Since 1975, the U.S. has restricted the export of crude oil in the name of energy security, and somehow that dirty protectionism even managed to make it through the Reagan era. But perhaps no longer. Republicans in Congress are pushing to allow oil companies to export crude to overseas refineries, and they could put the issue to a vote as soon as next month.
Ending the crude oil export ban would represent one of the largest tweaks in U.S. energy policy in decades, and, from an environmental perspective, not a positive one.
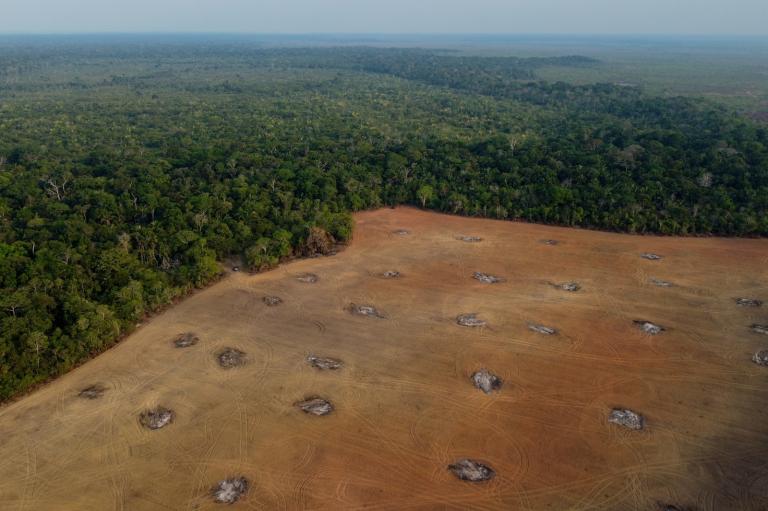
On Friday, the Center for American Progress (CAP) released an analysis pleading for congressional consideration of the broader risks at play, especially as they relate to the environment. The authors argue that the policy change would lead to more oil drilling in the U.S., resulting in an increase in annual carbon and methane emissions, the loss of open lands and wildlife habitats, and risks related to production and transportation like increased prevalence of crude oil train derailment and air quality problems for those living near drilling operations. This is to say nothing of the need to keep fossil fuels in the ground if we’re to fight off climate change.
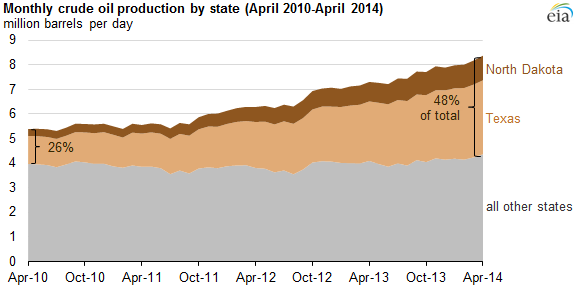
Why export in the first place? Aside from the fact that it means oil companies get a larger (more competitive) refinery market, it’s a function of our crusty pals supply and demand. In 2009, U.S. crude oil production started to grow for the first time in decades, and continues to do so today. Most of that growth comes from “tight oil” — the kind you can get at by fracking — and most of that tight oil comes from North Dakota and Texas:
A growing crude oil sector means there’s an increase in supply, which is sometimes grounds to consider exporting surplus to clean up any inefficiencies in the market. But something else tends to happen when you open up a market: Foreign demand increases. This increase means that domestic production of crude oil will have to bump up accordingly (at a faster rate than it’s already growing) to keep up with foreign buyers. As the authors of the CAP analysis write, this makes for a lot more oil wells:
According to data from IHS CERA’s study that was provided to CAP, oil companies would drill an average of 26,385 new oil wells in the United States every year between 2016 and 2030 if the crude oil export ban is lifted, or approximately 7,600 more wells on average per year than if the ban remains in place.
… If these development patterns continue, IHS CERA’s forecasts of new drilling activity suggest that increased oil exports would alone result in the loss of as much as 2,054 square miles of land between 2016 and 2030, or an area larger than the state of Delaware. This means the United States would lose approximately 137 square miles of land to oil infrastructure per year, or an area larger than Arches National Park in Utah, simply to feed foreign demand for U.S. crude oil.
Writing as someone who has gotten lost in Arches National Park, that’s a lot of land. Aside from the environmental reasons to stick with the status quo, the CAP authors make an economic case, too:
[M]any oil refiners argue that the U.S. refinery sector is capable of absorbing any new supply, making it unnecessary to lift export restrictions to balance the market. The AFL-CIO has expressed concern that lifting the export ban would scuttle plans to invest in and expand U.S. refining infrastructure. The United Steelworkers union has communicated similar concerns to Congress. According to a recent study by the Energy Information Administration, or EIA, allowing more crude oil exports could result in $8.7 billion less investment in U.S. refining capacity over the next 10 years.
Put that all together and the argument for lifting the ban falters. “A hasty decision to outsource U.S. refinery capacity might boost oil company profits, but it would also carry a high environmental price tag and create uncertainty for consumers,” said Matt Lee-Ashley, a senior fellow at CAP and an author of the analysis, in a statement. It’s a price tag we can’t afford.