For CO2-eating bacteria, climate change is kind of a sweet deal. It’s like someone sneaking into your kitchen every night and dumping a bunch of cookies on your counter — except, in this scenario, humanity is the one breaking and entering, your house is Earth, and those cookies are ruining everything.
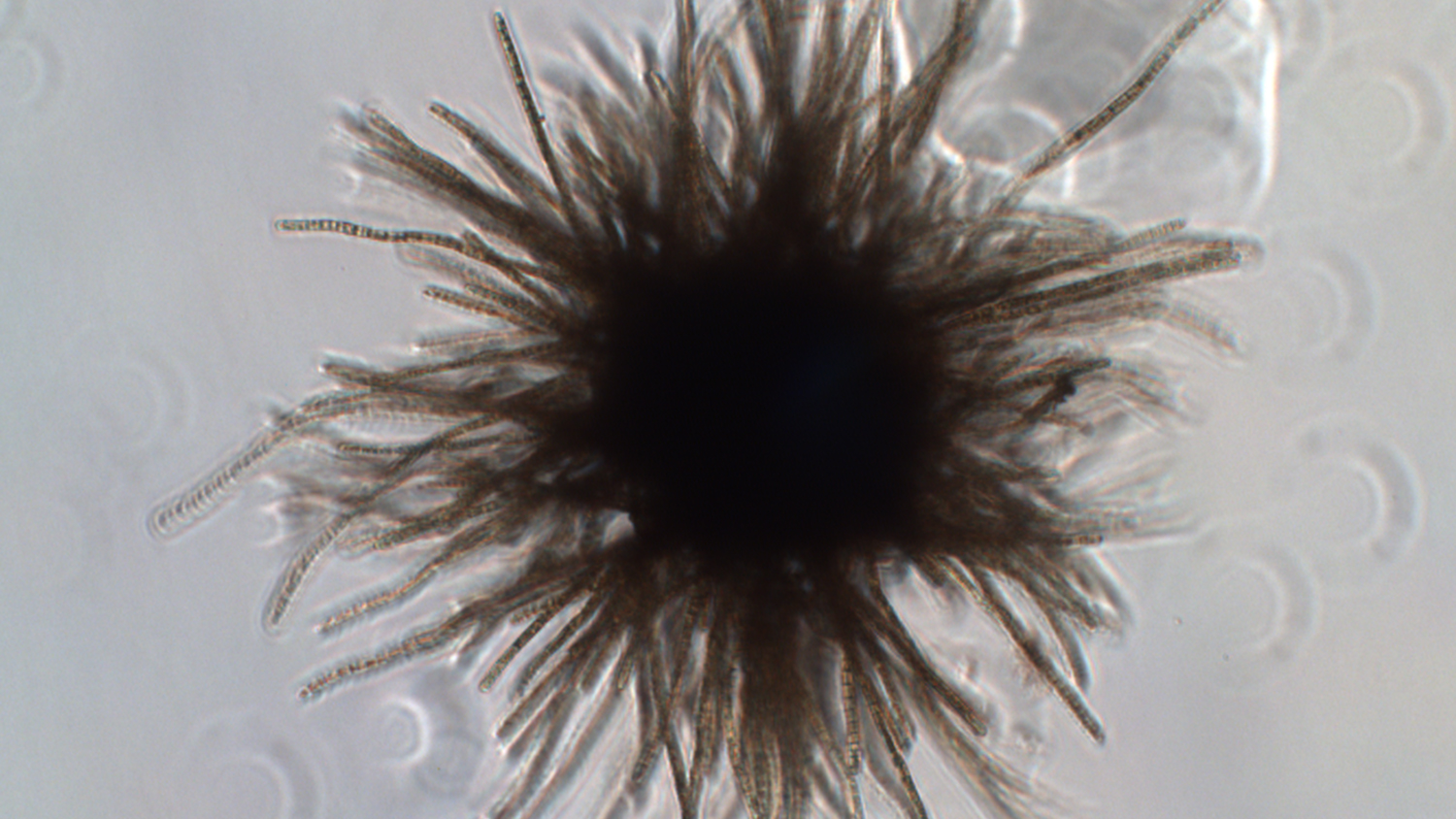
But if you’re a marine microbe just chillin’ in the tropics and subtropics, munching on CO2, and watching the rest of the world go up in flames, there’s no downside, right? Wrong! Researchers at USC and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute tested how Trichodesmium (nickname: Tricho), a cyanobacteria that consumes CO2 and pumps out crucial nitrogen for the rest of the marine food web, would behave under the high-CO2 conditions projected for 2100, and they found that poor lil Tricho faces death-by-gluttony.
In a study published Tuesday in Nature Communications, the researchers report that at first, things won’t look so bad for Tricho. With more CO2, the bacteria grow faster and produce 50 percent more nitrogen. So not only are the bacteria getting stronger, they’re also making more food for other marine organisms that eat nitrogen. But then things go sour, because of course there’s no such thing as a free lunch (or in this case, cookie). So here’s the bad news from USC News:
The problem is that these amped-up bacteria can’t turn it off even when they are placed in conditions with less carbon dioxide. Further, the adaptation can’t be reversed over time — something not seen before by evolutionary biologists, and worrisome to marine biologists, according to David Hutchins, lead author of the study.
“Losing the ability to regulate your growth rate is not a healthy thing,” said Hutchins, professor at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences. “The last thing you want is to be stuck with these high growth rates when there aren’t enough nutrients to go around. It’s a losing strategy in the struggle to survive.”
Let’s put this in terms of cookies, because I’m hungry. You can’t really have cookies without milk, right? (That’s not actually a question.) So if someone’s stocking your kitchen with extra cookies but not extra milk, and you start pigging out on cookies, you’ll eventually run out of milk. When that happens, you’ll probably be bummed out but will continue to stuff your face.
Unfortunately for Tricho, the milk in this metaphor is phosphorous and iron — crucial nutrients that are in limited supply — so when Tricho runs out of “milk,” it’ll die. Here’s more from USC News:
With no way to regulate its growth, the turbo-boosted Tricho could burn through all of its available nutrients too quickly and abruptly die off, which would be catastrophic for all other life forms in the ocean that need the nitrogen it would have produced to survive.
Even after the researchers put the bacteria back in a CO2-low environment, its enhanced appetite didn’t subside. They basically developed an irreversible evolutionary adaptation which, according to USC News, Hutchins described as “unprecedented.”
“Tricho has been studied for ages. Nobody expected that it could do something so bizarre,” he said. “The evolutionary biologists are interested in it just to study this as a basic evolutionary principle.”
The team is now studying the DNA of Tricho to try to find out how and why the irreversible evolution occurs. Earlier this year, research led by [Eric Webb of USC Dornsife] found that the organism’s DNA inexplicably contains elements that are usually only seen in higher life forms.
“… the organism’s DNA inexplicably contains elements that are usually only seen in higher life forms.” Twenty bucks says Tricho’s an alien. Hell, let’s make it $20 million. It’ll probably be dead before we get a chance to figure it out. (Unless, of course, part of its plan for invasion involves eating up all the phosphorous and iron, then entering a death-like dormant phase until the rest of the marine ecosystem spirals into chaos, and we find ourselves on the brink of extinction …)
Until then, I’ll just be eating cookies and milk.