On Wednesday, the Northern California animal sanctuary Animal Place will airlift — yes, you read that right: airlift — 1,150 elderly laying hens from Hayward, Calif., to Elmira, N.Y., in an Embraer 120 turbo-prop.
The price? $50,000.
Right. So obviously, this isn’t the most efficient way to spend your chicken-helping money. It didn’t take me very long to think of some alternatives: For example, you could couple all 1,150 hens off and buy each pair its own home. You could feed 367 chickens fancy organic food for an entire year. You could feed 157 people the very fanciest, most coddled, free-rangest, organic-est eggs ever for a year. You could buy flocks of chicks for 2,500 farmers in the developing world through the charity Heifer International.
Don’t get me wrong — it’s not that I think that these soon-to-be-airborn hens don’t deserve a better life. They come from an undisclosed California battery cage egg operation, and as most people know by now, that is no picnic. Animal Place’s Marji Beach explained to me that once laying hens reach the age of about 18 months, their egg production slows, and it’s no longer economically feasible for egg operations to keep them around. The result is that each plant has to get rid of thousands of “spent” hens every year. What happens to those hens? In most cases, they don’t end up in your chicken soup broth, or even in your cat or dog’s food. That’s because most slaughterhouses don’t accept them — they have too little meat on their bones to turn a profit. Instead, egg producers often kill spent hens with highly concentrated carbon dioxide gas. (That probably costs far less than flying the hens across the country, but it doesn’t appeal to Animal Place, whose website urges visitors over and over again to go vegan.)
When a few other Mother Jones staffers and I heard about the spent-hens problem, it got us wondering: Has the world reached peak chicken? Considering the fact that Americans eat 79 billion eggs a year, that’s an awful lot of laying hens. And that’s to say nothing of the so-called broiler operations that make chickens for supermarket shelves and fast-food sandwiches and nuggets.
According to UC Davis professor and poultry expert Rodrigo Gallardo, there are a few reasons why the world is eating more chicken and eggs than ever these days. “If you think about several years ago, most people ate beef or pork because there was more availability and because it was cheaper,” Gallardo says. But chickens have become more attractive as options over time: They’re lean, they’ve been bred over time to produce more meat, and raising them takes up much less land than raising cows or pigs.
“If you think about eggs, eggs are cheap, they are easy to consume, they are fun — people can cook them in different ways,” Gallardo explains. “Kids always like them, and they are the cheapest protein you can get from an animal source.”
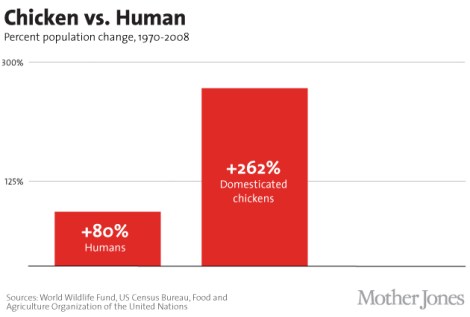
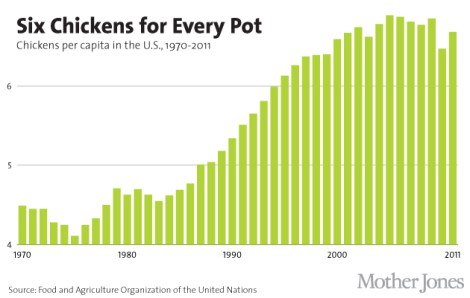
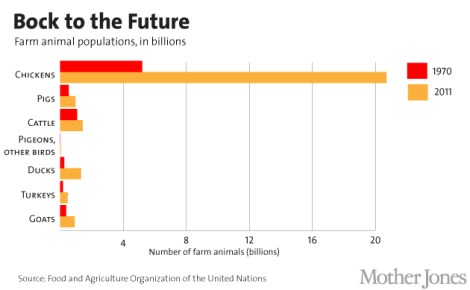
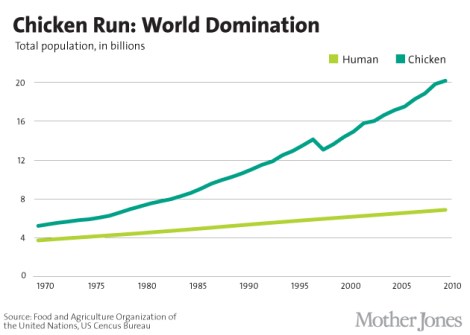
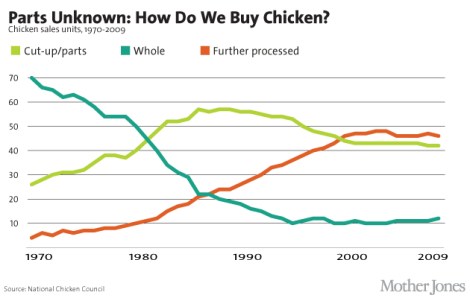
Exactly how many chickens does the world have? we wondered. The answer, we found, is a whole lot — and it’s increasing. Here are a few charts that will give you a sense of the scale of the chicken explosion:
 This story was produced by Mother Jones as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
This story was produced by Mother Jones as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.