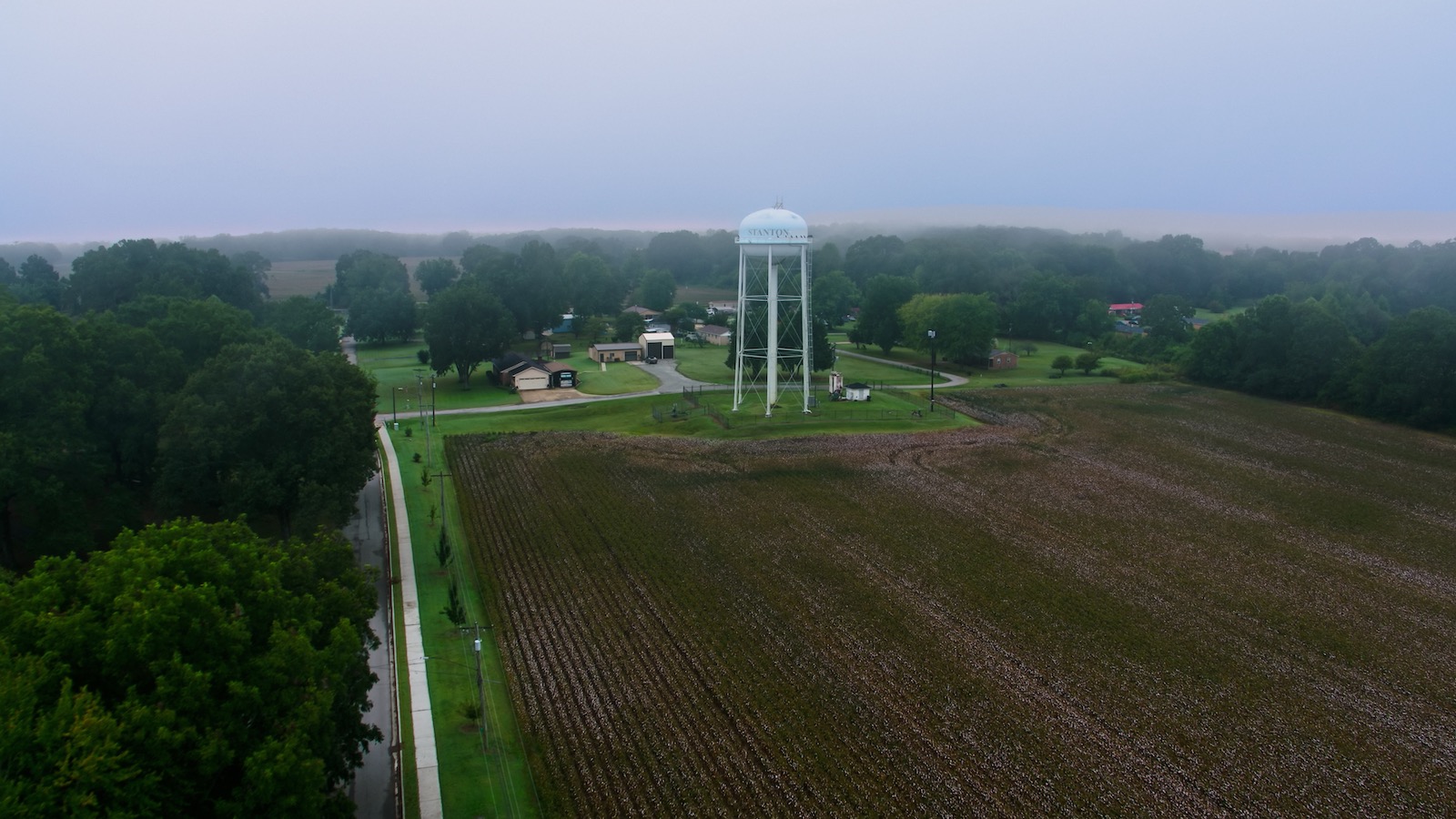
“Blue Oval City” sounds like some kind of fantastic, utopian megalopolis of the future. In reality, it’s a massive automotive manufacturing complex that will provide several links in the EV supply chain. The joint venture, between Ford and Korean company SK Innovation, promises 6,000 good-paying jobs for residents of the small, rural communities around Stanton, Tennessee. Many expect it to benefit surrounding towns like Covington, Brownsville, and Jackson as well, while reaching south into Mississippi and north into Kentucky, too.
But the multibillion-dollar project raises complicated feelings for many in the working-class, largely Black communities that dot the farm country and marshy bottoms of west Tennessee. They pride themselves on a slower way of life, and feel lucky to have good drinking water from a reliable aquifer. Development on such a large scale will, they fear, change the community, suck up water and electricity, and prompt an influx of newcomers and development.
They are only the latest to face uncertainties with energy transition projects, which, from solar fields to wind farms, have prompted reservations about their size, industrial activity, and environmental impacts. But rather than accept their fate, the constellation of towns orbiting Stanton are sitting down with Ford and SK to negotiate a binding agreement that will ensure they benefit from Blue Oval City as much as the companies do.
During a series of community meetings held over the past few months, the coalition has drafted a list of stipulations, called a community benefits agreement, that it wants Ford/Blue Oval SK to abide by. It is asking for community resources like youth facilities, support for road maintenance, and apprenticeship pathways run by local union chapters. It also seeks a binding assurance that the joint venture will dispose of its waste properly. And although Ford has announced many community programs, local residents want the automaker to give them some say in such things.
“They didn’t really reach out,” Michael Adriaanse, who serves on the committee drafting the agreement, said of Ford’s efforts. “I know a lot of people who feel like it happened overnight.”
So how does such a process begin? Generally with meetings that bring stakeholders together to draw up a list of demands in a broad public conversation the company cannot ignore.
“The argument a community can make is, ‘If you want our resources, you have to contribute back to the health and welfare of the community you’re gonna be a part of now,’” said Kathleen Mulltigan, who leads the National Labor Leadership Initiative at Cornell University. “What we’re really trying to do is bring real democracy into the economic realm, because a lot of the work of shaping the economy happens without workers having any voice in it.”
Ultimately, community benefits agreements, or CBAs, are a contract between a corporation and a coalition of local organizations that gives the community, through binding arbitration, leverage to ensure the commitments are kept.
Historically, CBAs have been used by those impacted by the entertainment and sports industries, which tend to get big municipal tax breaks and public funding. Some of the first were negotiated in Los Angeles in the early 2000s to address, separately, a sports arena and an entertainment district. After exhaustive negotiations, residents achieved many of their goals, including higher wages, guaranteed affordable housing, and revolving loans for local business. CBAs have since spread nationwide, with folks in Nashville negotiating a high wage floor, onsite childcare, and other provisions at Geodis Park, a $275 million stadium being built for the Nashville SC soccer team.
Now, CBAs are increasingly being used to address clean energy developments. According to the Sabine Climate Change Law Center at Columbia University, more than a dozen have been signed since 2015, many of them in the last three years. The contracts resulted in projects agreeing to give preference to local hires, and in companies sharing revenue with the county in which they operate. An offshore wind facility in Maine even underwrote rural broadband access.
Vonda McDaniel, the president of the Central Labor Council of Nashville and Middle Tennessee, is helping to formulate Blue Oval agreement and plan town halls. The process has been lively. “We haven’t had a whole lot of wilting flowers that have showed up at our meetings, to be honest,” she said.
One reason for that is that locals already see changes. “The community is feeling a bit squeezed; there’s heavy equipment up and down the road every day,” said McDaniel.
Farmland counties in the region known as Middle Tennessee endured rapid urbanization when automakers arrived in Spring Hill, south of Nashville. As investment increased and people began moving in, housing costs skyrocketed. They’re beginning to creep up around Stanton, too. McDaniel says a CBA could forestall that.
“Community benefits agreements are based on the power and leverage that communities build within themselves,” she said. “They’re not just gonna give you a list of things you say you want.” In her mind, these agreements help ensure a measure of democracy in a part of the country where voter disenfranchisement, especially in rural, Black communities, is high and private interests have the ear of state government.
The Blue Oval project received a $9.2 billion loan from the Department of Energy. As clean energy funding and incentives have proliferated under the Inflation Reduction Act and bipartisan infrastructure law, much investment has gone to the Southeast and America’s vaunted EV “Battery Belt.” The region’s famously climate-unfriendly governors have opened their doors wide, with Tennessee Governor Bill Lee seemingly keen on snatching the automaking mantle from the Great Lakes. With $900 million in public incentives approved by the Tennessee legislature, it’s the largest single manufacturing investment in the state’s history.
Amidst the green boom, many have speculated that a part of the South’s draw is its generally lax environmental and safety regulations. Tennessee is a “right-to-work” state; such locales typically support lower average wages. Tennessee’s preemption ordinance also prevents municipalities from enacting worker standards beyond what state law requires.
This does not mean publicly supported clean energy projects in the South are doomed to a lower standard than those in other places. The president of the Nashville chapter of the United Auto Workers Union has promised that Blue Oval City will be a “union facility.” The Inflation Reduction Act and bipartisan infrastructure law require those seeking federal funding to submit a “community benefits plan” outlining how they will invest in domestic labor, local communities, and diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives. Although similar to CBAs, they’re not the same. Advocates of such arrangements say CBAs are needed to secure accountability and transparency, and to give communities direct input into projects that impact them.
Will Tucker works as the Southern Programs Manager with Jobs to Move America, a national labor advocacy nonprofit. It recently negotiated a CBA with New Flyer, an electric bus manufacturer in Anniston, Alabama, and Tucker feels confident this approach to the transition can work in the South.
“What sets a real community benefits agreement apart from a dressed up community outreach program by another name is the element of negotiations with the company,” he said. Though many companies will set aside funding for local sports leagues, schools, and the like, Tucker considers such moves more of a PR strategy than a way of giving the community power.
If community organizations can present a united front, that pressure usually pushes the company to negotiate, though in some cases, protests and demonstrations heighten the stakes. Michael Adriaanse hopes such pressure will send the Blue Oval City CBA over the finish line.
Ultimately, for a CBA to work, the company in question must sit down with the community. Adriaanse said the coalition invited Ford representatives to a town hall to discuss preliminary demands, but it didn’t work out. McDaniel speculated that the company’s ongoing negotiations with United Auto Workers, which recently concluded a strike, may have slowed some things down. There’s a long road ahead, but Adriaanse and McDaniel are hopeful that with a strong enough coalition, the company won’t be able to dodge any longer.
The coalition still plans to go to the table with Ford, with a complete draft of the agreement in hand, early in the new year. Even if the effort is not immediately successful, community members say, the relationships they’ve built with one another will only get stronger, leaving possibilities for further organizing open down the road.