The spin of the earth is a constant in our lives. It’s quite literally why night follows day.
And while that cycle isn’t going away, climate change is messing with the axis upon which our fair planet spins. Ice melting has caused a drift in polar motion, a somewhat esoteric term that tells scientists a lot about past and future climate and is crucial in GPS calculations and satellite communication.
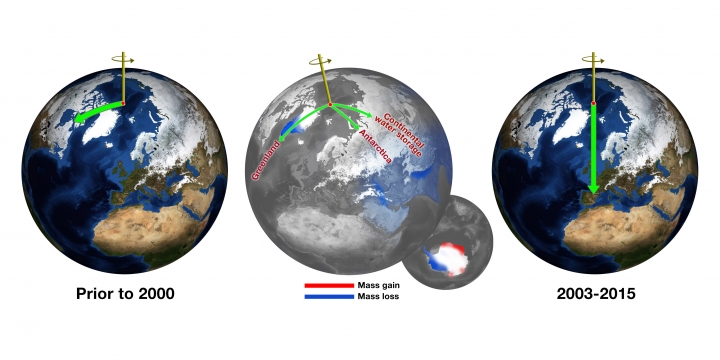
Before 2000, Earth’s spin axis was drifting toward Canada (left globe). Climate change-driven ice loss in Greenland, Antarctica and elsewhere is pulling the direction of drift eastward.NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Polar motion refers to the periodic wobble and drift of the poles. It’s been observed for more than 130 years, but the process has been going on for eons driven by mass shifts inside the earth as well as ones on the surface. For decades, the north pole had been slowly drifting toward Canada, but there was a shift in the drift about 15 years ago. Now it’s headed almost directly down the Greenwich Meridian (sorry Canada, no pole for you, eh).
Like many other natural processes large and small, from sea levels to wildfires, climate change is also playing a role in this shift.
“Since about 2000, there has been a dramatic shift in this general direction,” Surendra Adhikari, a researcher at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, said. “It is due to climate change without a doubt. It’s related to ice sheets, in particular the Greenland ice sheet.”
That ice sheet has seen its ice loss speed up and has lost an average of 278 gigatons of ice a year since 2000 as temperatures warm. The Antarctic has lost 92 gigatons a year over that time while other stashes of ice from Alaska to Patagonia are also melting and sending water to the oceans, redistributing the weight of the planet.
Adhikari and his colleague Erik Ivins published their findings in Science Advances on Friday, showing that melting ice explains about 66 percent of the change in the shift of the Earth’s spin axis, particularly the rapid losses occurring in Greenland.
It’s a huge, mind boggling process on the global scale, but imagine it like a top. Spinning a top with a bunch of pennies on it will cause wobble and drift in a certain pattern. If you rearrange the pennies, the wobble and drift will be slightly different.
That’s essentially what climate change is doing, except instead of pennies, it’s ice and instead of a top, it’s the planet. Suffice to say, the stakes are a little higher.
Ice loss explains most but not all of the shift. The rest can mostly be chalked up to droughts and heavy rains in certain parts of the globe. Adhikari said this knowledge could be used to help scientists analyze past instances of polar motion shifts and rainfall patterns as well as answer questions about future hydrological cycle changes.
Ice is expected to continue melting and with it, polar motion is expected to continue changing as well.
“What I can tell you is we anticipate a big loss of mass from West Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets and that will mean that the general direction of the pole won’t go back to Canada for sure,” Adhikari said.
If it continues moving down the Greenwich Meridian or meanders another way remains to be seen, though.
“This depends highly on the region where ice melts, or if the effect of ice melt would be counterbalanced by another effect (for example sea level rise, increased water storage on continents, changes of climate zones),” Florian Seitz, the director of German Geodetic Research Institute, said in an email.
In the here and now, polar motion shifts matter for astronomical observations and perhaps even more importantly for the average person, GPS calculations.




