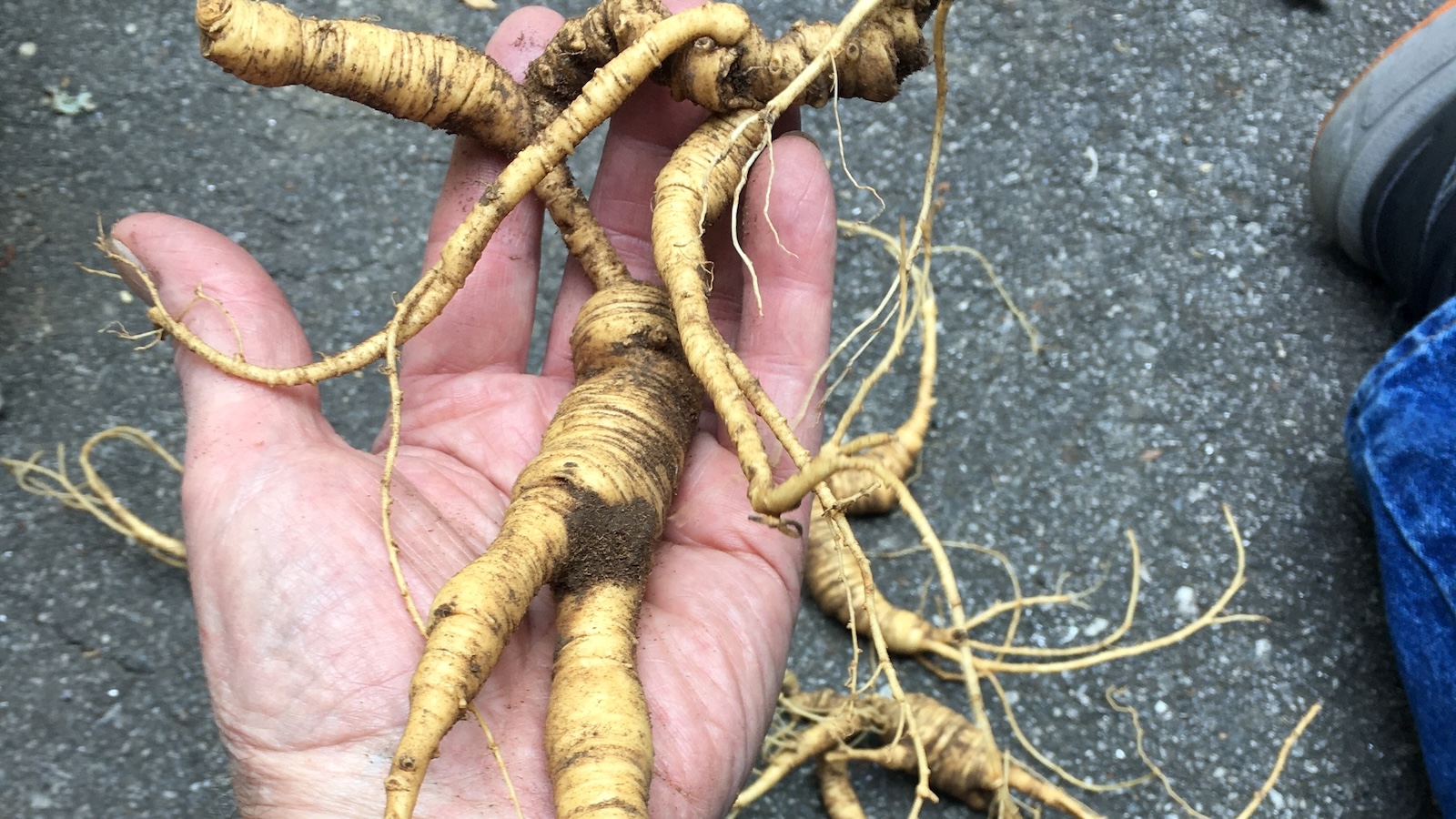
Each fall, hopeful foragers throughout the Appalachian mountains don heavy work pants and sturdy boots to clamber into dark, steep, moisture-laden coves in hopes of finding Old Man Sang.
The name is a colloquialism for ginseng, a perennial with a gnarled and bulbous root prized for its medicinal qualities. The plant, a staple of traditional medicine and flavorful addition to many recipes, can reach 80 years of age but grows so slowly it takes five to reach maturity. Demand is so great that it has largely been extirpated in Asia, driving prices for American varieties to $1,000 a pound. That’s got conservationists concerned that overzealous diggers could be pinching them out of existence as they harvest plants too early and too often.
“When it got really valuable, it was just too many people going over and over to the same ground,” said North Carolina ethnobotanist David Cozzo. “There never was a chance for it to recover.”
Although found in much of the eastern United States, ginseng is most prevalent in Appalachia and the Ozarks. The risk of excessive foraging is particularly great in Kentucky, West Virginia, North Carolina, and Tennessee, something one expert on the subject attributes to the high unemployment and widespread poverty found there. In response, the Forest Service has taken the step of limiting harvesting on public lands. Although Nantahala and Pisgah national forests have been closed indefinitely in the wake of Hurricane Helene, a federal ban on harvesting the root there will remain in place for at least another year. Getting caught digging up the plant, found primarily in deciduous hardwood forests, can result in a fine of $5,000 and six months in a federal prison.
The Forest Service has said the prohibition, which began in 2021, could last up to a decade. Taking such a step requires balancing the preservation of a valuable resource and respecting a practice intertwined with the region’s history. “Sanging” is for many people a way of life, one that has supplemented rural incomes for generations, particularly in areas dependent on the volatile coal industry.
The Appalachian relationship with east Asian markets extends over 200 years. The Cherokee, who used the root medicinally, took advantage of the globalizing world that colonization thrust them into and started shipping ginseng root to China by the middle of the 1700s. Revenue from such deals helped the tribe buy back a small portion of its ancestral lands in the 1870s, establishing the trust on which the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians now lives, said Cozzo, who is also the director emeritus of the Traditional Cherokee Artisan Resources Program.
Formerly enslaved people, unmarried women, and even entire towns cultivated ginseng in the forests of Appalachia throughout the 19th and and early 20th centuries, harvesting the roots alongside things like cohosh and mayapple and establishing a thriving industry in places known for timbering and mining. Even now, Cozzo recalls talking to high-mountain diggers who used their autumn haul to pay for their kids’ school clothes and other expenses. Historians have attempted to rectify the stereotype of the ignorant, backward harvester, and have attributed some responsibility for ginseng’s decline to poaching and to habitat destruction driven by the coal and timber industries.
In some communities, mineworkers and their families supplemented their incomes foraging for ginseng and other forest products, particularly as work-related disabilities like black-lung disease took hold. “These guys who got black lung from the mines, they might go out in the morning when it was still cool and they could breathe,” Cozzo said.
A 2020 Smithsonian oral history project features people from throughout the region describing foraging and selling what they’d picked or pulled alongside furs and skins to support themselves during unemployment or retirement and to supplement the wages of full-time work. One participant, Carol Judy, a digger and environmental activist who sanged in the mountains around the coal community of Eagan, Tennessee until she died in 2017, is described as a believer in the power of agroforestry to provide for communities struggling to meet their needs, particularly in light of coal’s decline. A friend recalled Carol Judy’s hope of fostering a foraging culture that looks “seven generations forward and seven generations back.”
John-Paul Schmidt, a University of Georgia ecologist who has studied the factors contributing to overharvesting on public lands, noted that stress on the plant’s numbers often correlates with high unemployment and low incomes, particularly in southern Appalachia. That, he said, suggests harvesters compelled by need will find ways around a ban. A wiser policy, he said, would be to explore funding education and pathways to sustainable forest farming, something many harvesters already practice. “There’s a real missed opportunity to really promote active wild cultivation of these plants,” he said.
Many old-time diggers, particularly Indigenous people, have patches they tend. Cozzo’s oral histories tell of people returning to the same patch every five to seven years, giving it plenty of time to recover. Careful harvesters save the seeds and plant them an inch deep, making it more likely that they’ll sprout. “Old-timers knew this, and they managed the woods, and they managed the forest,” Cozzo said.
Greater education around sustainable harvesting is needed, particularly as diggers are less likely to have a long-term relationship to the land and more likely to be driven by the value of the root. “All it takes is one generation to skip knowing how to do things properly,” said Cozzo.
The hope behind the ban, said Forest Service botanist Gary Kauffman, is to give these fragile plants time to flourish, particularly older specimens that are key to the root’s survival. “It’s the older individuals that produce more seed and actually regenerate the plant,” Kauffman said. The Forest Service is monitoring more than 100 ginseng plots across Nantahala and Pisgah national forests. It also is working with a seed nursery at the North Carolina State Extension to increase the number of seedbeds in the biodiverse, nutrient-rich soils in which ginseng thrives.
Sustainable harvesters know to seek plants at least five and ideally over 10 years old with clear signs of maturity: red berries, stem scars, and three to five leaflets. Healthy ginseng communities consist of about 50 to 100 plants, Kauffman said, but many have closer to 25 — a good basis for growth, but not enough to allow harvesting. That’s got the Forest Service thinking that its conservation efforts could last at least a few years, and possibly longer. That may frustrate diggers and herbalists, he said, but it’s necessary to protect a historically important plant..
“It’s very important to look at that and try to preserve some of that culture,” Kauffman said. “To think of how we can preserve it in the future, so our kids and grandkids can also go out and see ginseng, and maybe in the future, harvest some ginseng.”