Last week, a long, narrow section of the Earth’s atmosphere funneled trillions of gallons of water eastward from the Pacific tropics and unleashed it on California. This weather event, known as an atmospheric river, broke rainfall records, dumped more than a foot of rain on parts of the state, and knocked out power for 800,000 residents. At least nine people died in car crashes or were killed by falling trees. But the full brunt of the storm’s health impacts may not be felt for months.
The flooding caused by intensifying winter rainstorms in California is helping to spread a deadly fungal disease called coccidioidomycosis, or Valley fever. “Hydro-climate whiplash is increasingly wide swings between extremely wet and extremely dry conditions,” said Daniel Swain, a climate scientist at University of California, Los Angeles. Humans are finding it difficult to adapt to this new pattern. But fungi are thriving, Swain said. Valley fever, he added, “is going to become an increasingly big story.”
Cases of Valley fever in California broke records last year after nine back-to-back atmospheric rivers slammed the state and caused widespread, record-breaking flooding. Last month, the California Department of Public Health put out an advisory to health care providers that said it recorded 9,280 new cases of Valley fever with onset dates in 2023 — the highest number the department has ever documented. In a statement provided to Grist, the California Department of Public Health said that last year’s climate and disease pattern indicate that there could be “an increased risk of Valley fever in California in 2024.”
“If you look at the numbers, it’s astonishing,” said Shangxin Yang, a clinical microbiologist at the University of California, Los Angeles. “About 15 years ago in our lab, we only saw maybe one or two cases a month. Now, it’s two or three cases a week.”
Valley fever — named for California’s San Joaquin Valley, where the disease was discovered in a farmworker in the late 1800s — is caused by the spores of a fungus called Coccidioides. When inhaled, the spores can cause severe illness in humans and some animal species, including dogs. The fungus is particularly sensitive to climate extremes. Coccidioides doesn’t thrive in regions of the U.S. that get year-round rain, nor can it withstand persistent drought.
What the spores really love is exactly the type of rain-drought cycle that California is caught in. Until last year’s series of drought-busting atmospheric rivers, California was in the throes of a long-term drought pattern; 2000 to 2021 was the driest two-decade stretch in the Southwest in 12 centuries. Climate models predict the Golden State will endure more droughts in the future. Rising global temperatures fuel dry conditions by sucking moisture out of the soil and depleting California’s water reserves. Meanwhile, the warmer atmosphere is also supercharging atmospheric rivers as they move from the tropics to the West Coast, causing the “rivers in the sky” to unleash more rain than they would on a planet untouched by human-made warming.
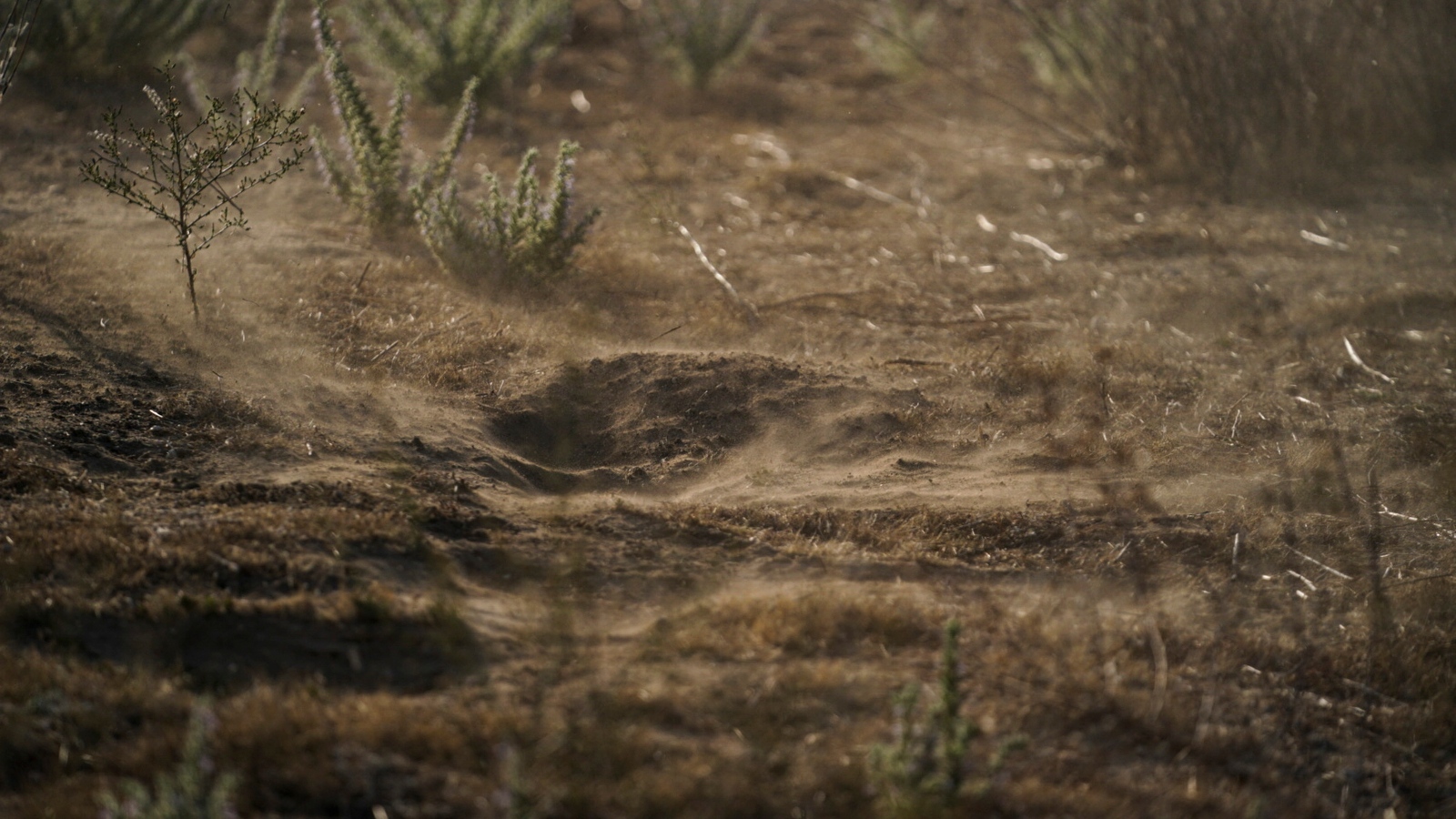
The oscillation between extreme dryness and extreme wetness causes Coccidioides to flourish. During rain events, flushes of fungi colonize the soil. As the ground dries out, the invisible spores can be lifted out of the soil by a bulldozer, a rake, a hiking boot, an earthquake, or even a strong gust of wind. When those flying spores land in soil, they begin to reproduce. If they’re sucked through an open mouth or nostril, they colonize the lungs.
The progression of the illness in humans depends on the strength of the individual’s immune system: The majority of people who contract Valley fever — some 60 percent — will never know they crossed paths with killer spores, because their immune system is able to rapidly vanquish the fungal intruder. But quashing Valley fever isn’t always a given, even for healthy individuals. The disease disproportionately impacts Latinos, Filipinos, Black people, Native Americans, and pregnant people for reasons researchers and physicians are still trying to puzzle out.
When it causes symptoms, Valley fever starts with a fever, headache, or cough — similar to the symptoms of COVID-19, a disease it is often confused with. If the immune system can’t fight off the Coccidioides spores, the illness can move past its initial phase and become a chronic condition that produces a severe cough, chest pain, weight loss, pneumonia, and nodules in the lungs. This stage, known as disseminated Valley fever, can also cause skin lesions and ulcers, swollen joints, meningitis — swelling of the membranes surrounding the spinal cord and brain — and even death. Between 1 and 5 percent of Valley fever cases reach the disseminated stage. Antifungal medications can help hold Valley fever at bay, but recovery ultimately depends on the individual’s immunological defenses. There is no cure for the disease, and approximately 200 people in the United States die from disseminated Valley fever every year.
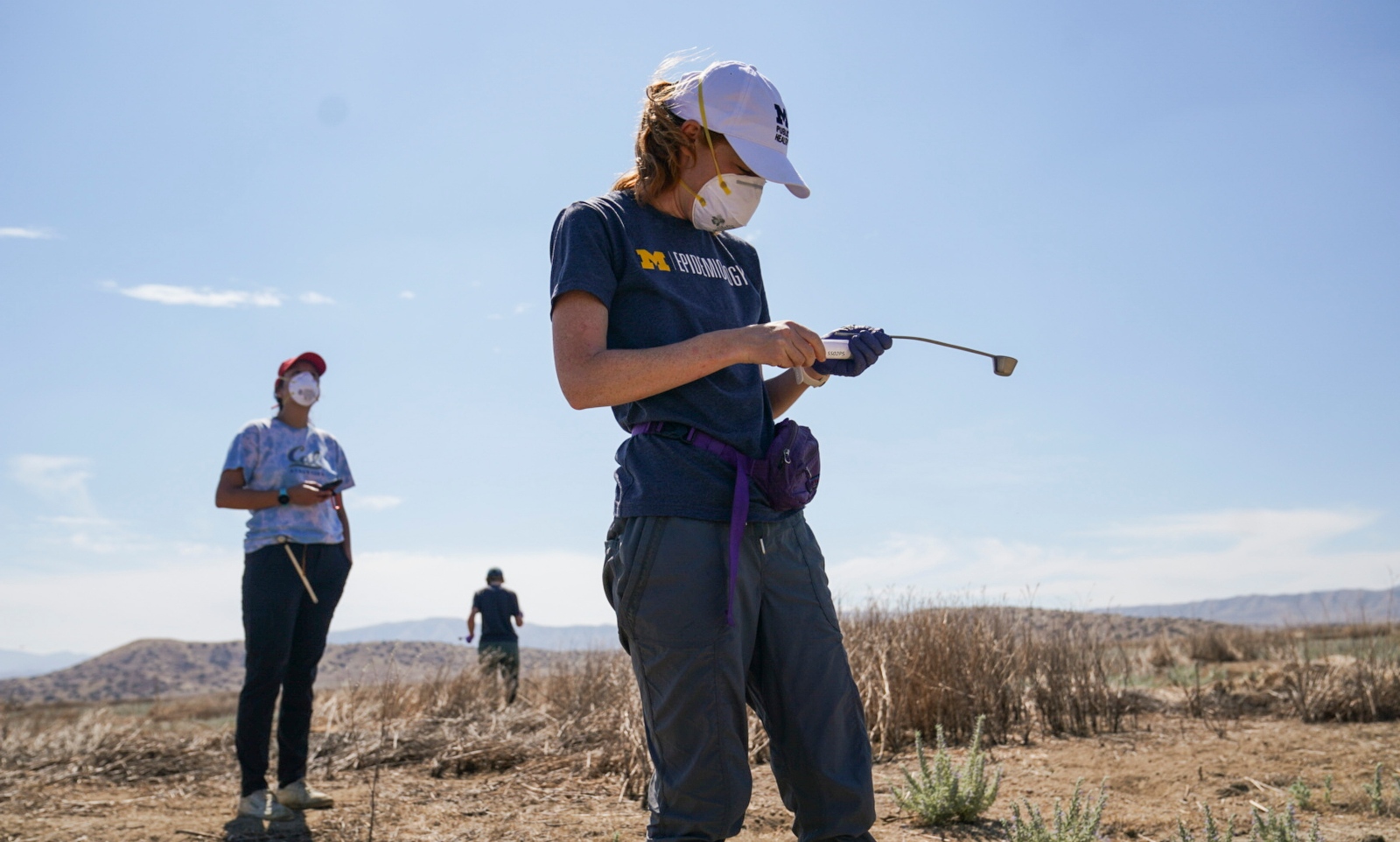

There’s evidence that Coccidioides is already taking advantage of a warming U.S. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that Valley fever cases in the U.S. rose from 2,271 in 1998 to 20,003 cases in 2019 — a 780 percent increase. In Arizona, where two-thirds of Valley fever diagnoses typically occur, cases rose 600 percent. But Coccidioides spores have cropped up in new regions in recent years, expanding through Southern California and into Northern California, even up into the drier parts of Oregon and Washington states. The rate of growth of Valley fever in California is higher than in Arizona; cases there rose more than 1,000 percent over the same time period. “What kind of disease do you see a 1,000 percent increase in a matter of two decades?” Yang asked. “This is one of the few.”
Some percentage of these cases can be attributed to increased public awareness of the disease and a related uptick in testing for it. But the size of the spike, experts told Grist, cannot be explained by testing rates alone. Climate change, researchers hypothesize, is supercharging Valley fever, and increasingly intense atmospheric rivers — responsible for roughly 50 percent of the West Coast’s annual water supply — are creating ideal conditions for the spores to spread.
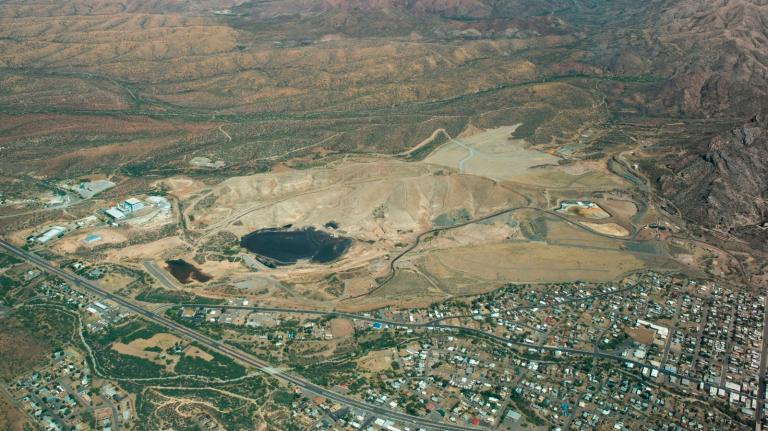
The scale of Valley fever in California in the coming years depends in large part on what happens to the state’s soil. “Many areas that have blooms of the Valley fever fungus never get disturbed, so it’s not an issue,” said Antje Lauer, an environmental microbiologist at California State University Bakersfield. Housing and energy infrastructure and other landscape-level changes kick up soil and produce dust. She worries that as developers build more infrastructure and expand into virgin areas of the state, and as climate change creates ever more convenient conditions for Coccidiodes, Valley fever will pose an increasingly profound threat to public health. Last year was a harbinger of things to come, Lauer said. “We will see more cases.”




