Here’s a fun fact about “sea-level rise”: The seas aren’t actually level to begin with. Because of predictable, long-term patterns in climate, global winds push more water into some oceans than others. This leaves the seven seas (not really a thing) divided into six “basins” (actually a thing). Water in these interconnected systems can slosh around to different areas while the overall volume stays the same — much like water in a bathtub.
Or so we thought!
Last month in the super-sexy-sounding journal Geophysical Research Letters, scientists published research suggesting that changes to the Earth’s climate are driving changes in the way sea level rises in some of these ocean basins. Historically, the oceans of the Southern Hemisphere operate as a closed system, with an inverse relationship between the Indian and South Pacific basin and the South Atlantic basin: When one goes up, the other must come down. Using satellite measurements of sea level to track the flux in level, the researchers were surprised to find that, starting in the late ’90s, both basins began to rise in unison.
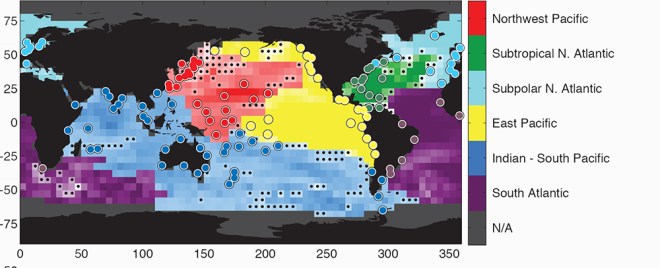
This is a map of the ocean basins — those big blue and purple blotches at the bottom of the map have been behaving strangely, thanks to climate change. Click to embiggen. Philip R. Thompson and Mark A. Merrifield
The total increase in this basin is about 2 millimeters a year — for you Americans, that adds up to a little more than an inch since 2000. It’s not weird that the oceans are rising, obviously, but it is strange to see such a distinct shift in the way they rise. The scientists trace this weirdness back to changes in the east-west wind patterns — changes for which they have several hypotheses, all of them linked to climate change.
Meanwhile, the other oceans seem to be behaving normally. Though let’s be clear: By “behaving normally,” we mean “rising in predictably terrifying ways as opposed to new weirdly terrifying ways.”




