This story was originally published by Mother Jones and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
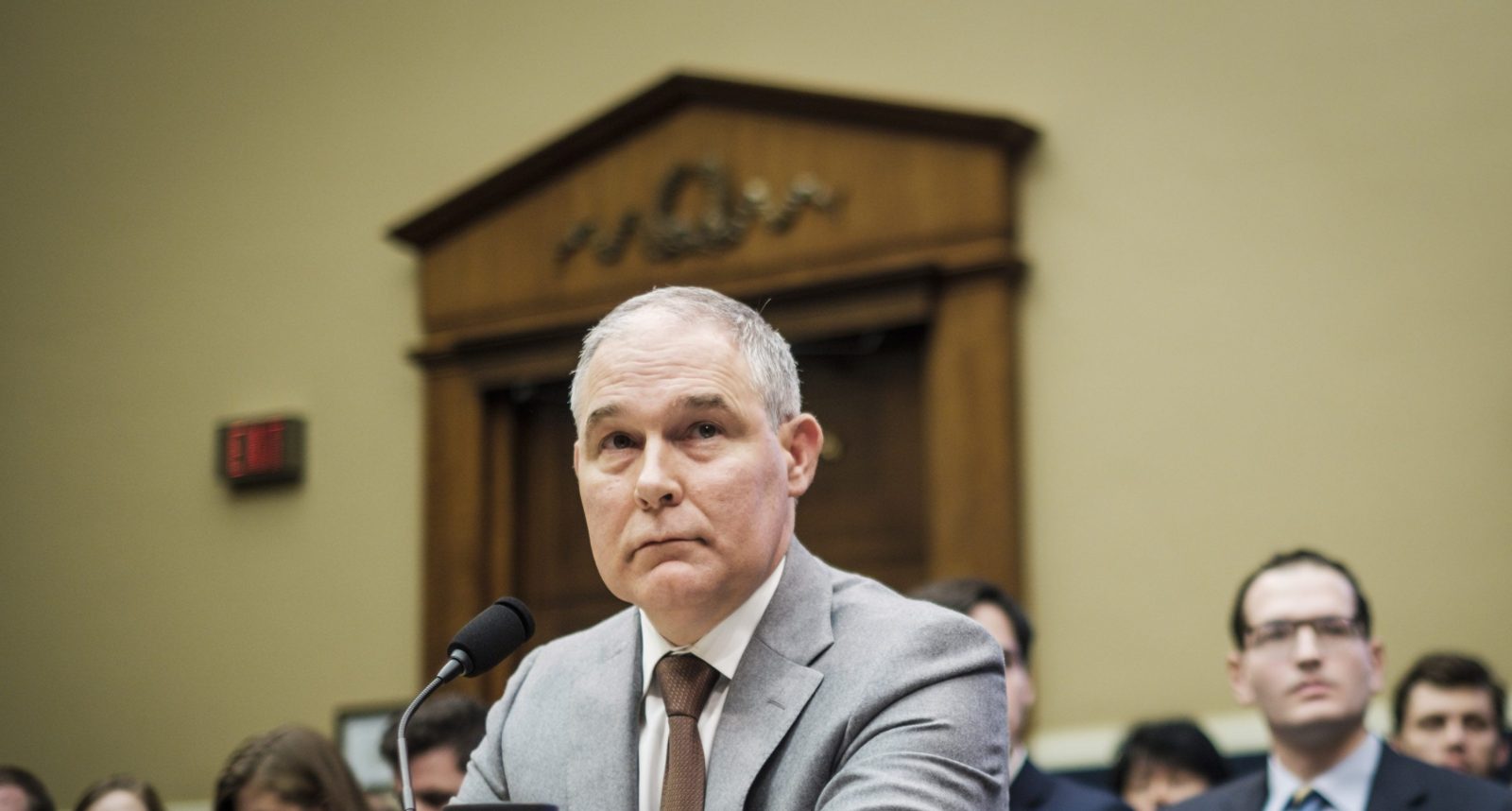
About a month after President Donald Trump’s inauguration, Scott Pruitt arrived at the Environmental Protection Agency for his first full day of work. The new administrator had weathered a contentious confirmation battle, with bitter debate over his long-standing ties to the industries he was now responsible for regulating — not to mention the 14 lawsuits he had filed against the agency as Oklahoma’s attorney general. But as he stepped into the EPA’s stately Rachel Carson Green Room, Pruitt wore the satisfied grin of a man in charge.
He took the stage with Catherine McCabe, the acting head of the agency. In the front rows sat some members of the EPA’s “beachhead team,” a group of mostly men whom Trump had installed to begin the process of dismantling the department of the Obama years. Among them were some familiar faces, such as David Schnare, a former career EPA official and prominent climate-science skeptic. A conspicuous number of security staffers circulated among the crowd.
McCabe handed Pruitt two gifts. One was a beige baseball hat inscribed with the EPA’s logo — a nod to Pruitt’s career as a college second baseman and a minor league co-owner. The other was an EPA pin, which she advised he should “proudly wear … on your lapel as you represent the agency.” Pruitt considered the pin for a moment and then set it on the podium. He appeared uncomfortable sharing the spotlight; as he stood next to McCabe, I saw him fidgeting with his glasses, his eyes shifting between her and the audience while she read a version of his biography that omitted the lawsuits.
Half a head shorter than many members of Trump’s Cabinet, a bit stocky, and balding on top, Pruitt didn’t visibly command the space. But once McCabe stepped aside, he relaxed as cameras broadcast his address to 15,000 EPA staffers nationwide. “I am excited about being in a city that actually has a Major League Baseball team,” he said, using his new hat as a prop. The speech was light on the environment and the agency’s mission and heavy on where the Obama administration had gone wrong. He covered talking points that he would repeat ceaselessly during the next few months: “Regulations ought to make things regular”; it was time to be “pro-energy and -jobs”; “process matters”; he would “listen, learn, and lead.” When it was over, Trump’s men enthusiastically pumped his hand while career staffers silently filed out the back.
It was not quite the fire and brimstone of his boss, but Pruitt’s quieter style masks the extent to which his approach to governing is the practical implementation of the president’s wrecking-ball rhetoric. On the campaign trail, Trump promised to “get rid” of the EPA “in almost every form.” In just his first year in office, Pruitt has already made stunning strides in that direction. He’s dismantling the Obama administration’s landmark Clean Power Plan, which imposed greenhouse gas limits on fossil fuel-fired power plants. He has slashed enforcement efforts against polluters and tried to repeal rules meant to safeguard drinking water supplies. He has threatened to roll back fuel economy standards. He’s moved to weaken new rules for smog, coal ash, and mercury pollution, poorly enforced a new toxic-chemical law, and refused to ban the dangerous pesticide chlorpyrifos. He’s taken aim at dozens of lesser-known rules covering everything from safety requirements for replacing asbestos to emergency response plans in hazardous chemical facilities. In the process, Pruitt has driven away hundreds of experienced EPA staffers and scientists while putting old friends and industry reps in charge of key environmental decisions — a troubling trend that has led former EPA administrators from both parties to warn that he is doing irreversible damage to the agency.
For the president, Pruitt has become a trusted partner. “We’ve been through our battles, Scott,” Trump said a few weeks after sharing his Rose Garden podium with Pruitt as they announced plans to withdraw the United States from the landmark Paris climate agreement. “Not with each other, with the world.”
Thanks to his habit of tenting his fingers, Pruitt has prompted comparisons to C. Montgomery Burns, the villainous nuclear power plant owner in The Simpsons. And indeed, Pruitt has been almost cartoonishly contemptuous of the EPA’s work, pushing draconian cuts to the agency’s science, climate, regulatory, and enforcement offices. Meanwhile, in just his first year, he has reportedly expanded his around-the-clock security detail at a cost of at least $2 million annually. He spent $25,000 on a secure phone booth inside his office, at least $12,000 for flights around the country between March and May (each of which included a leg in Tulsa), $58,000 on chartered and military flights over the summer, and nearly $40,000 on a trip to Morocco to promote natural gas exports. His frequent first-class trips with his security detail have added more than $200,000 to that tally. He also issued a $120,000 no-bid contract to a Republican opposition research firm to target and track journalists, though the contract was canceled after I exposed it.
Mother Jones
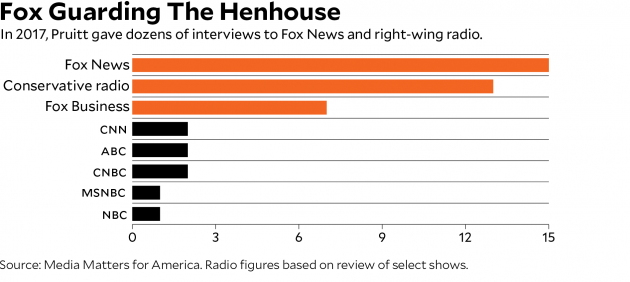
Like Trump, Pruitt has engaged in a continuous battle against the press. Within weeks of his arrival, the EPA’s public affairs office stopped responding to many reporters’ questions and sharing his complete schedule. Instead, the agency has mostly focused on spreading its message through the right-wing media, talking frequently to Fox News and conservative radio hosts while dismissing less favorable coverage as fake. The EPA’s social media accounts spent the first months of Pruitt’s tenure blasting out photos of him fist-bumping EPA staffers and meeting with politicians. In the Obama years, the EPA tweeted about the agency’s programs and environmental issues. During Pruitt’s first three weeks in office, 90 percent of the agency’s tweets were about him.
For those of us who cover the EPA, Pruitt’s profound impact on policy has been hard to miss. What’s tougher to see, behind the secrecy and paranoia, is how his new job has advanced his own future plans. There have been rumors he is interested in replacing Jeff Sessions as attorney general and whispers that he sees himself as a future president. His zeal — or overzealousness — might be seen as typical behavior for an inexperienced man thrust into the major leagues of a Cabinet position. But his political calculations and driving ambition can all be traced 1,210 miles west of Washington, D.C., to the place he’s called home for nearly three-fifths of his life.
Broken Arrow, Oklahoma, 15 miles southeast of Tulsa, is a prosperous town, named for Native Americans forcibly relocated there in 1836, during the Trail of Tears expulsion organized by Trump’s hero President Andrew Jackson. Like much of Oklahoma, it’s dominated by the energy industry. A largely white town of 107,000 residents, with a median income 43 percent higher than the rest of the state, Broken Arrow is also home to many evangelical mega-churches.
One is the First Baptist Church of Broken Arrow, whose campus is marked by a water tower, emblazoned with its name, that’s visible for miles. With a coffee shop, a bookstore, and an indoor basketball court, the church has expanded to meet the needs of 2,800 members and, as its website proclaims, “to reach everyone that we can with the Gospel of Jesus Christ in Broken Arrow, Tulsa, Oklahoma, North America, and the Ends of the Earth.”
I met Nick Garland, an animated 66-year-old senior pastor who had just returned from a trip to D.C. There, he and a few dozen others — Pruitt’s friends from around the country and other influential Oklahomans — attended a private reception in the EPA administrator’s offices. Garland was one of the few who had known Pruitt for decades, not from his political life, but as a family man and deacon, deeply committed to his evangelical faith. Garland has watched Pruitt since the early ’90s, when Pruitt was a law student and the pastor recruited him and his wife to First Baptist. Over the years, Pruitt’s commitment to the congregation has been unwavering. His two children grew up in this church. Shortly after law school, he joined fellow parishioners on a missionary trip to Romania. When he was the state’s attorney general, he taught a seminar on how to blend one’s faith into communication and current events.
During his early days in Oklahoma, Garland says, Pruitt knew “there was something more he’s supposed to do than be a student of law.” Garland, who has a collection of eagle-themed memorabilia scattered around his office, compares Pruitt to the bird. “Eagles are one of the rare creations of God that delight in the storm,” he says. The 114-year-old Broken Arrow church subscribes to a conservative branch of the Southern Baptist tradition. When dozens of evangelical leaders endorsed Pruitt’s nomination in late 2016, they wrote an open letter explaining their rejection of “any ideology that sees human beings as a blight upon the planet and would harm human flourishing by restricting or preventing the rightful use and enjoyment of creation.” This echoed a view of environmental stewardship that has become widely accepted in conservative evangelical communities: “He created human beings in His own image, bearing responsibility to advance human flourishing through many forms of human activity, from agriculture and enterprise to technology and innovation,” the religious leaders wrote. In other words, the planet’s resources are there for the purpose of human use.
This approach is the polar opposite from that of other religious leaders — including Pope Francis — who interpret stewardship as the responsibility humans have to protect God’s creation for as long as possible. “Is true environmentalism ‘do not touch’?” Pruitt remarked last year. “It’s like having a beautiful apple orchard that could feed the world, but the environmentalists put up a fence around the apple orchard and say, ‘Do not touch the apple orchard because it may spoil the apple orchard.’”
I asked Garland to shed some light on the remark. “Either we’re going to steward the Earth and use it for God’s glory and man’s good, or we serve the Earth,” Garland says. Failing to use the Earth for our benefit, he notes, would violate Genesis 2:15, which concerns the relationship between humans and the natural world: “The Lord God took the man and put him in the Garden of Eden to work it and take care of it.” Garland does not believe humans are the main cause of climate change, and neither does Pruitt. “I would not agree that it’s a primary contributor to the global warming that we see,” Pruitt said in March 2017. But his biblical references are not restricted to climate change. Pruitt’s two guiding stars — evangelical faith and political zeal — sometimes seem interchangeable. In October, when he announced a controversial new “conflict of interest” policy barring researchers who receive EPA grants from serving on the agency’s science advisory boards, he quoted the Book of Joshua: “Choose this day whom you’re going to serve.”
If the roots of Pruitt’s religious approach to policy are deep, so is his yearning for power and influence. In a 2010 campaign ad, Pruitt explained that his will to succeed began at his birth as a three-pound premature baby. He grew up in Kentucky, spent his freshman year at a state university, and then graduated in 1990 from Georgetown College, a Christian school, with a degree in political science and communications. He played second base and dreamed of going pro. His friends told E&E News that his appearance inspired the nickname “the possum” — a creature that deceives its enemies by playing dead.
Pruitt married Marlyn Lloyd in Louisville, Kentucky, after graduation and they moved to Tulsa for law school. I visited Jim Thomas, Pruitt’s administrative law professor, at the small firm he shares with his son. Wearing an Oklahoma sweatshirt, he settled into an armchair at a large conference table. The 89-year-old recalled Pruitt as conservative, personable, and striving, someone who had already set his sights on elected office, with hopes to perhaps become governor someday. Pruitt was driven not by a fascination with the workings of government — Thomas remembers he had little interest in environmental law or policy in general — but by sheer political ambition. “I’ve had a lot of politicians go through the University of Tulsa,” says Thomas, who’s been active in Oklahoma’s Democratic Party and says he knows how “to spot somebody who seems suited for politics … And that’s the way I saw Scott Pruitt.”
Pruitt remained in Tulsa and ran a small private practice, Christian Legal Services, where he specialized in constitutional and employment law and worked with several local firms. One of his first major clients, whom he met through church, was J.D. Young, an executive at a well-known oil equipment company, Tulsa Rig Iron. Young had deep connections in the community. David Page, the senior attorney who worked alongside Pruitt for the client, recalls that “on more than one occasion, [Young] said that Scott’s real ambition in life, from his perspective, was to be a well-known politician.”
When Pruitt turned 30 in 1998, he ran for the state Senate against a longtime incumbent Republican. He won on the unexpected strength of the evangelical turnout. David Blatt, a political scientist then working as a budget analyst for the Oklahoma state Senate, remembers colleagues taking note of the surprise win. As a state senator and eventually the Republican whip, Pruitt was a conventional social conservative and a member of the right-wing American Legislative Exchange Council. He was particularly focused on the religious right’s core causes, including prayer in public schools and stopping same-sex marriage and abortion.
Pruitt left the Legislature after eight years, following losses in Republican primaries for a U.S. House seat in 2001 and the lieutenant governor’s office in 2006. In 2003, while he was still in his state seat, Pruitt returned to his first love by becoming the co-owner and managing general partner of the RedHawks, a minor league baseball team based in Oklahoma City. Why might a legislator from Tulsa want to run a baseball team in Oklahoma City? Blatt, who now heads Oklahoma Policy Institute, a nonpartisan think tank, says it made sense in the context of Pruitt’s ambition: “Owning the RedHawks would have definitely cemented relationships with the business elite of Oklahoma City and some of the oil industry folks.”
By 2010, when Pruitt announced his candidacy for attorney general, he had built a deep network, and with help from the new Citizens United ruling and the rise of the tea party, donors who had previously supported him — the likes of Devon Energy’s Larry Nichols and Koch Industries — stepped up. He campaigned on a platform of resisting the Obama administration, promising to file a lawsuit against Obamacare and pledging to push back against Washington at every opportunity, which often meant fighting environmental regulations. He won easily.
By this time, Pruitt’s old colleague David Page had been working with the attorney general’s office for five years on a major case against poultry companies accused of dumping manure that seeped into the Illinois River watershed. These same poultry companies contributed to Pruitt’s campaign. So when Page saw Pruitt at Tulsa’s Dilly Diner one Sunday after church, he thought he’d ask about his plans for the case. “I don’t believe in using lawsuits to change public policy,” Pruitt replied. Eventually, Pruitt agreed to a settlement that set aside some money for a study on the issue but required no concrete action.
Even more striking for Page was that while Pruitt insisted he had no interest in changing policy through the courts, he soon launched lawsuit after lawsuit to do just that. Pruitt enthusiastically joined more than a dozen suits filed by Republican-led states and energy companies against the federal government over environmental policy and health care. He also fulfilled a campaign promise to set up a Federalism Unit, committed to battling so-called interference from Washington. And he disbanded Oklahoma’s environmental protection unit.
This was in contrast to Pruitt’s Democratic predecessor, Drew Edmondson, who is now running for governor. “We were there to enforce consumer protection laws and antitrust laws and environmental laws,” he says. “That’s what the attorney general is supposed to do. I’m certainly not naive enough to believe that other philosophies don’t exist.”
Pruitt’s philosophy went over well within Oklahoma’s conservative policy circles. When oil prices sank globally and state revenue plunged, most agencies saw their budgets cut. Pruitt’s expanded by 40 percent, and he hired nearly 60 new employees focused on fighting legal battles against the Obama administration, according to the Associated Press.
On the national level, Pruitt became active in the Republican Attorneys General Association, which has received substantial money from the fossil fuel industry, and served as chairman of the dark-money nonprofit the Rule of Law Defense Fund. A Pulitzer Prize-winning New York Times series detailed the web of connections Pruitt developed through these groups. In one instance, he copied and pasted a letter that the oil and gas corporation Devon Energy had drafted in opposition to an Obama administration attempt to rein in methane leaks from drilling operations. After making a few small changes and printing it on government letterhead, he signed his name to fight the regulation.
“I think he’s made the bet that the fossil fuel industry will take care of him one way or another,” says Rhode Island Democrat Senator Sheldon Whitehouse, a member of the committee that oversees the EPA. “They reward obedience, and nobody has been more obedient than Scott Pruitt.” Indeed, what environmentalists see as Pruitt’s boundless loyalty to corporate interests, or “stakeholders,” as he invariably calls them, is considered an asset by his supporters. One of them is former GOP Oklahoma Governor Frank Keating, who was serving the second of his two terms while Pruitt was in the state Senate. “Scott Pruitt is a conservative icebreaker. He doesn’t tread water,” he says. “Pruitt always tried to find a hard solution. I found him to be focused but sensible.”
Throughout Pruitt’s tenure as Oklahoma’s attorney general, activists tried to pry open his email records, which his office refused to disclose. On Pruitt’s first day at the EPA, his former office finally released some of those emails under a court order. They included correspondence from Pruitt’s staff thanking Devon Energy executives for their help drafting an argument against Obama’s methane regulations, and others from executives thanking Pruitt’s office. “You are so amazingly helpful!!!” read an email from Pruitt’s chief of staff to Devon Energy. The messages also revealed that Pruitt had used a private email account for state business, despite having denied doing so during his EPA confirmation hearing.
This case is ongoing as public interest groups try to obtain thousands of other messages that appear to have been left out of the public disclosure. The Oklahoma chapter of the American Civil Liberties Union is suing for the emails. For Brady Henderson of the ACLU, Pruitt’s lack of transparency as attorney general and his claim under oath that he didn’t use a private email account were early indications of what has become business as usual in the Trump administration. “It’s very possible to have enough confidence to say, ‘Yeah, I’m just going to lie, and who’s going to do anything about it?’”
In an administration full of deregulators, Pruitt stands out, bringing to the EPA the anti-Washington playbook he developed with industry in Oklahoma. In December 2017, the White House trumpeted presidential accomplishments from Trump’s first year — a list dominated by handouts to the energy industry. Pruitt’s fingerprints were everywhere, from “exiting the Paris climate agreement” to “ending the war on coal.” It’s an agenda that taps directly into the right-wing populism that was integral to Trump’s success — and a corporate donor base that will be vital to Pruitt’s future.
One of Trump’s first actions as president was the creation of a new (and illegal, according to a complaint filed by the Natural Resources Defense Council and other groups) order requiring agencies to jettison two existing regulations for every new one created. Once more, Pruitt was an overachiever. After 10 months, the EPA had put forward just one new rule — restricting the amount of mercury that dentists’ offices can release — while leading other agencies by freezing or reversing 16 regulations. By early 2018, Pruitt had placed nearly 50 existing regulations under review.
The EPA’s regulatory framework is vast and complex, meaning little can be built in a year. Often, the legal battles over rule-making span multiple administrations. During Obama’s eight years, the EPA pushed forward several long-delayed regulations — some mandated by courts — to strengthen the nation’s ozone standards, impose limits on pollution that crosses state lines, curtail mercury emissions from coal-fired plants, and protect drinking water.
Under Trump and Pruitt, much of the hard-won progress of the Obama administration has been attacked, including landmark climate policies such as the Clean Power Plan’s caps on carbon pollution from power plants and limits on methane emissions from oil and gas operations. So have dozens of rules that, with the Clean Power Plan, would have prevented tens of thousands of premature deaths and saved billions of dollars in public health benefits.
Meanwhile, enforcement has dropped precipitously, with fines on offenders down 60 percent in just the first seven months of 2017. “We have a full-on captive agency right now that is obedient not to the public, but to the fossil fuel polluters,” says Whitehouse.
The situation may be permanent. Staffers who have served at the agency for decades predict that the EPA of the future will be a regulatory body essentially controlled by industry — operating on a shoestring budget, unable to fill entry-level roles, and lacking institutional knowledge at higher stations. About 800 employees have already left, meeting Trump’s goal of cutting agency staffing to levels not seen since the 1980s. At the end of 2017, Pruitt put a check mark next to “Reagan-era staff levels” on a list of his accomplishments from the year.
Another accomplishment on Pruitt’s list was “science board transparency” — a reference to one of the more obscure ways in which well-established facts have come under relentless assault. The EPA has two major independent scientific advisory boards, the Science Advisory Board and the Board of Scientific Counselors, which serve as a backstop to ensure the agency’s policy reflects the best available science. Appointments can include experts from academia, government, or industry. Because the government also funds environmental research, it’s not uncommon for a scientist, appointed to the board for her public health expertise, to also receive EPA grants to conduct her own research.
On Halloween, to an audience that included few reporters but several industry reps — including Steve Milloy, the former policy and strategy director of Murray Energy and a prominent climate denier — Pruitt announced a new plan. No scientist who received agency grants could serve on the boards. Seven board members were forced to leave immediately; two more chose to decline the EPA grants. Rush Holt, CEO of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, called the move a “desire to limit expert perspectives and the role of scientific information.”
To replace the departing scientists, Pruitt appointed industry supporters, including Michael Honeycutt, a toxicologist from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality who has built his career arguing that the impacts of air pollution are overstated. He is now the chair of the Science Advisory Board. Pruitt picked more than a dozen people to fill the empty seats of the 18-member Board of Scientific Counselors and 15 others for the 47-member Science Advisory Board, many of them former executives and staffers from organizations that have a stake in limiting the EPA’s chemical and air quality work, such as the utility Southern Co., Phillips 66, Total, and the American Chemistry Council.
Many of Trump’s appointees arrived in Washington with agendas that conflict with their agencies’ historic missions. Trump’s energy secretary, Rick Perry, famously called for eliminating the Department of Energy when he ran for president in 2011. But here, too, Pruitt led the pack. “I’ve never known any administrator to go into office with such an apparent disregard for the agency mission definition or science,” says former New Jersey Governor Christine Todd Whitman, a Republican who ran the EPA under President George W. Bush. Politics has always been part of agency decision making, she acknowledges, but now it “is starting to override science and the mission of the agency.”
Pruitt has proved especially creative in pursuing this political agenda by drumming up public confusion around climate science. Instead of taking any formal action, he’s interested in hosting what’s basically a reality show contest on the legitimacy of science. Take the endangerment finding, the agency’s key scientific determination that carbon pollution’s impact on climate change harms human health. Prompted by a 2007 Supreme Court decision, it allows the agency to regulate carbon emissions under the Clean Air Act and served as the basis for Obama’s Clean Power Plan. Climate deniers detest the endangerment finding, and many hoped the Trump administration would do away with it entirely. Pruitt has thrown red meat to the skeptics, saying on television that humans aren’t the “primary contributor” to global warming.
But a direct attack by Pruitt on the endangerment finding would entail a great deal of work, lots of lawsuits, and an unclear payoff. As former EPA air and radiation officer Janet McCabe told me, “Review of the endangerment finding would need to consider all the available science and respond to the public comments that will certainly be provided to the agency on such an important issue.” Big energy companies and industry groups tend to prefer a less risky strategy and have lobbied instead for simply replacing Obama’s Clean Power Plan with weaker rules.
Pruitt has opted for an idea floated in conservative editorials that would undermine the finding in the minds of the public. He proposed holding high-profile “red team, blue team” debates over climate science. On one side would be scientists who represent the consensus that greenhouse emissions are dangerously warming the atmosphere, and on the other would be the tiny minority of skeptics and fossil fuel advocates. Perhaps with an eye to Trump’s voracious viewing habits, Pruitt said he wanted the debate, which has been put on hold, televised.
Still, that hasn’t been enough for some Trump allies. A month after the new administrator took office, Trump’s EPA appointee David Schnare resigned, later explaining that Pruitt never tried to understand the regulations he was dismantling, refused to meet with experts on staff, and only relied “on the extremely short briefs I provided at his morning staff meeting.” Myron Ebell, who led Trump’s EPA transition team, reportedly told fellow climate deniers that Pruitt’s lassitude in filling rank-and-file jobs amounted to a “totally dysfunctional personnel process.”
There are other, less visible influencers in Pruitt’s work as well. During Trump’s campaign, a photograph appeared in OKC Friday, a small Oklahoma newspaper, of local politicians and powerful oil and gas executives attending a September 2016 fundraiser. One photograph was of Pruitt, laughing with Devon Energy’s Nichols, who had previously supported Senator Marco Rubio. A co-chair of the event was oilman Harold Hamm, a self-made billionaire who pioneered hydraulic fracturing and chaired Pruitt’s reelection campaign for attorney general in 2014.
After the inauguration, Hamm revealed one of his expectations for the new administration. At an oil and gas panel in Houston, he made an observation that seemed to cause the other two oil executives onstage to shift uncomfortably in their seats. He announced that the Obama administration “wanted to eliminate our industry like they wanted to eliminate coal,” despite the fact that oil and gas enjoyed boom times under Obama. But it was clear what Hamm intended: By positioning itself as a victim of the Democratic administration, his industry would receive even more robust protection from Trump.
What transpired may have exceeded his expectations. In December, Pruitt flew with a seven-person entourage and security personnel to Morocco. He toured some solar and thermal energy projects, and there were photos of him deep in conversation with Moroccan leaders. But he also went, according to an EPA press release, to promote U.S. exports of liquefied natural gas (from companies such as Hamm’s). When asked to respond to the criticism that the trip was outside the scope of the administrator’s duties, the EPA replied with a link to its press release.
Inside the agency, Pruitt has surrounded himself with security and walled himself off from the experts on staff. Before Betsy Southerland retired from her position in the EPA Office of Water in protest, she remembers observing him walk down the halls of the agency flanked by two men with earpieces. Employees tend to notice the guard who now surrounds the administrator because it’s a departure from customary EPA practices; past administrators relied on door-to-door protection only for events outside the agency. The 24/7 security detail is composed of staffers who would otherwise likely be investigating enforcement cases for the agency. The EPA’s reasoning for Pruitt’s guard is that this administrator has faced more threats than others. He has built a secure communications facility inside his office, justifying the expense as “necessary for me to be able to do my job,” though the EPA already has one in its buildings. Staffers have reported not being allowed to take notes in meetings or carry their cellphones, limiting the paper trail that can be requested under the Freedom of Information Act.
This kind of secrecy is unprecedented and absurd, says Bush-era EPA chief Whitman: “We’re not talking about the FBI. We’re not talking about Homeland Security.” None of it adds up — that is, until you consider that the security provides another layer of opacity to the agency’s operations and makes it more difficult for whistleblowers to undermine Pruitt’s efforts. “I think he views his administration as a hostile takeover of the agency,” says Southerland.
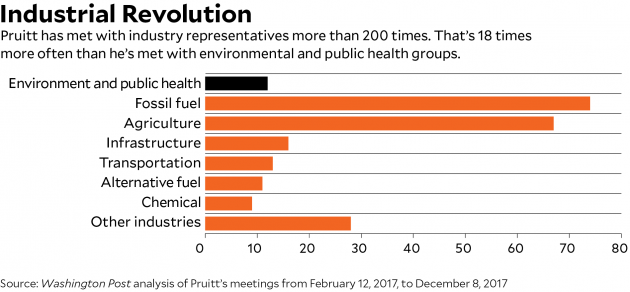
As part of that hostile takeover, Pruitt spent most of his first year meeting with his stakeholders in industry. According to a Washington Post analysis of his public schedule, Pruitt held 218 meetings in 2017 with representatives of industries he regulates. He also gave dozens of interviews to Fox News and right-wing talk radio and delivered speeches in front of conservative groups such as the Heritage Foundation. He met just a dozen times with environmental and public health groups.
During Hurricane Harvey, while a scattered, demoralized EPA was handling its emergency response, Pruitt’s press office was focused on challenging accounts of disarray. In one memorable press release, the EPA attacked an Associated Press report about the lack of agency presence at flooded Superfund sites as “yellow journalism.” The agency pointed to the fact that it had conducted an aerial review of the sites and referenced Breitbart News to further discredit the AP’s additional reporting.
Without much hope that the agency will answer questions, mainstream reporters have turned to its glacial open records process for answers. Senators have complained that the agency has done no better for them. Democrats, who have already asked for EPA inspector general audits of Pruitt’s travel, including his frequent trips to Oklahoma, recently requested that the independent office add the Morocco visit to their list and examine “whether the purpose of travel is consistent with the EPA’s mission.”
At the same time, Pruitt installed fellow Oklahoma conservatives in EPA positions that don’t require Senate confirmation. He has hired several old friends, as well as four staffers who have worked for the Senate’s most prominent climate denier, Oklahoma Republican James Inhofe.
One of those hires was Albert Kelly, a former banker with no environmental experience, whose company issued three mortgages to the Pruitts, according to an investigation by the Intercept, for their $605,000 home in an upscale Tulsa neighborhood. Kelly’s company also financed Pruitt’s stake in the RedHawks. Last year the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation fined Kelly for his alleged involvement in a loan that hadn’t received FDIC approval. Two weeks later, Pruitt hired him to lead the EPA’s Superfund Task Force — which Pruitt has singled out as a priority for the agency and an early success story.
As almost everyone I spoke with noted Pruitt is a far more political creature — and quite talented in that respect — than his predecessors have been. When I was in Oklahoma, his old friends and associates openly speculated about which office he would set his sights on next: Maybe the seat held by the 83-year-old Inhofe? A governor’s race? The White House?
One way or another, “I don’t think EPA is his ultimate destination,” University of Tulsa law and environmental professor Gary Allison says. According to Politico, Pruitt is reportedly interested in Attorney General Jeff Sessions’ job, should Sessions resign from his post — a move that could put Pruitt squarely in the middle of the Russia investigation. (Jahan Wilcox, a spokesman for the EPA and a longtime Republican operative, told news outlets the rumors were “not true.”)
Will Pruitt remain as EPA chief for Trump’s entire four — or eight — years? That’s anybody’s guess. But what’s clear is that this position will not be the pinnacle of Pruitt’s career. Before each previous campaign, Pastor Garland recalls, Pruitt “would come and visit and say, ‘Pray for me. I’ve got something I feel like I’m supposed to run for.’” He describes a similar pattern after Trump won and Pruitt was summoned to Trump Tower in New York City. “We prayed for him through that process when he went up there for the interview,” he says. “He felt very humbled but very eager to serve in a national capacity.”
So, I asked Garland, what’s next?
“Stay tuned,” he replied with a big, loud laugh. “We may have this conversation again sometime.”




