The best part about the end of the world will undoubtedly be the photo ops. Whatever the cause — aliens, viral outbreak, our own self-destruction — the apocalypse will be nothing if not full of ruin porn. Planet of the Apes gave us this iconic image of the fallen Statue of Liberty; The Day After Tomorrow brought us a Manhattan skyline half covered in snow; 28 Days Later showed us the eerily quiet streets of a deserted London. But in real life, things might get a bit more Waterworld.
A recent report from NASA warned that a significant portion of the space agency’s infrastructure is now under threat due to climate change-induced sea-level rise. And as great as a defunct and inundated Kennedy Space Center would look in black and white, this is bad news. Here’s more from NASA:
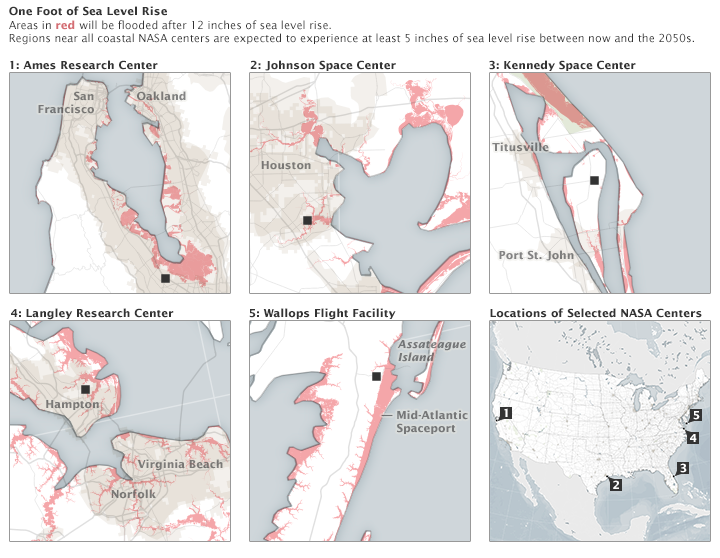
Sea level rise hits especially close to home because half to two-thirds of NASA’s infrastructure and assets stand within 16 feet (5 meters) of sea level. With at least $32 billion in laboratories, launch pads, airfields, testing facilities, data centers, and other infrastructure spread out across 330 square miles (850 square kilometers)—plus 60,000 employees—NASA has an awful lot of people and property in harm’s way.
The average global sea-level has risen eight inches since 1870, NASA reports, but the rate of rise is getting faster and actually doubled over the last 20 years. NASA’s Climate Adaptation Science Investigators (CASI) Working Group recently reported that the agency’s five coastal facilities can expect between 5 and 27 inches of sea-level rise by 2050. It also warned that the coastal flooding that usually happens about once a decade in these areas will become more frequent. In the case of the San Francisco Bay/Ames Research Center area, it could become up to ten times more frequent. Here’s a look at how these areas will fair under a rise of 12 inches:
John Jaeger, a coastal geologist from the University of Florida, told NASA that waves could be “lapping at the launch pads” of the Kennedy Space Center within decades.
So it looks like the moon-landing, Mars-exploring, child-inspiring space agency is in a bit of a pickle. On the one hand, it wants to keep civilians safe by launching off of coasts. On the other hand, the ocean is trying to engulf it. At the same time, mean old Uncle Sam is cutting NASA’s allowance so much that it has to ask its Russian friends for rides to the International Space Station.
The agency’s report ended with a look toward the future. It’s pretty depressing, but if you imagine James Earl Jones reading it aloud amid slow pans of launch pads and space shuttles, astronauts walking in slow motion, and something symphonic playing in the background, you can’t help but believe that NASA’s going to figure this one out:
In some places, they will need to design smarter buildings; in others, they will retrofit and harden old infrastructure. If a facility must stay within sight of the water, then maybe the important laboratories, storage, or assembly rooms should not be on the ground floor. For the launch facilities, which must remain along the shore, beach replenishment, sea wall repair, and dune building may become part of routine maintenance.
But across the space agency, from lab manager to center director to NASA administrator, people will have to continually ask the question: is it time to abandon this place and move inland? It’s a question everyone with coastal property in America will eventually have to answer.
Seriously, though, more than half of U.S. citizens live on the coasts, and a recent study estimated that between $66 billion and $106 billion in infrastructure could be under water by 2050, and between $238 billion to $507 billion in infrastructure could be under by the end of the century. That’s a hell of a lot of ruin porn, but we seem to be doing OK with sparse abandoned factories and boarded up homes. How about we leave the serious stuff to Hollywood?