Humans eat a stunning amount of meat every year — some 800 billion pounds of it, enough flesh to fill roughly 28 million dump trucks. Our carnivorous cravings, particularly in industrialized, beef-guzzling countries like the United States, are one reason the planet is warming as fast as it is. Raising animals consumes a lot of land that could otherwise soak up carbon. Cows, sheep, and goats spew heat-trapping methane. And to grow the corn, soy, and other plants that those animals eat, farmers spray fertilizer that emits nitrous oxide, another potent planet-warming gas.
For all those reasons, and many more, activists and scientists have called for people to eat less meat or abstain altogether. At last year’s United Nations climate conference in Egypt, activists chanted slogans like “Let’s be vegan, let’s be free.” At this year’s conference, which starts November 30, world leaders are expected to talk about ways to shift diets toward plant-based foods as a way to lower animal agriculture’s climate pollution, the source of 15 percent of the planet’s greenhouse gas emissions.
Cutting out meat can be an effective tool: The average vegan diet is linked to about one-quarter the greenhouse gas emissions of a meat-intensive one, according to a paper published in Nature in July.
But what would happen if everyone actually stopped eating meat tomorrow?
“It would have huge consequences — a lot of them probably not anticipated,” said Keith Wiebe, a senior research fellow at the International Food Policy Research Institute.
Such a quick shift probably wouldn’t cause the sort of turmoil that would come if the planet immediately ditched fossil fuels. But still, the upshot could be tumultuous, upending economies, leaving people jobless, and threatening food security in places that don’t have many nutritious alternatives.
Livestock accounts for about 40 percent of agricultural production in rich countries and 20 percent in low-income countries, and it’s vital — economically and nutritionally — to the lives of 1.3 billion people across the world, according to the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization. One-third of the protein and nearly one-fifth of the calories that people eat around the world come from animals.
Researchers say the economic damage caused by the sudden disappearance of meat would fall disproportionately on low-income countries with agrarian economies, like Niger or Kenya, where farming and raising livestock are critical sources of income. Niger’s livestock industry makes up about 13 percent of the country’s gross domestic product; in the U.S., the entire agricultural system accounts for only around 5 percent.
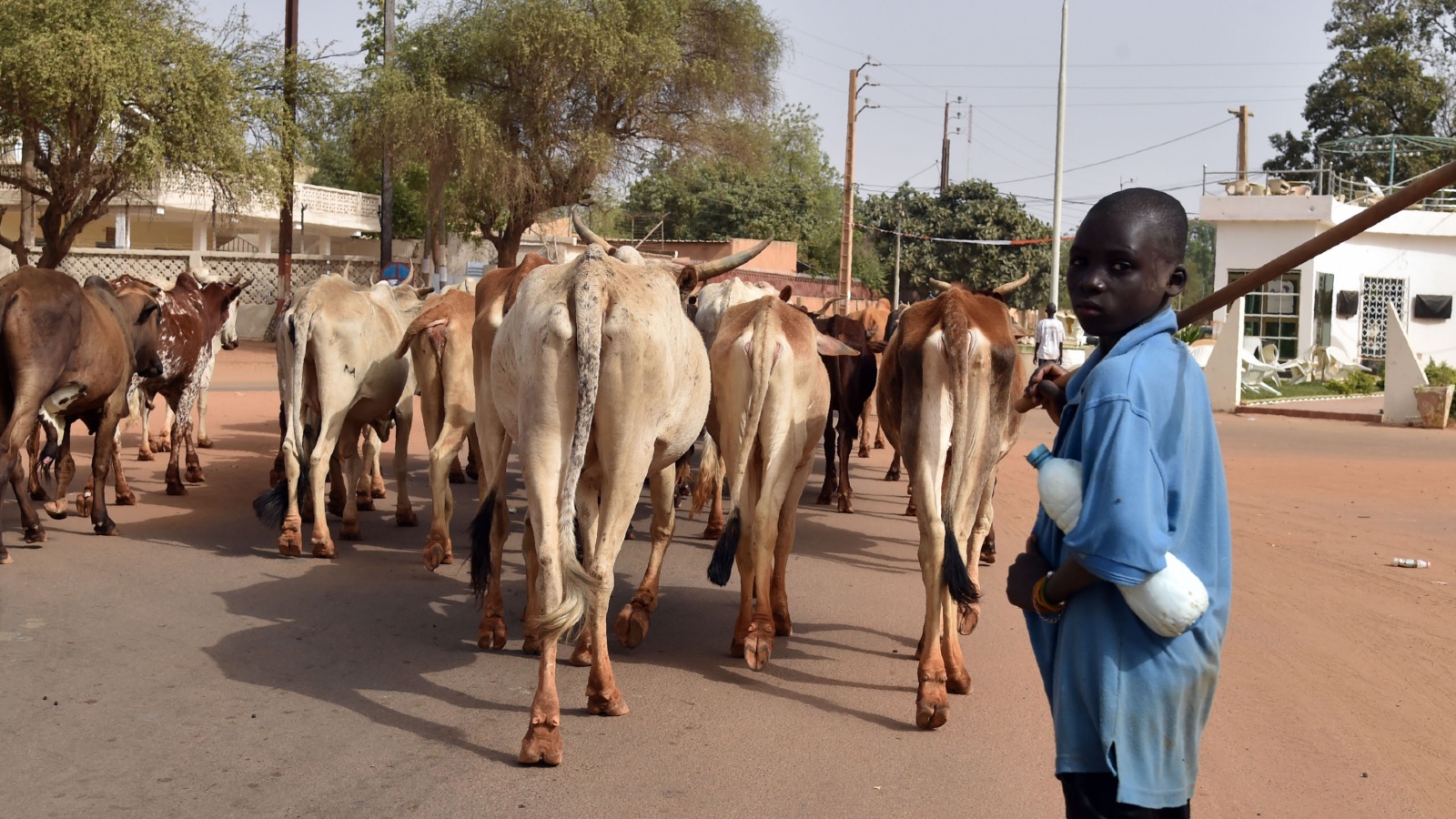

It’s tough to predict exactly what the economic shock would look like on a global level. There has been “relatively little” research on how phasing out meat would affect employment around the world, Wiebe said. “It’s an issue that deserves a lot more attention.”
Millions of people would lose jobs, but demand for other sources of calories and protein might rise and offset some of those losses. Some workers might be drawn into agriculture to grow more crops like legumes. That shift in labor, some researchers hypothesize, could slow economic growth by pulling people out of more profitable industries.
Still, the effects would vary across cultures, economies, and political systems, and they aren’t as clear-cut as, say, the amount of methane that would be saved if cows ceased to exist. “It depends on the species of livestock. It depends on the geographic location,” said Jan Dutkiewicz, a political economist at the Pratt Institute, in New York City. “It’s very difficult, if not impossible, to talk in universal terms about addressing those kinds of things.”
It’s easier to talk in broad terms about another challenge with getting rid of meat: nutrition. Eliminating livestock overnight would deprive many people of essential nutrients, especially in regions like South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, where meat comprises a small but crucial sliver of the average person’s starch-heavy diet. Animal-based foods are high in vitamin B12, vitamin A, calcium, and iron. That’s why researchers say preserving access to meat, milk, and eggs is key to keeping people healthy in low- and middle-income countries right now, where nutritious plant-based options are harder to come by.
And then there’s the issue of cultural damage. Taking away meat, according to Wilson Warren, a history professor at Western Michigan University, would do more than just deprive Americans of hot dogs and hamburgers and Italians of salami.
“Historically, the way that most people understood animals was through farming and having close contact with their livestock,” said Warren, who’s also the author of Meat Makes People Powerful, a book about the global history of meat. “You get rid of that sort of close connection, [and] I envision people in some ways being even less environmentally in touch.” (Warren grapples with this idea in a self-published novel called Animeat’s End about a future world in which eating meat is a serious crime.)
Many researchers agree that phasing out meat entirely, let alone immediately, isn’t an ideal solution to the climate crisis. It would be plenty, they say, to reduce consumption methodically and to focus on the countries that eat the most, particularly wealthy ones like the United States that have no shortage of alternatives.
It might be easier for the average American, who eats about 220 pounds of red meat and poultry each year, to trade a daily hamburger for a bowl of lentils than for someone in rural sub-Saharan Africa, who eats 10 times less meat, to give up the occasional goat or beef stew for something less nutritious. Such a shift in beef-loving countries also might reduce heart disease and cancer linked to eating a lot of red and processed meat.
Dutkiewicz suggested using guidelines established by the EAT-Lancet Commission, an international group of scientists who have designed a diet intended to give people the nutrients they need without destroying the planet. It consists of roughly 35 pounds of meat per year. Adopting that diet would require a drastic reduction of cows and chickens in countries like the United States, Australia, China, Brazil, and Argentina, and a slight increase in parts of Africa and South Asia.
Gradually replacing meat with plants could have immense benefits for the planet. “It would be a huge net win for the environment,” Dutkiewicz said. By one estimate, a complete phaseout of meat over 15 years would cut as much as one-third of all methane emissions and two-thirds of all nitrous oxide emissions. Water use would fall drastically. Biodiversity loss would slow. Animal welfare advocates would be happy to see fewer animals packed into tight pens wallowing in their own poop awaiting slaughter. And there would be ample opportunity to rewild abandoned rangelands and pastures at a scale that would sequester a whole lot of carbon — as much as 550 gigatons, enough to give us a pretty good shot at keeping warming below catastrophic levels.
Given the complexities and pitfalls of a complete phaseout, researchers and advocates have pointed instead to a more modest goal: cutting meat production in half. Replacing it with plant-based alternatives would lower agricultural emissions 31 percent by 2050, a recent study found.
“It doesn’t have to be an all-or-nothing approach,” Raychel Santo, a food and climate researcher at the World Resources Institute, said in an email.
The solution, in other words, lies somewhere between culling cows in Niger and gorging ourselves on factory-farmed flesh.