This story was originally published by CityLab and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
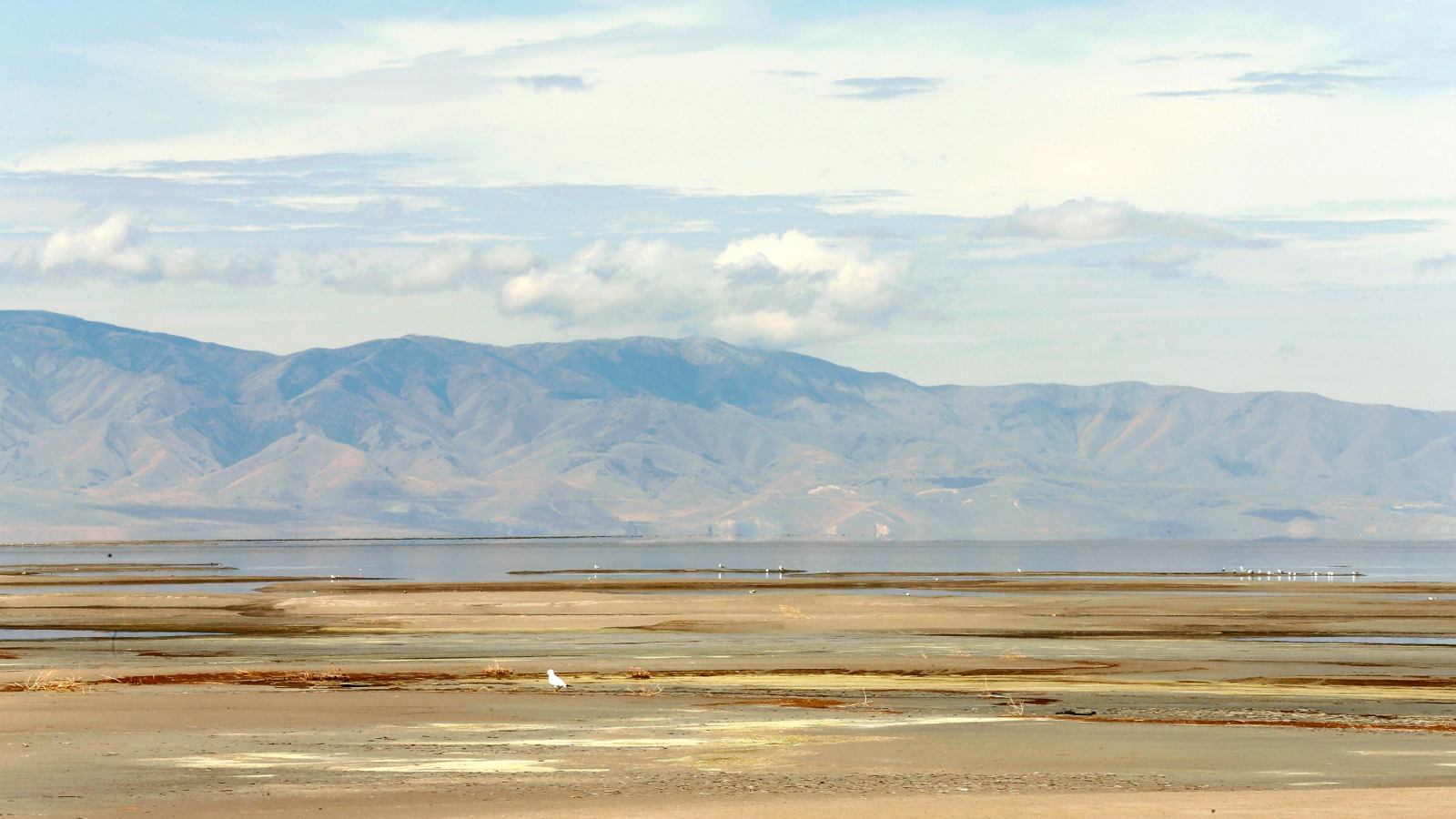
The Great Salt Lake is drying up, thanks to 150 years of human diversions from the rivers that feed it. That’s the takeaway of a white paper released by a team of Utah biologists and engineers. And if those diversions continue ramping up, as a bill working its way through the Utah legislature proposes, the waterbody may face a withering fate similar to other dried-up salt lakes around the world.
The namesake of Utah’s capital city, the Great Salt Lake is the the state’s defining geographic feature and one of its economic anchors. A 2012 report by the Great Salt Lake Council estimated that the total economic output of the waterbody at $1.32 billion, between mineral extraction from the lake, brine shrimp egg production (used in aquaculture all over the world), and recreation that takes place in and around it. It also serves as an essential migration flyway for millions of birds each year.
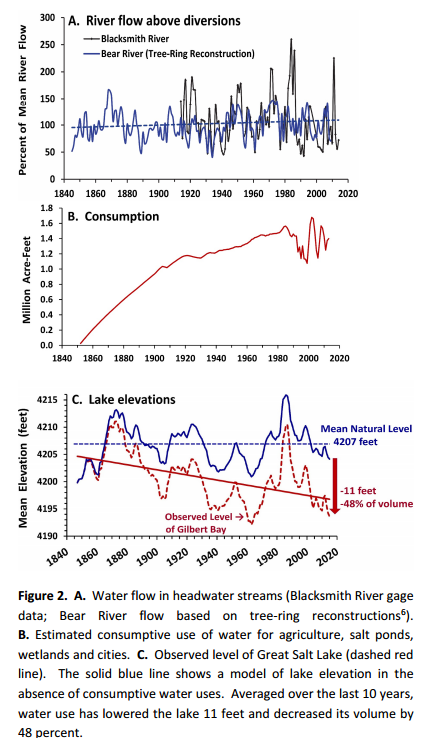
But the lake, which approached record-low water levels last year, is under threat. According to the Utah researchers’ calculations, since the mid-19th century, consistent reductions from the rivers that feed the lake have caused the lake’s elevation to drop by 11 feet, lose roughly half its volume, increase the lake’s salinity, and expose approximately 50 percent of the lake bed.
Those numbers are unrelated to natural fluctuations over wet and dry periods, including the current drought. Since the lake is a closed basin, the only way water leaves it is through evaporation. That makes it fairly simple to calculate just how much water has been lost to agriculture and urban growth.
Utah State University
Currently, the Utah Senate is debating a bill that would fund a number of water infrastructure projects, including the controversial Bear River Development Project, which would dam and divert more water from one of the Great Salt Lake’s main feeds. Supporters of the project say it’s designed to support the state’s growing population and water consumption needs. But the researchers estimate that the project would lead to an additional 8.5 inch drop in the Great Salt Lake’s elevation, and another 30 square miles of exposed lake bed.
Not only does that spell trouble for the lake’s economic and ecological importance, a dried-up lake would ramp up dust storms in the Salt Lake City area, which already suffers some of the worst air pollution in the country. It doesn’t take much searching to find an example of how damaging such withered lakes are for the people around them. In nearby California, the researchers write:
Diversions from the Owens River for the city of Los Angeles desiccated Owens Lake by 1926, causing it to become one of the largest sources of particulate matter (PM10) pollution in the country. This dust affects about 40,000 permanent residents in the region, causing asthma and other health problems.
Lake Urmia in Iran and the Aral Sea in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan are other examples of how massive water diversions from closed basins for human uses can create environmental health disasters.
To meet the needs of a growing population, and to protect their future health, the researchers stress that Utah policymakers should focus on taking less water, not more, from the Great Salt Lake — especially when it comes to agriculture, which consumes the majority of all that diverted water. Like so many states throughout the arid American West, Utah has to weigh its future against a history of overdrawn resources.