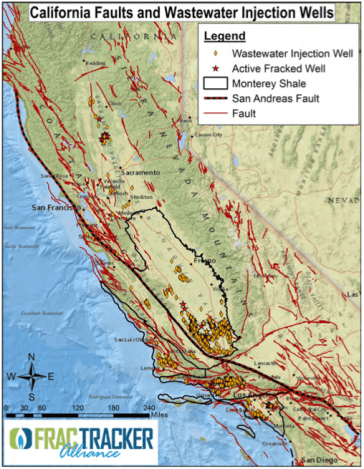
The Ring of Fire, an earthquake-prone area around the edges of the Pacific Ocean, might not be the best spot for earth-rumbling fracking practices. But fracking is exploding in the ringside state of California, raising fears that the industry could trigger the next “big one.”
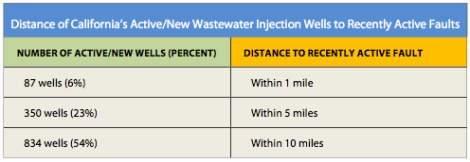
More than half of the 1,553 active wastewater injection wells used by frackers in California are within 10 miles of a seismic fault that has ruptured within the past two centuries, according to a jarring new report. The fracking industry’s habit of injecting its wastewater underground has been linked to earthquakes. (And Ohio officials are investigating whether fracking itself was enough to trigger temblors early this week.)
From the report:
“Some of California’s major population centers, such as Los Angeles and Bakersfield, are located in regions where high densities of wastewater injection wells are operating very close to active faults,” according to the report, which was conducted by Earthworks, the Center for Biological Diversity, and Clean Water Action. It further notes that California has “no plan to safeguard its residents from the risks of earthquakes” induced by injection wells or drilling and fracking operations.
“This isn’t rocket science,” said report coauthor Jhon Arbelaez. “We’ve known for decades that wastewater injection increases earthquake risk. … [O]ur only option to protect California families is to prevent fracking altogether.”