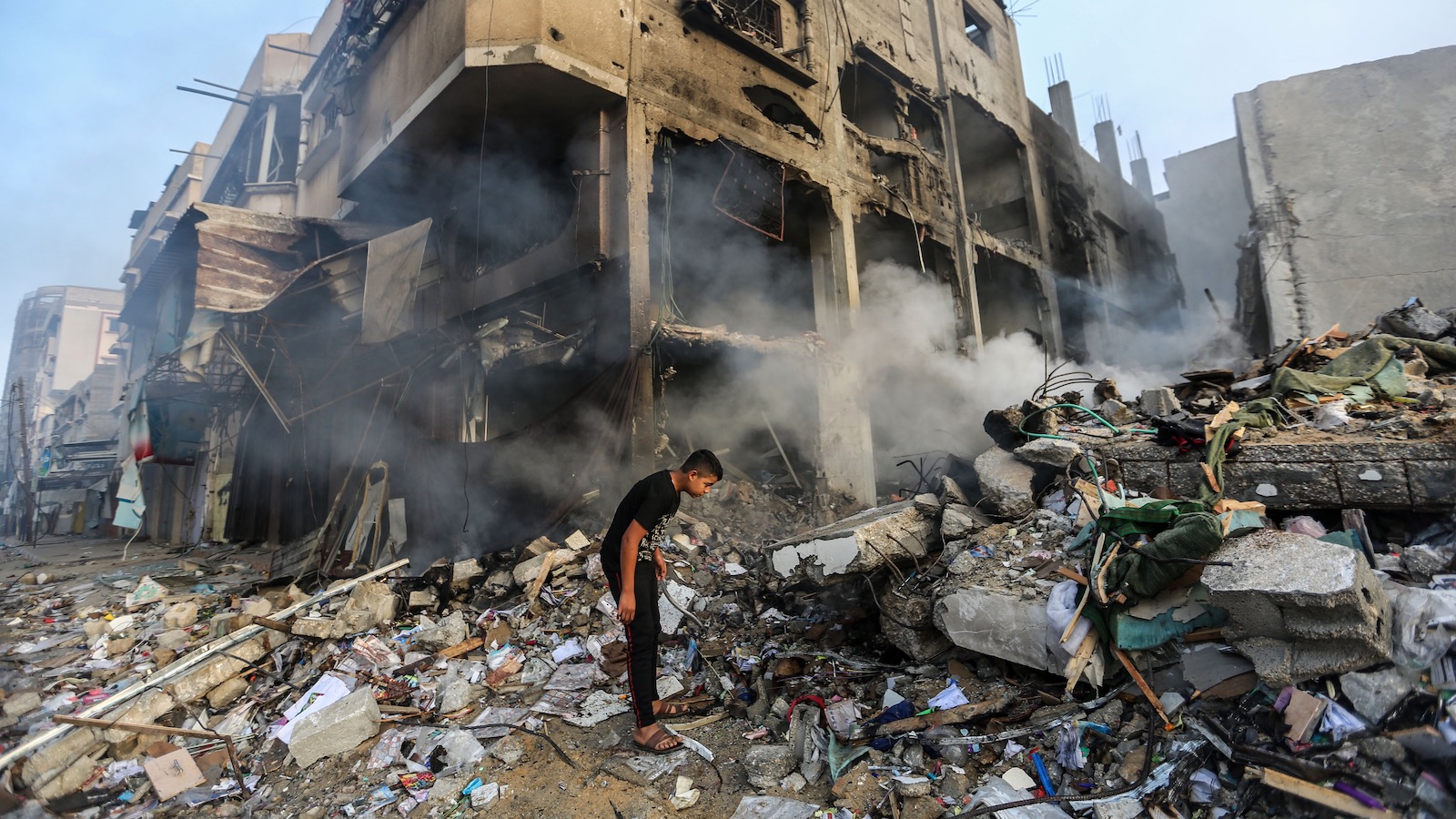
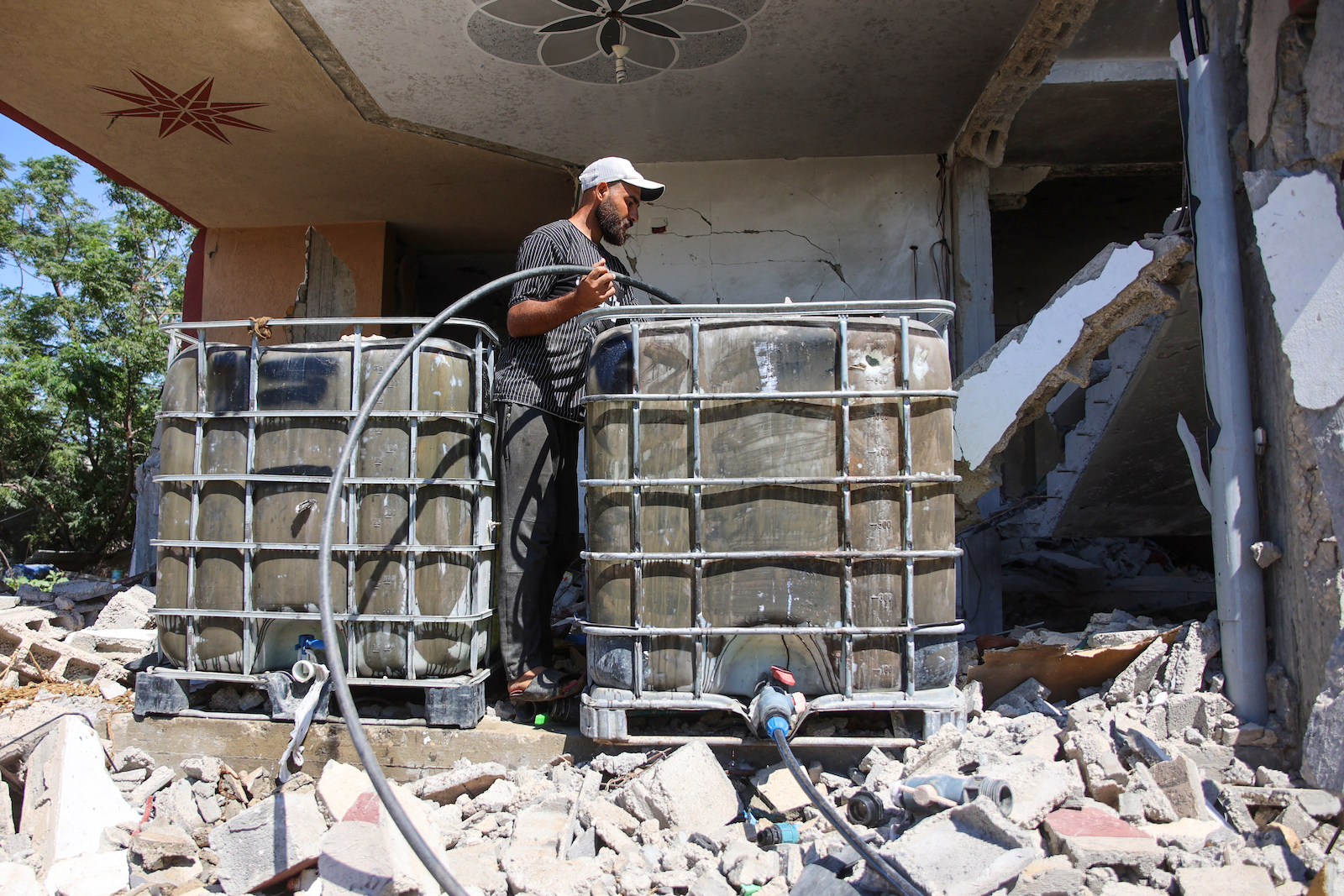
Israel has answered with a military campaign that has so far claimed the lives of at least 38,000 Gazans. Its near-complete blockade of food and water into Gaza has aid groups warning of famine. Some United Nations experts say Israel’s conduct is approaching genocide.
The war has caused upheaval in Jordan, a country whose government is historically one of Israel’s closest partners in the Arab world but also one whose public — at least half of whom are of Palestinian heritage due to successive displacements by Israel — feels a deep kinship with the Palestinian cause. Jordan’s foreign minister has said Israel’s campaign amounts to genocide. On November 16, amid protests near the American and Israeli embassies in Amman, Jordan said it would not finalize the water-for-energy deal. It has since accelerated plans for a $3.2 billion desalination project on its own coast that could provide a volume of water comparable to what Project Prosperity would have supplied.
The developments show how the war between Israel and Hamas is shaking not just the geopolitics of the Middle East, but its climate politics as well.

Before October 7, Israel was seen as a growing hub for clean technologies like water recycling, ultra-efficient irrigation, and green hydrogen; it had planned to send 1,000 people, including representatives of 100 companies, to COP28. Project Prosperity demonstrated the Arab world’s growing willingness to collaborate with Israelis on climate solutions, and hinted at how climate change might become an area of constructive cooperation in a fractious region.
“The COP was meant to capitalize on this growing momentum of regional collaboration,” said Karim Elgendy, a climate consultant and associate fellow at Chatham House, a London think tank. “I think that world is behind us now.”
Many Palestinian and Jordanian environmentalists find nothing to mourn in that. Even before the war, most opposed engaging with Israel without a fair and just resolution of the Israel-Palestine conflict. “Why would we collaborate with someone killing us and controlling our resources?” said one Palestinian official. “How can I collaborate with someone occupying me? Controlling me?”
But a small group of scientists, researchers, and environmentalists in the region see it the other way around. Having devoted their careers to cross-border cooperation, they say the war has only deepened their conviction that this is the kind of work that’s necessary for any lasting peace.
“We’ve done war, shooting, rockets since 1948. Guess what? It came up with no solutions. History is repeating itself,” one young Palestinian environmentalist said, referring to the year Israel was founded. He requested anonymity because he feels expressing support for cooperation, amid the trauma of war, is risky. “I’m trying to use climate change and the environment in general as a starting point for peace. The only way is to come to the same table.”
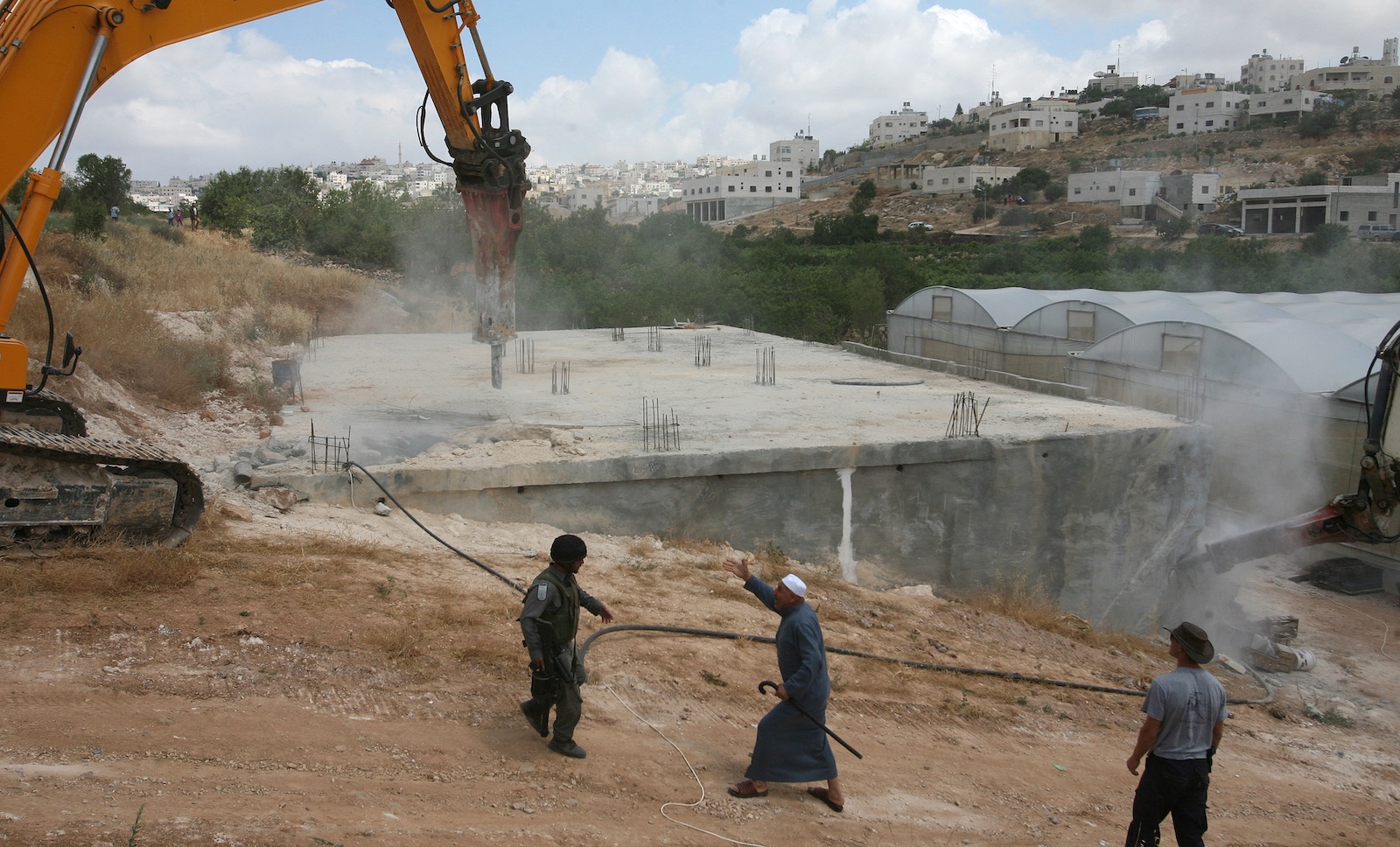
In the Holy Land, water is political in a way that most Westerners would not recognize. Competition over the Jordan River basin helped spark a war between Israel and the Arab states of Egypt, Syria and Jordan in 1967. Afterward, Israel occupied the West Bank and Gaza Strip, which are today called the Palestinian territories, and declared control of their water resources. Israel had reached the limits of its domestic water reserves before the war; these seized resources allowed it to expand in its core territory and build settlements in its newly occupied ones. (Palestinians, the U.N., and most governments deem these settlements illegal.)
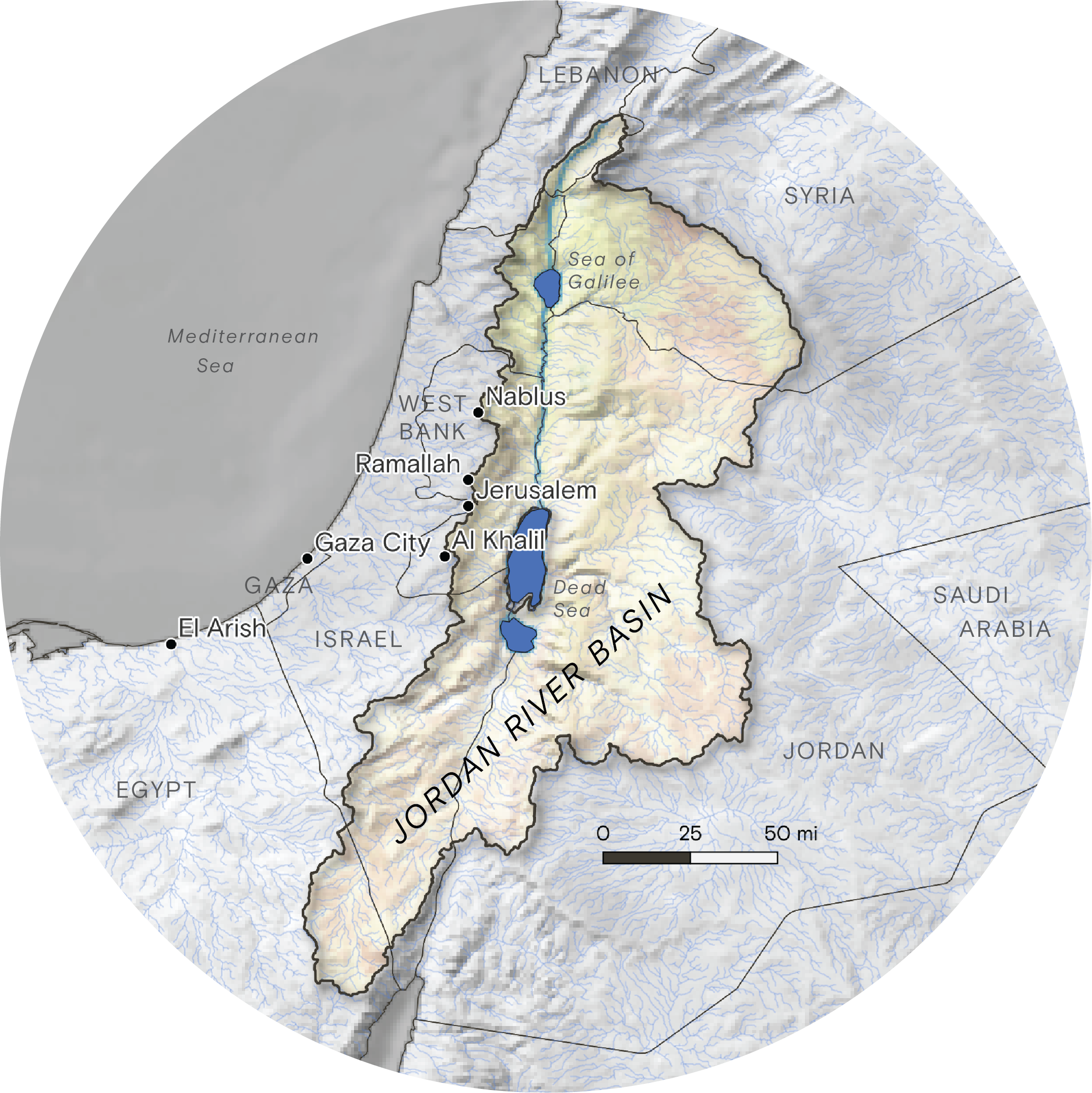
In the 1990s, Israel signed treaties with Jordan and the Palestinian Liberation Organization that set new rules for dividing the water resources that intersected their lands. The division was hardly equal. Israel ended up with control over 80 percent of the natural water resources within the borders of the West Bank, leaving Palestine largely reliant on it for water. Israel was obligated to provide a share of flows in the Jordan River to Jordan but also allowed to keep diverting a large share upstream.
This became the policy foundation of the world seen today: Israel enjoys abundant water thanks to these agreements, state-of-the-art desalination plants on the Mediterranean Sea, and world-leading efficiencies in recycling. Yet Palestinians experience what Amnesty International calls a “truly staggering” water disparity. The average Israeli consumes 52 to 79 gallons a day. (Americans use roughly 80 to 100 gallons daily.) Those in the West Bank average around 24, but in particularly deprived parts, the level approaches that of disaster zones. Gazans accessed around 22 gallons a person before the war; in March the aid group Anera estimated the average across Gaza was less than half a gallon. (The World Health Organization recommends a minimum of 13 to 26 gallons per day.)
Israel strictly controls new water infrastructure for Palestinians in the West Bank, where many residents are used to their pipes going dry even as Israelis in nearby settlements play in swimming pools. B’Tselem, an Israeli human rights group, has documented 234 instances between 2012 and 2022 in which Israeli authorities have seized, damaged, or destroyed structures like pipelines, reservoirs, and cisterns. The Palestinian Authority is perhaps the only government in the world that envisions different climate adaptation strategies with and without military occupation. “It is challenging to adapt to climate change and implement our plans under the limited access of water under occupation,” Hadeel Ikhmais, head of the climate change section for the Palestinian Environment Quality Authority, told Grist.
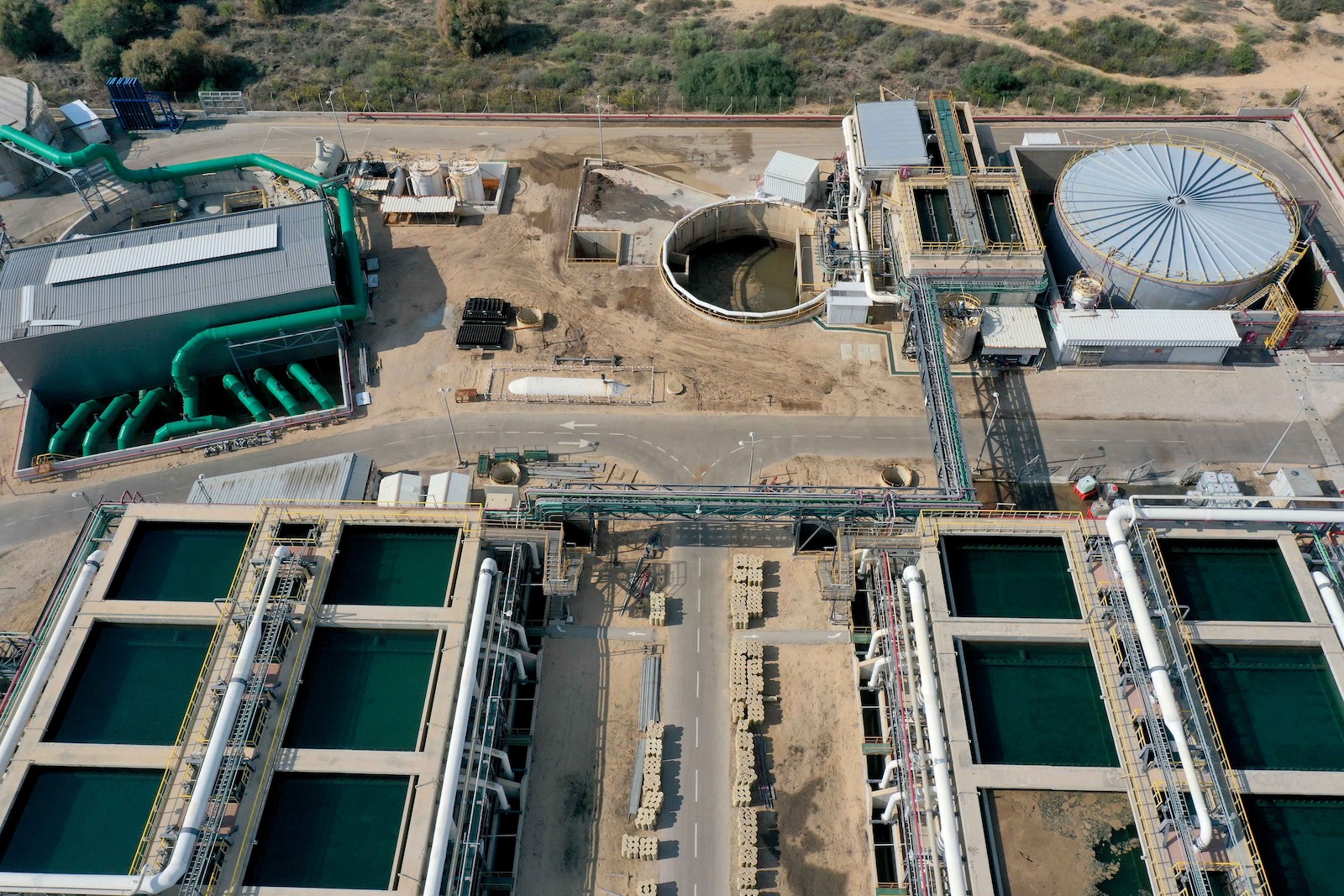

Jordan, meanwhile, has slid from scarcity to perpetual crisis. Residential averages range from 12 to 20 gallons per person each day. The major driver, as with its neighbors, is population. Over the last 20 years, population growth and refugee arrivals, mostly from Syria, have doubled the country’s population to over 11 million. There’s been no corresponding increase in water supplies, said Suleiman Halasah, a fellow at Oxford University’s Institute for Science, Innovation, and Society.
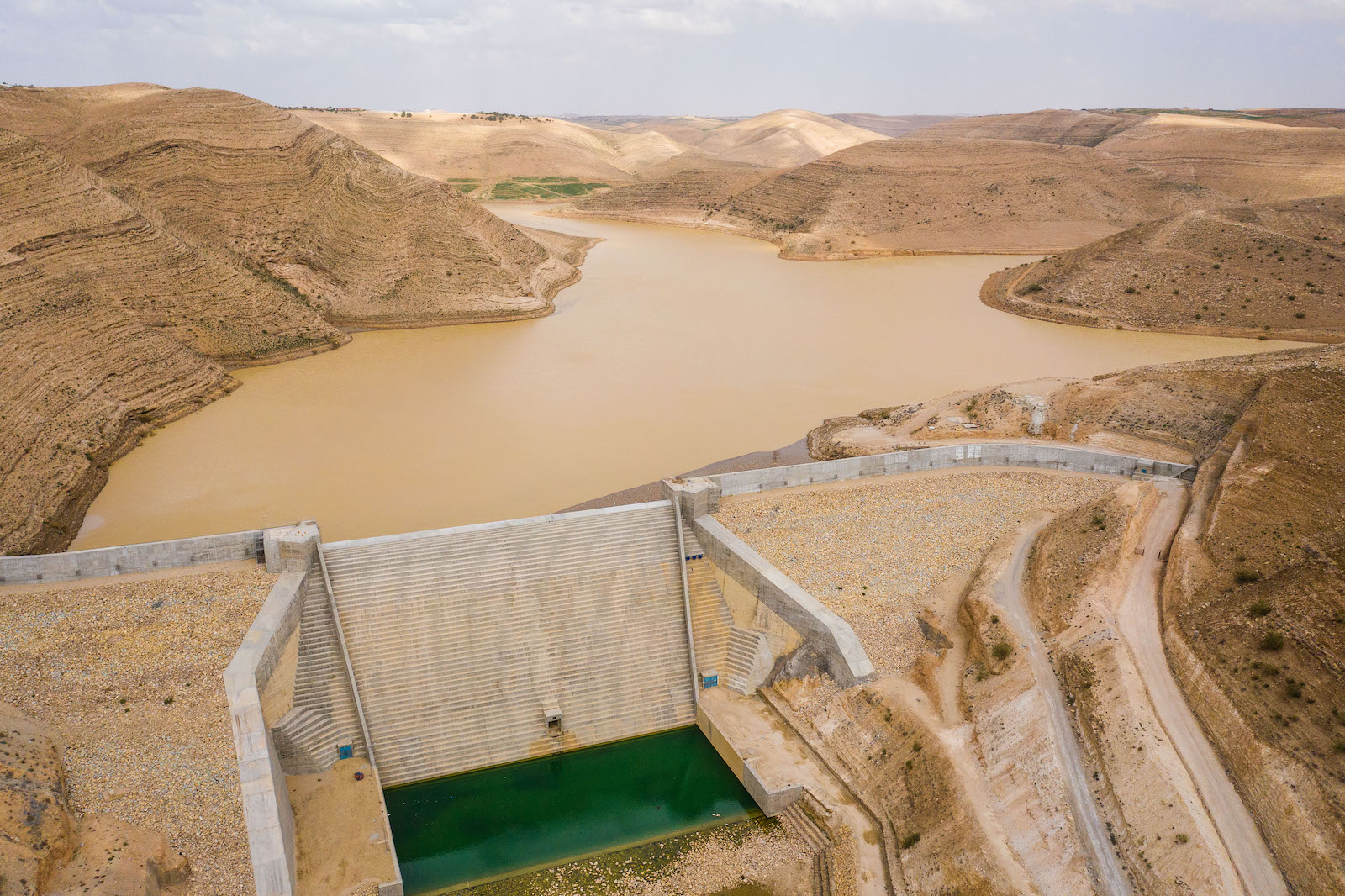
Climate change and politics aren’t helping. Hotter days, deeper droughts, and changing rain patterns are pushing Jordan’s rivers and groundwater reserves to exhaustion. Israel continues to divert huge shares of the Jordan River upstream. Damming and overuse in Syria and Jordan have further pushed the river to its critical level today: about 10 percent of historic flows, appearing in some places as a stale brown trickle.
Unable to supply everyone at all times, Jordanian utilities ration water by area. Families get a weekly allotment — based on the local population and whatever supply Jordan could procure that year — which they store in tanks and try to make last until the next week. Anyone needing more must buy it on the open market at roughly triple the baseline rate for municipal water. This structural undersupply has prompted the Jordanian government to pursue what Halasah calls a “chase after every drop” policy — to consider every conceivable source, domestic and foreign.
For 30 years, a band of allies in Israel, Jordan, and the Palestinian territories — all defying public sentiment in their homelands — have argued that problems like these could be alleviated through cross-border efforts. Through conflict and calm, they’ve argued that this cooperation embodied how to sidestep the region’s toxic politics to address the climate threat they all face — and, in the minds of the most optimistic, maybe even advance the cause of peace. “We share the same borders, same environment, same everything. Whatever happens here will also happen there,” said the young Palestinian environmentalist. “There should be cooperation — by all the neighbors.”

Clive Lipchin, an Israeli resource ecologist who has for decades worked with Arab counterparts on local water quality issues, remains passionate about the power of “people to people” programming. The morning of October 7, he said, “one of the first people that messaged me was a Palestinian friend from Ramallah who I’ve been working with for years, and the only thing he said to me was, ‘Are you OK?’ That said to me, Clive, everything you’ve done is worth it.”
In 2020 an NGO called EcoPeace Middle East proposed an idea that it called the Green Blue Deal. Inspired by the coal and steel partnerships between France and Germany after World War II, it argued that renewable energy and water could be the Middle East equivalent — a resource trade that could improve all sides’ security. EcoPeace outlined a scheme under which Israel and Gaza would bolster desalination capacity on the Mediterranean Sea. Jordan would build new solar farms. And everyone would expand their power and water interconnections, collectively making their grids greener and their water supplies more robust.
EcoPeace, which was founded in 1994 and today has co-directors in Amman, Jordan; Ramallah in the West Bank; and Tel Aviv, Israel, has argued that such projects build trust between people who wouldn’t normally meet, forming social ties that bolster the overall cause of peace. In 2022, for example, the U.S. State Department gave EcoPeace a $3.3 million grant to finance collaboration between Israeli and Palestinian scientists working to address water issues and educational partnerships between Israeli and Palestinian teachers. (EcoPeace did not respond to requests for comment.)
“Every country in the Middle East is basically an energy island. That’s not how you move forward to decarbonize the grid and your economy,” Alon Tal, an Israeli politician who’s called for cross-border coordination on electricity, water, and pesticide policies, told Grist. “If we could figure out a way to work together, that’s the real significance of Project Prosperity — its ability to really show that it’s win-win.”
In 2021, after Israeli elections brought in a new, technocratically-minded government, the Green Blue Deal became the basis for policy discussions between Israel and Jordan — but, notably, not the Palestinians — that led to Project Prosperity.
It wasn’t the first time a major resource trade had been suggested, or even the biggest such proposal. What gave this one more purchase with Israeli and Jordanian officials was the mutual leverage it implied, said Galit Cohen, a former director general of the Israeli environment ministry. Historically, any water trade had been defined by imbalance; Israel had plenty, and Jordan needed it desperately. This arrangement had greater parity: Israel, which gets 90 percent of its electricity from coal and natural gas, lacked renewable energy, which Jordan’s sprawling deserts positioned it to provide. “There isn’t one party who’s giving and one party who’s taking,” Cohen said. “Both sides are in an equal position.”

It was, for a significant wing of the Israeli environmental movement, exactly the kind of thing they wanted to see their government pursue. Tal, EcoPeace, and others have long argued that while the Israeli-Palestinian conflict tends to poison Israel’s relations with Arab countries, working on shared environmental problems has sometimes offered a calmer, more pragmatic forum in which to deliver projects that benefit people and nature.
This idea is far more divisive in Jordan and the Palestinian territories, where plenty of officials and environmentalists reject it either as “normalization” — granting Israel the privilege of normal engagement at the expense of Palestinians’ human rights — or to avoid community criticism. Existing resource trades, such as Jordan buying natural gas from Israel, and the West Bank getting almost all of its electricity from Israel — are described resentfully. Nonetheless, several successful cross-border projects since the 1990s prove some willingness to collaborate. These include efforts to reduce pesticide use in Jordan Valley farms, clean up the Jordan River, and help off-grid Palestinian villages manage wastewater.

As a scientific and technical matter, the case for cooperation is straightforward. The geographic area of Israel, Jordan, and the Palestinian territories is roughly that of Ohio. This means their air, water, and land are intimately linked and that they face similar projected changes in climate. The countries at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea, already a hot and water-scarce place, are heating at twice the global average. Forecasts suggest average temperatures will likely jump around 5.4 degrees Fahrenheit by 2100 — and up to 7.2 degrees F in the Jordanian summer — and total precipitation could drop 10 to 30 percent by century’s end. The combination of heat and diminished rain represent a double-whammy for natural water sources; more water will cook off into the air and replenish at lower rates.
There’s also logic to sharing electricity. Pooling power over large geographic areas makes it easier to add renewables to the mix. While the Israeli and Palestinian grids are well intertwined, their connections to neighboring states are effectively nil. Modeling by Oxford University shows that if Israel, Jordan, and the Palestinian territories worked together to build interconnections and renewable energy, they could decarbonize their grids by 2050 for $11 billion less than if each went solo.
What technocratic arguments fail to do, say Palestinian and Jordanian critics, is address the underlying political order that created these vast inequalities. Inès Abdel Razek, an advocate for Palestinian rights who is now executive director of the Palestine Institute for Public Diplomacy, has argued that Israel’s water surplus is built on dispossession of Palestinian water. She said initiatives like Project Prosperity entrench this control under the color of helping the environment.
“It’s basically here to promote UAE investments and Israeli investments and interests and completely erase Palestinians from the picture,” she said in 2022. “We see that the Palestinians will either receive or be sold some water by the Israelis, the very water that Israel stole from them, or they will be completely erased from the equation so far.”
“You cannot justify this project from climate change; this is a normalization project,” Omar Sushan, head of Jordan’s Environmental Union, told Al Jazeera in 2021, the year the initiative became public.
Tal, the Israeli politician, said his country’s water surplus offers a chance to change from the zero-sum thinking of the past — and start using the water to help Palestinians and Jordanians who are suffering today. “Let’s just change, let’s do things a little differently. Israel too,” he said.

Project Prosperity found new momentum after the Trump administration helped Israel forge a series of diplomatic agreements, known as the Abraham Accords, with Arab governments in 2020. A flurry of deals between Israeli clean-tech companies and Arab partners ensued, including a green hydrogen project in Morocco and a sale in the UAE of mobile units that extract water from air.
Palestinian commentators have blasted the accords as selling out their hopes of an independent state. Saeb Erekat, a Palestinian diplomat who died in 2020, once called the Emirati-Israeli entente “an Arab dagger — a poisonous dagger — in my back.” Historically, most Arab countries refused to even recognize Israel diplomatically unless it reached a political settlement with the Palestinians. The Abraham Accords signaled a mood shift toward dealmaking. Elgendy, of Chatham House, sensed a “buzz around the idea of environmental peace-building … a positive atmosphere in which there was going to be collaboration against all the odds.”
Joining this cooperative spirit, in November 2021, Israel, Jordan, the UAE, and the U.S. declared interest in the water-for-energy trade that became Project Prosperity. Their four flags were printed at the top of the announcement; the Palestinian flag was absent. A Jordanian official, speaking on condition of anonymity, said his country approached the Palestinian Authority but it opted out due to tensions with Israel at the time. “We thought we’ll go ahead with the project and include them later,” he said. A spokeswoman for the Palestinian Water Authority did not respond to requests for comment.
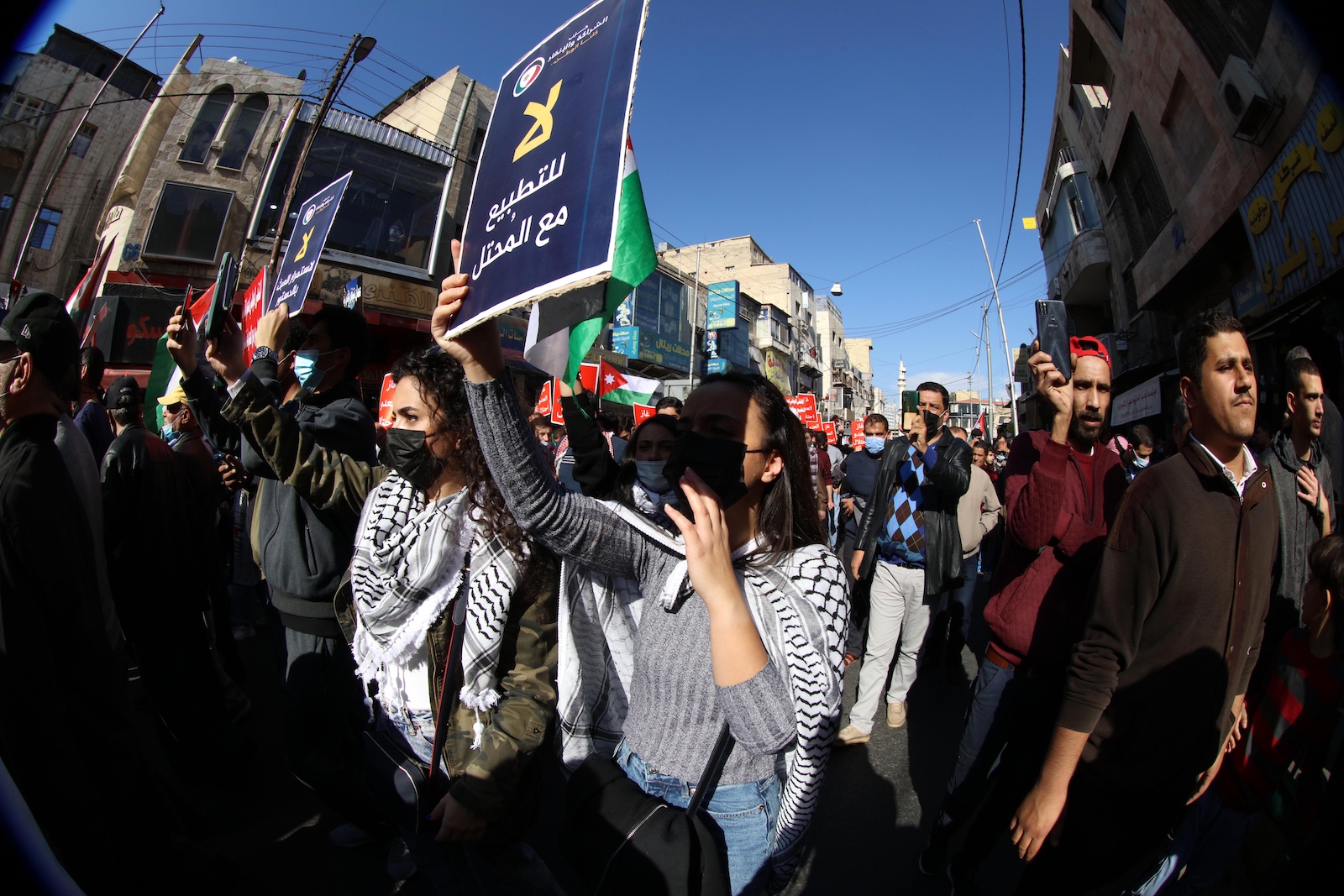
The announcement sparked protests in Jordan. Thousands marched in downtown Amman to decry what they called an “agreement of shame” that would benefit Jordanians, in their view, at Palestinians’ expense. Some Jordanian parliament members staged a walkout to protest not being looped into the decision.

Jordanian leaders held firm. This was not out of love for Israel, the Jordanian official said, but a fiduciary responsibility to secure water supplies, which the government considers a matter of national security. Each year, Jordan’s water supply falls 325,000 to 405,000 acre-feet short of demand, enough to supply almost a million U.S. homes for a year. Project Prosperity would have roughly halved that deficit.
By 2022, the parties had reaffirmed their commitment in a memorandum of understanding. Minister-level meetings in mid-2023 had officials confident they could finalize the deal at COP28 in Dubai. All that remained was signing purchase agreements, wrote Gidon Bromberg, an EcoPeace co-director.
In a March statement, a spokeswoman for Israel’s energy ministry said it plans to “continue and promote” cooperative projects in the region. Jordanian officials have been more cagey, saying they can’t conceivably sign the deal while Israel inflicts mass civilian casualties in Gaza. “Today under the existing conditions, it’s quite inconceivable for any Jordanian minister to just sit on a podium and have that type of interaction and transaction with an Israeli counterpart,” Prime Minister Bisher Khasawneh, commenting on the water-for-energy deal, said in January.
That said, the project could revive quickly — possibly by the middle of next year — should the war end soon, said the anonymous Jordanian official. The technical and policy agreements made before the war have not been made public, sources said, but policymakers could presumably pick them up if politics allow. For now, Jordan is refocusing on its next best alternative. King Abdullah II has ordered the government to accelerate development of a $3.2 billion desalination and distribution project proposed for Aqaba, a Red Sea port city. It would generate 243,000 acre-feet of water a year, enough to supply 4 to 5 million people. But this would have to be pumped hundreds of miles, uphill, to reach Amman and other population centers. Water from Israel would travel less than half the distance, suggesting that it would be cheaper.
Despite the cost, there are those who think a domestic project is better for Jordan’s peace of mind. “If [Israel] can cut the water in Gaza, they can do it to Jordan,” said Dureid Mahasneh, who in the 1990s co-chaired the joint Israeli-Jordanian committee managing transboundary water resources. Mahasneh, now chairman of EDAMA, a Jordanian environmental nonprofit, said Israel’s increasingly extreme politics make it an unreliable partner — and that a domestic project would generate thousands of jobs. “We have this Jordanian national option,” he said, “and I would go for it.”

In Amman, red stickers that depict bullets falling from a faucet like droplets, with the slogan “The water of the enemy is occupation,” have appeared on lampposts. Stars of David have been spray-painted onto sidewalks for pedestrians to trample. A roiling antinormalization movement, which opposes diplomatic relations with Israel, has called for Jordan to annul its peace treaty with Israel. Some campaigners have labeled EcoPeace a “normalization organization par excellence” and called to terminate the water-for-energy option.
Arabs who have collaborated with Israelis before are laying low, to avoid the epithet of “normalizer.” Many joint projects have been paused or dissolved. Some are proceeding but avoid attention. Even around family or friends, to speak of environmental issues, much less cooperation, can be taken as tone-deaf or insulting as each day of war reveals fresh horrors.
Ghassan Hammad, a Palestinian entrepreneur developing a circular-economy startup, says he’s been grieving the deaths of both Israeli friends and Gazan family since October 7. Having moved between both worlds his whole life, he feels deep empathy for both sides — but can see in the anguished eyes of his Palestinian family that now is not the time to argue that point.
“Romance is what keeps me going,” he said. “Romanticization of that idea that peace is possible. It doesn’t matter if it’s realistic or not. I know it’s not realistic right now, but maybe … if a lot of people make small changes, maybe the net positive impact of that might be great.”
At the Arava Institute for Environmental Studies, an educational center and think tank in southern Israel where Israelis, Palestinians, and others from abroad live, eat, and study together, students decided early in the war to complete the semester in each other’s company. They held weekly, private dialogues in which they shared their innermost, rawest feelings about life since October 7. Tareq Abu Hamed, the institute’s executive director, marveled at the vulnerability, honesty, and love they’ve shown. “This is the Middle East that I want to see,” he said. “This is the light that we all want to see in the middle of this darkness.”
But enrollment fell by half the next semester, and with no students from the Palestinian territories or Jordan.
Naomi Geri Naslavsky, a 22-year-old Israeli who remained at Arava for much of the war, said she remains as committed as ever to working across borders to address the climate crisis. She’s increasingly persuaded that leaders in her country and elsewhere are the ones sowing division.
“There are people on both sides who care about this issue, who want peace, who still want to work together,” she said. “How to make that happen, I’m not sure. I think it has to be a bottom-up process. I think this is where we start.”





