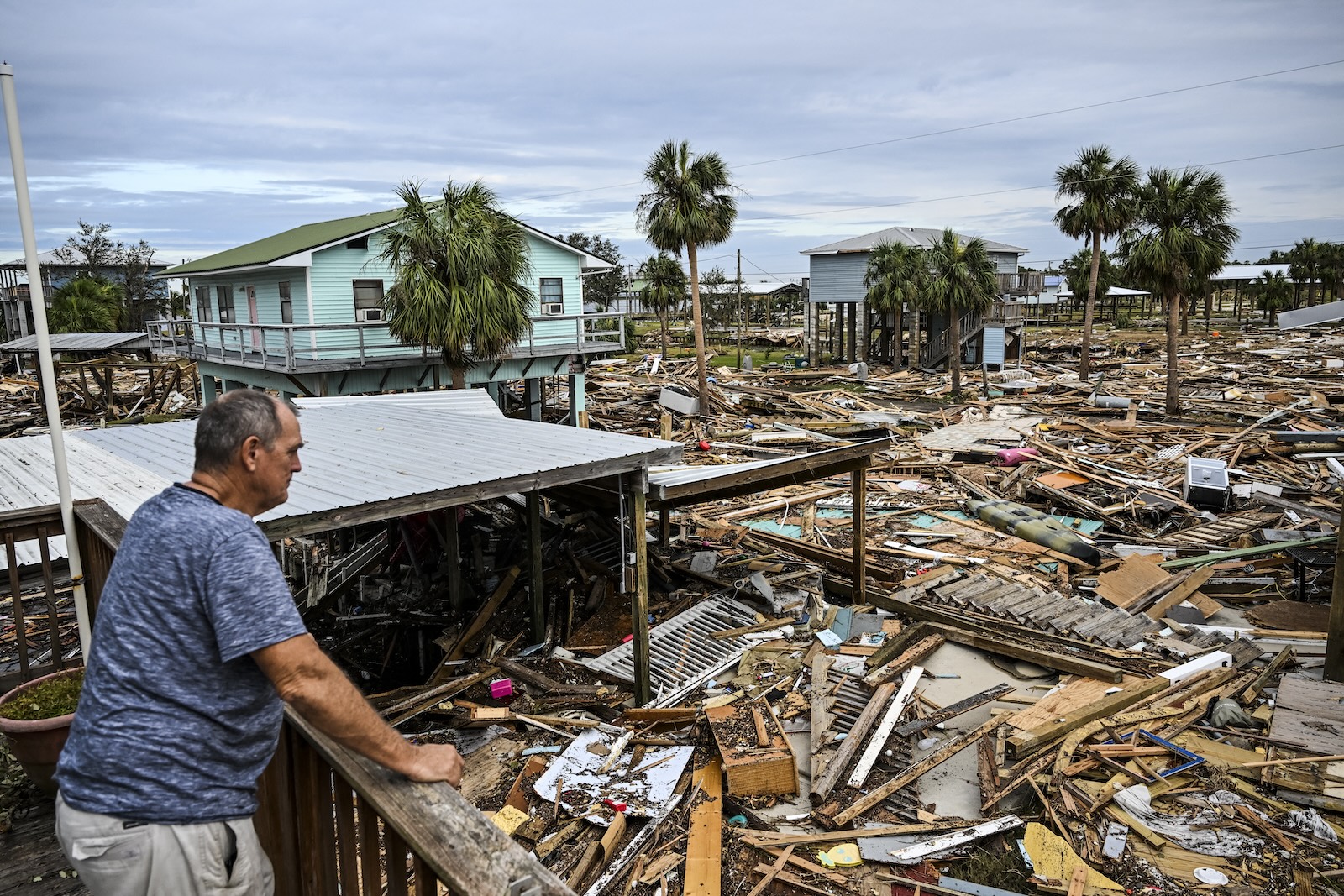
Like wildfires chewing through dried-out forests, hurricane after hurricane fed on extra-hot ocean water during the summer and fall of 2024 before slamming into communities along the Gulf Coast, causing hundreds of billions of dollars in damages and killing more than 300 people. The warmer the sea, the more potent the hurricane fuel, and the more energy a storm can consume and turn into wind.
Human-made climate change made all of 2024’s 11 hurricanes — from Beryl to Rafael — much worse, according to an analysis released on Wednesday from the nonprofit science group Climate Central. Scientists can already say that 2024 is the hottest year on record. By helping drive record-breaking surface ocean temperatures, planetary warming boosted the hurricanes’ maximum sustained wind speeds by between 9 and 28 miles per hour.
That bumped seven of 2024’s storms into a higher category on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, including the two Category 5 storms, Beryl and Milton. “Our analysis shows that we would have had zero Category 5 storms without human-caused climate change,” said Daniel Gilford, climate scientist at Climate Central, on a press call. “There’s really this impact on the intensity of the storms that we’re experiencing in the real world on a day-to-day basis.”
In a companion study also released Wednesday, Climate Central found that between 2019 and 2023, climate change accelerated hurricane wind speeds by an average of 18 mph. More than 80 percent of the hurricanes in that period were made significantly more intense by global warming, the study found.
That’s making hurricanes more dangerous than ever. An 18 mph boost in wind speeds might not sound like much, but that can mean the difference between a Category 4 and a Category 5, which packs sustained winds of 157 mph or higher. Hurricanes have gotten so much stronger, scientists are considering modifying the scale. “The hurricane scale is capped at Category 5, but we might need to think about: Should that continue to be the case?” said Friederike Otto, a climatologist who cofounded the research group World Weather Attribution, on the press call. “Or do we have to talk about Category 6 hurricanes at some point? Just so that people are aware that something is going to hit them that is different from everything else they’ve experienced before.”
Hurricanes need a few ingredients to spin up. One is fuel: As warm ocean waters evaporate, energy transfers from the surface into the atmosphere. Another is humidity, because dry air will help break up a storm system. And a hurricane also can’t form if there’s too much wind shear, which is a change in wind speed and direction with height. So even if a hurricane has high ocean temperatures to feed on, that’s not necessarily a guarantee that it will turn into a monster if wind shear is excessive and humidity is minimal.
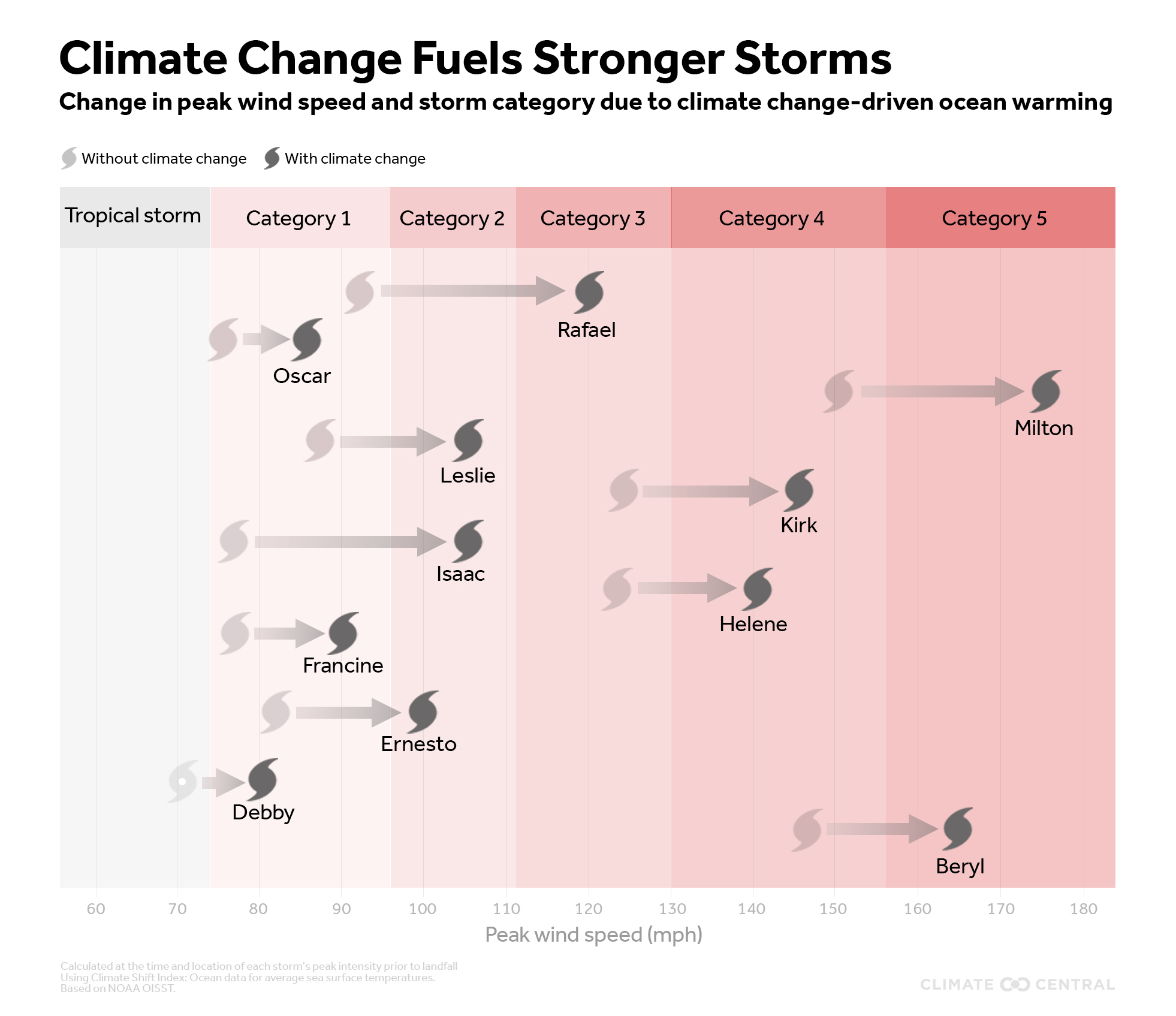
But during 2024’s hurricane season — which ran through the end of November — those water temperatures were so extreme that the stage was set for catastrophe. As the storms were traveling through the open Atlantic, Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of Mexico, they exploited surface temperatures made up to 800 times more likely by human-caused planetary warming, according to the Climate Central analysis. Four of the most destructive hurricanes — Beryl, Debby, Helene, and Milton — had their wind speeds increased by an average of 17 mph, thanks to climate change. In early November, Hurricane Rafael managed to jump from Category 1 to Category 3.
Climate Central’s companion study, published in the journal Environmental Research: Climate, looked at the five previous years and found that climate change boosted three hurricanes — Lorenzo in 2019, Ian in 2022, and Lee in 2023 — to Category 5 status. That isn’t to say climate change created any of these hurricanes, just that the additional warming from greenhouse gas emissions exacerbated the storms by raising ocean temperatures. Scientists are also finding that as the planet warms, hurricanes are able to dump more rain. In October, World Weather Attribution, for instance, found that Helene’s rainfall in late September was 10 percent heavier, making flooding worse as the storm marched inland.
All that supercharging might have helped hurricanes undergo rapid intensification, defined as an increase in wind speed of at least 35 mph within 24 hours. Last month, Hurricane Milton’s winds skyrocketed by 90 mph in a day, one of the fastest rates of intensification that scientists have ever seen in the Atlantic basin. In September, Hurricane Helene rapidly intensified, too.
This kind of intensification makes hurricanes particularly dangerous, since people living on a stretch of coastline might be preparing for a much weaker storm than what actually makes it ashore. “It throws off your preparations,” said Karthik Balaguru, a climate scientist who studies hurricanes at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, who wasn’t involved in the new research. “It means you have less time to evacuate.”
Researchers are also finding that wind shear could be decreasing in coastal areas due to changes in atmospheric patterns, removing the mechanism that keeps hurricanes in check. And relative humidity is rising. Accordingly, scientists have found a huge increase in the number of rapid intensification events close to shore in recent years.
The hotter the planet gets overall, and the hotter the Atlantic Ocean gets specifically, the more monstrous hurricanes will grow. “We know that the speed limit at which a hurricane can spin is going up,” Gilford said, “and hurricane intensities in the real world are responding.”




