Hooboy, it’s gonna get hot. A U.N. climate panel on Sunday painted a sizzling picture of the staggering volume of greenhouse gases we’ve been pumping into the atmosphere — and what will happen to the planet if we keep this shit up.
By 2100, surface temperatures will be 3.7 to 4.8 degrees C (6.7 to 8.7 F) warmer than prior to the Industrial Revolution. That’s far worse than the goal the international community is aiming for — to keep warming under 2 C (3.7 F). The U.N.’s terrifying projection assumes that we keep on burning fossil fuels as if nothing mattered, like we do now, leading to carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere of between 750 and 1,300 parts per million by 2100. A few centuries ago, CO2 levels were a lovely 280 ppm, and many scientists say we should aim to keep them at 350 ppm, but we’re already above 400.
These warnings come from the third installment of the latest big report from the U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, compiled by hundreds of climate scientists and experts. (WTF is this IPCC? See our explainer. Feel like you’ve heard this story before? Perhaps you’re thinking of the first installment of the report, which came out last fall, or the second installment, which came out last month. Maybe the IPCC believes that breaking its report into three parts makes it more fun, like the Hobbit movies.)
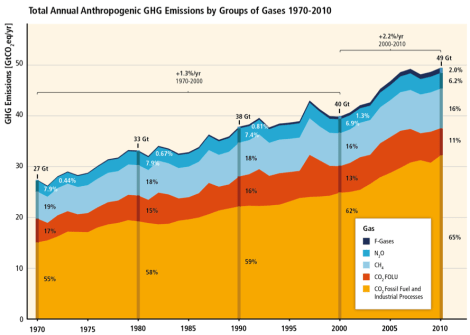
Here’s a paragraph and a chart from the 33-page summary of the latest installment that help explain how we reached this precarious point in human history.
Globally, economic and population growth continue to be the most important drivers of increases in CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion. The contribution of population growth between 2000 and 2010 remained roughly identical to the previous three decades, while the contribution of economic growth has risen sharply … Between 2000 and 2010, both drivers outpaced emission reductions from improvements in energy intensity. Increased use of coal relative to other energy sources has reversed the long-standing trend of gradual decarbonization of the world’s energy supply.
Of course, we could change our fossil-fuel-burning, globe-warming ways. It’s too late to avoid climate change — it’s already here — but the scientists who collaborated on the latest IPCC report think they know what it would take to keep warming within 2 degrees. It would require “substantial cuts” in greenhouse gas emissions by mid-century “through large-scale changes in energy systems,” and maybe also changes in how we use land and protect CO2-slurping forests. By 2050, we would need to be pumping far less pollution into the atmosphere than we were in 2010 — perhaps 40 to 70 percent less. And by 2100, we would need to stop polluting the atmosphere entirely.
Achieving these seemingly impossible but utterly crucial reductions in greenhouse gas pollution will require international agreement, the report notes. The trans-boundary nature of the climate crisis means no one government or group can fix this problem on its own. So come on, everybody — let’s get to it!